GRIN2B Polyklonaler Antikörper
GRIN2B Polyklonal Antikörper für ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
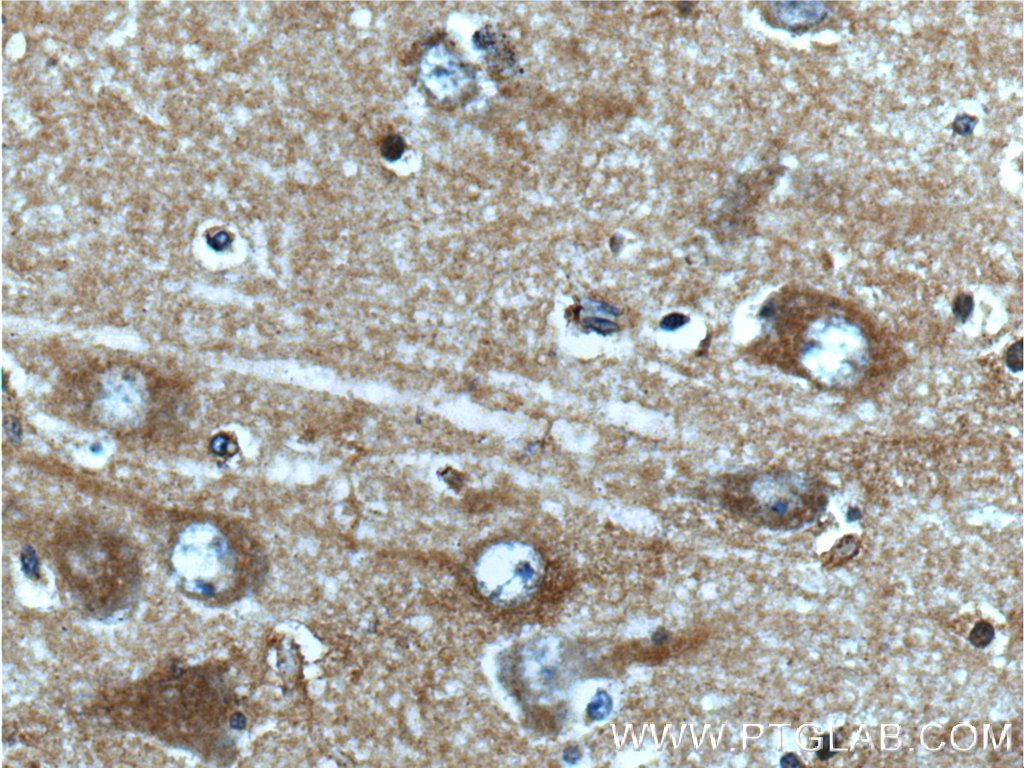
WB, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 19954-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
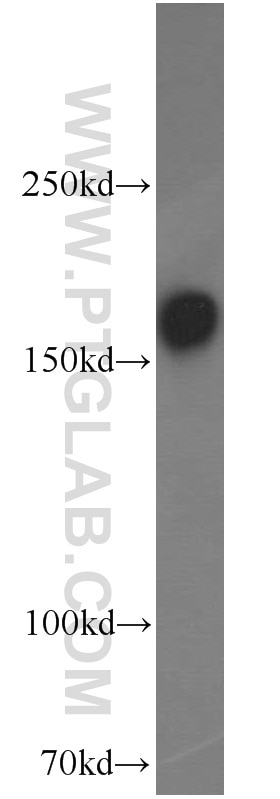
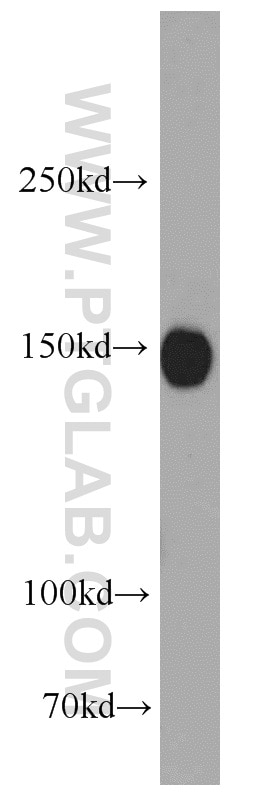
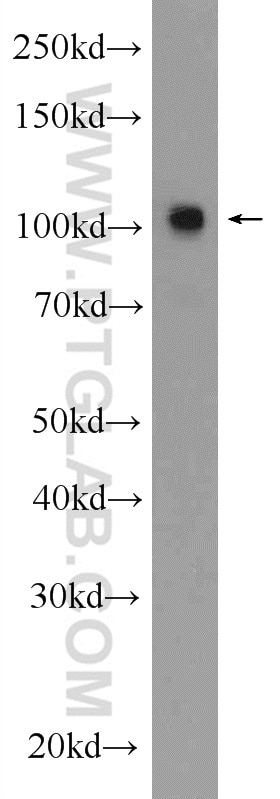
19954-1-AP bindet in WB, IF, ELISA GRIN2B und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 166 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_000834 |
| Gene symbol | GRIN2B |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2904 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
GRIN2B (also known as GluN2B or NMDAR2B) is a member of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor family within the ionotropic glutamate receptor superfamily. NMDA receptors are widely expressed in the central nervous system and play a major role in excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity (PMID: 23223336). NMDA receptors large multi-subunit complexes arranged into heteromeric assemblies composed of four homologous subunits within a repertoire of over 10 different subunits: eight GluN1 isoforms, four GluN2 subunits (A-D) and two GluN3 subunits (A and B) (PMID: 21395862). Naturally occurring mutations within GRIN2B gene are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, epilepsy, and schizophrenia.
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Neurosci Microglial Tmem59 Deficiency Impairs Phagocytosis of Synapse and Leads to Autism-Like Behaviors in Mice. | ||
Front Cell Dev Biol RAB39B Deficiency Impairs Learning and Memory Partially Through Compromising Autophagy. | ||
Front Cell Dev Biol Profiling of Sexually Dimorphic Genes in Neural Cells to Identify Eif2s3y, Whose Overexpression Causes Autism-Like Behaviors in Male Mice. | ||
Brain Res Central nervous system-specific knockout of Brg1 causes growth retardation and neuronal degeneration. | ||
Neurochem Int Protective effects of EphB2 on Aβ1-42 oligomer-induced neurotoxicity and synaptic NMDA receptor signaling in hippocampal neurons. | ||
J Cell Mol Med Increased level of RAB39B leads to neuronal dysfunction and behavioural changes in mice |