LPL Polyklonaler Antikörper
LPL Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 16899-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
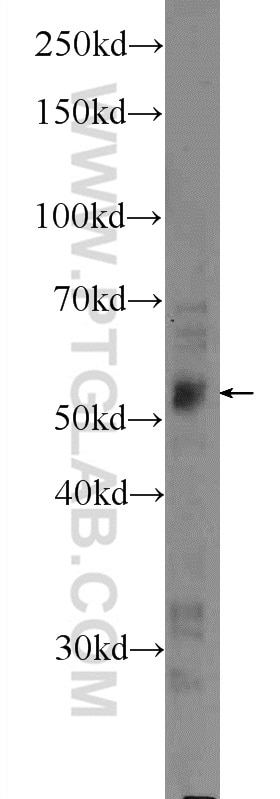
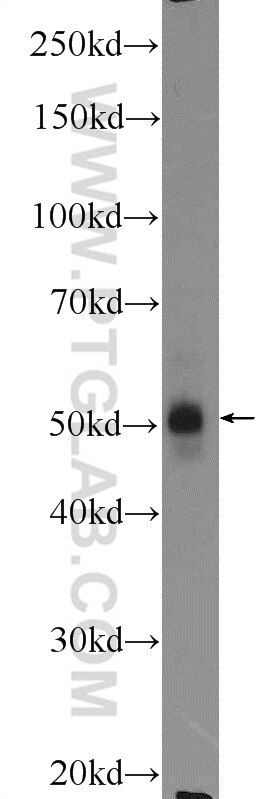
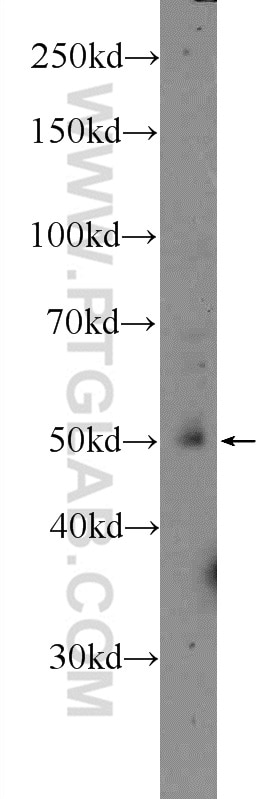
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | MCF-7-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, Maus-Skelettmuskelgewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:200-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
16899-1-AP bindet in WB, ELISA LPL und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | LPL fusion protein Ag10431 |
| Vollständiger Name | lipoprotein lipase |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 475 aa, 53 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 53 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC011353 |
| Gene symbol | LPL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4023 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
LPL(lipoprotein lipase) is also named as LIPD and belongs to the AB hydrolase superfamily. LPL catalyses the hydrolysis of the triacylglycerol component of circulating chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins. It plays a role in the binding of lipoprotein particles to cell-surface molecules, including sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)(PMID:21177248). The gene encodes a protein of 475 amino acids that becomes a mature protein of 448 residues after cleavage of a signal peptide. This protein is highly glycosylated and functions as a head-to-tail dimer under well-defined conditions(PMID:11154699).
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Diabetes Rab8a Deficiency in Skeletal Muscle Causes Hyperlipidemia and Hepatosteatosis Via Impairment of Muscle Lipid Uptake and Storage. | ||
Diabetes Tissue-specific splicing and dietary interaction of a mutant As160 allele determine muscle metabolic fitness in rodents. | ||
Biology (Basel) Curcumin-Rich Diet Mitigates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) by Attenuating Fat Accumulation and Improving Insulin Sensitivity in Aged Female Mice under Nutritional Stress |