- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
Ferritin heavy chain Polyklonaler Antikörper
Ferritin heavy chain Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 11682-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
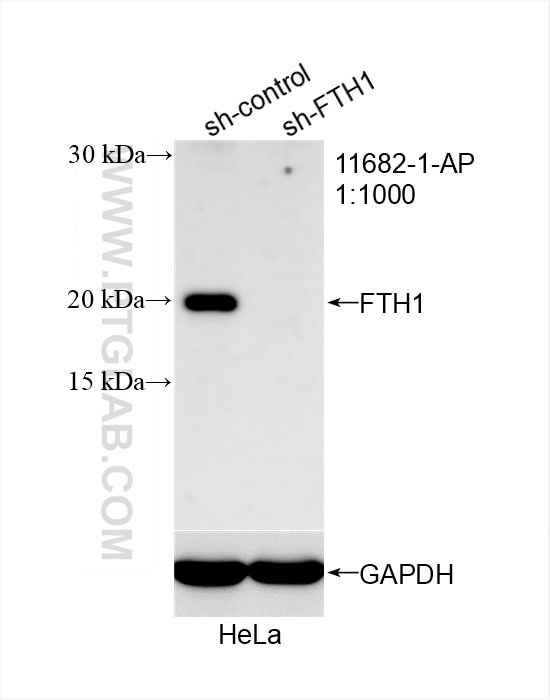
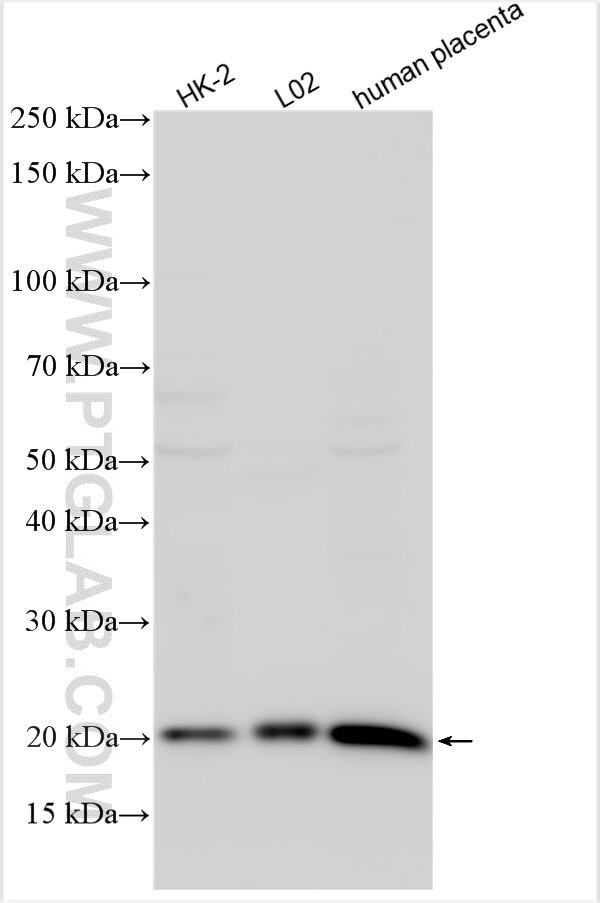
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HK-2 cells, HeLa-Zellen, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe, L02-Zellen |
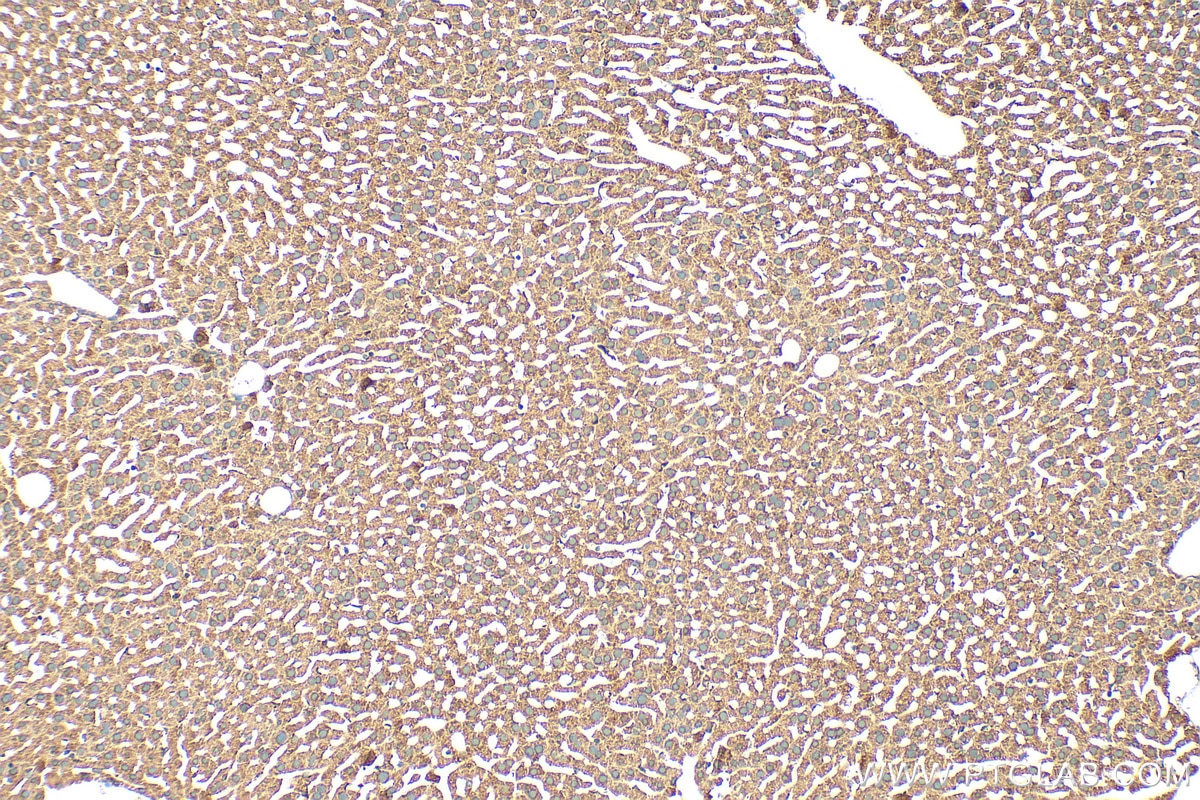
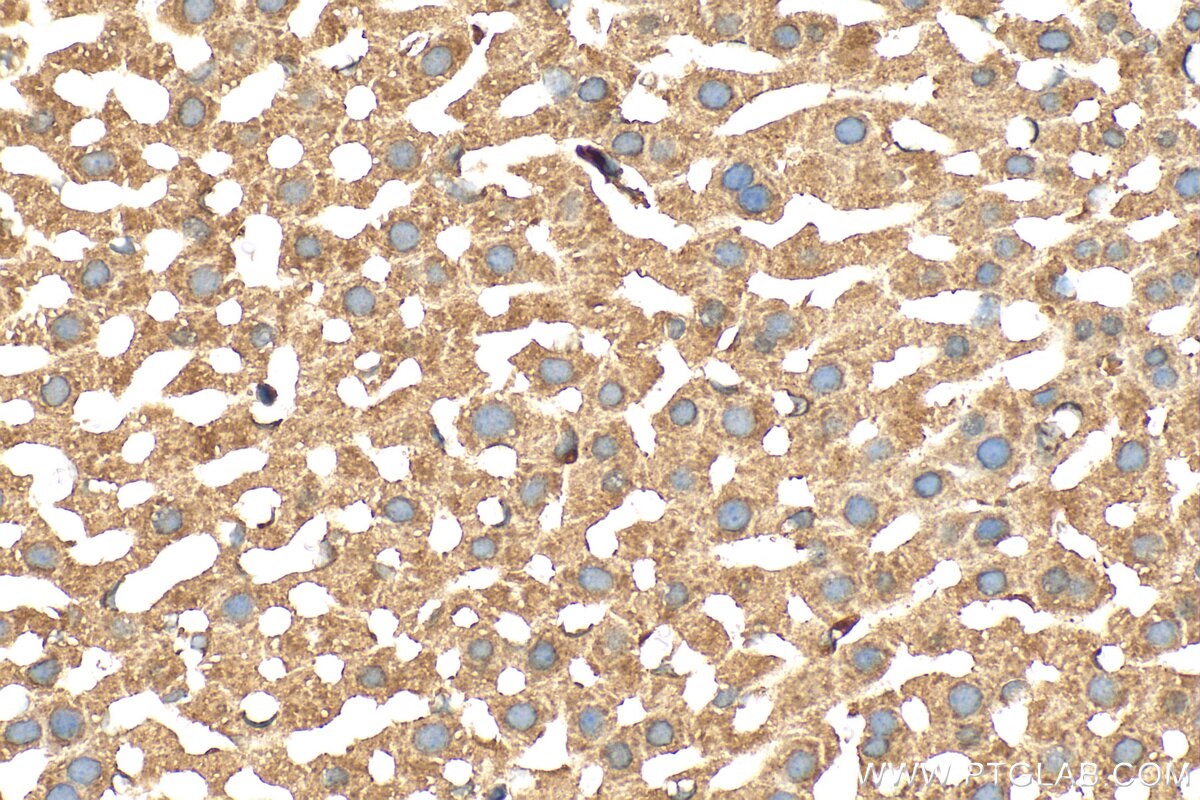
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | Mauslebergewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
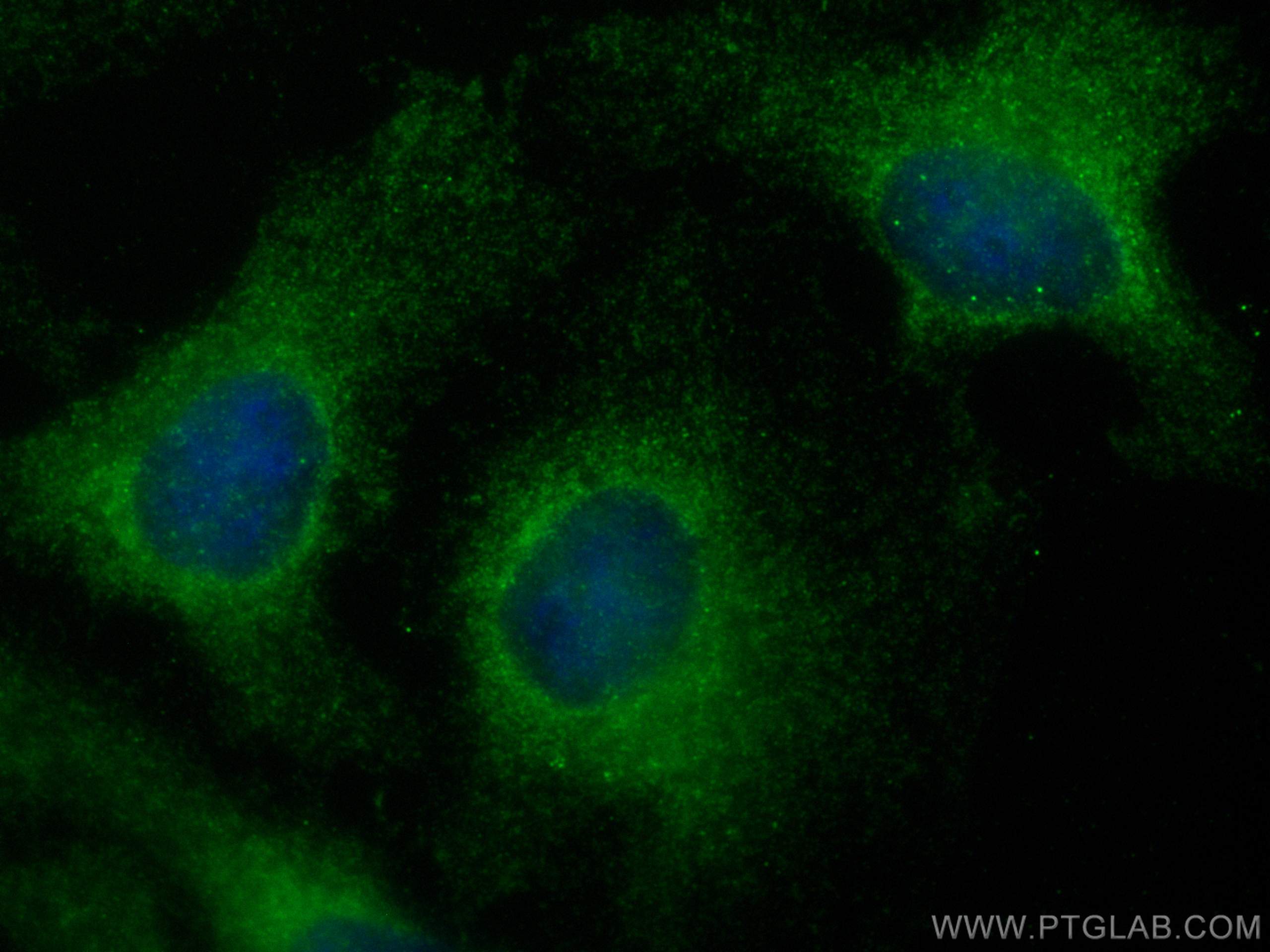
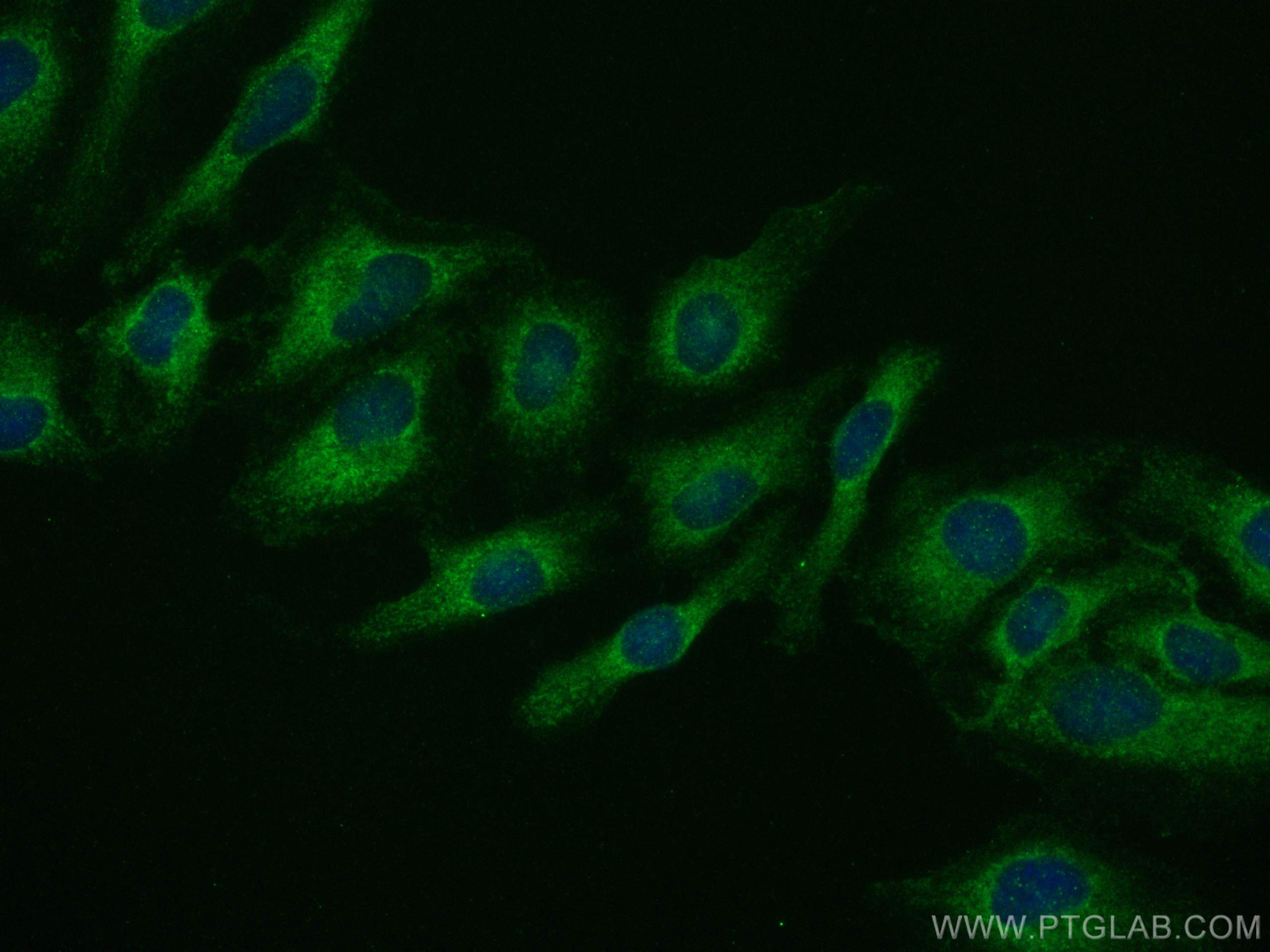
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HeLa-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
11682-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA Ferritin heavy chain und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Ferritin heavy chain fusion protein Ag2290 |
| Vollständiger Name | ferritin, heavy polypeptide 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 183 aa, 21 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 21 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC000857 |
| Gene symbol | FTH1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2495 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Ferritin heavy chain(FTH1, ferritin, heavy polypeptide 1 ), as a 21 kDa subunit of the ferritin complex, exhibits ferroxidase activity, which serves an essential role in catalyzing the conversion of the ferrous ions (Fe2+) to the ferric form (Fe3+). FTH1 regulates angiogenesis during inflammation and malignancy by binding to high molecular weight kininogen (HKa) and blocking its anti-angiogenic activity on endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo(PMID: 33260500). FTH1 has been shown to protect proximal tube epithelial cells and kidneys against the activity of free iron in reactive oxygen species generation. FTH1 plays an important role in the maintenance of the cellular iron balance in ferroptosis.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Ferritin heavy chain antibody 11682-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Ferritin heavy chain antibody 11682-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for Ferritin heavy chain antibody 11682-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Inflammopharmacology Sulfasalazine promotes ferroptosis through AKT-ERK1/2 and P53-SLC7A11 in rheumatoid arthritis | ||
Mol Neurobiol A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase-8 Protects Against Erastin-Induced Neuronal Ferroptosis via Activating Nrf2/HO-1/FTH1 Signaling Pathway | ||
BMC Cancer Oridonin-induced ferroptosis and apoptosis: a dual approach to suppress the growth of osteosarcoma cells | ||
Aging (Albany NY) Eriocitrin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) in lung adenocarcinoma cells via triggering ferroptosis | ||
Hum Exp Toxicol Protective effects of brain and muscle ARNT-like gene 1 on oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injury by alleviating ferroptosis | ||
Exp Cell Res A novel tsRNA-5008a promotes ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes that causes atrial structural remodeling predisposed to atrial fibrillation |