DOPA decarboxylase Polyklonaler Antikörper
DOPA decarboxylase Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10166-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
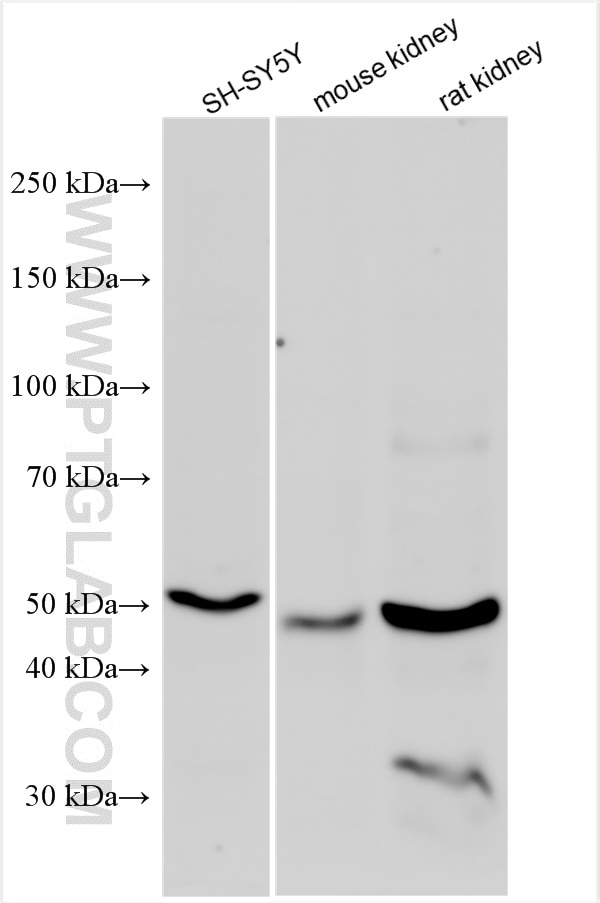
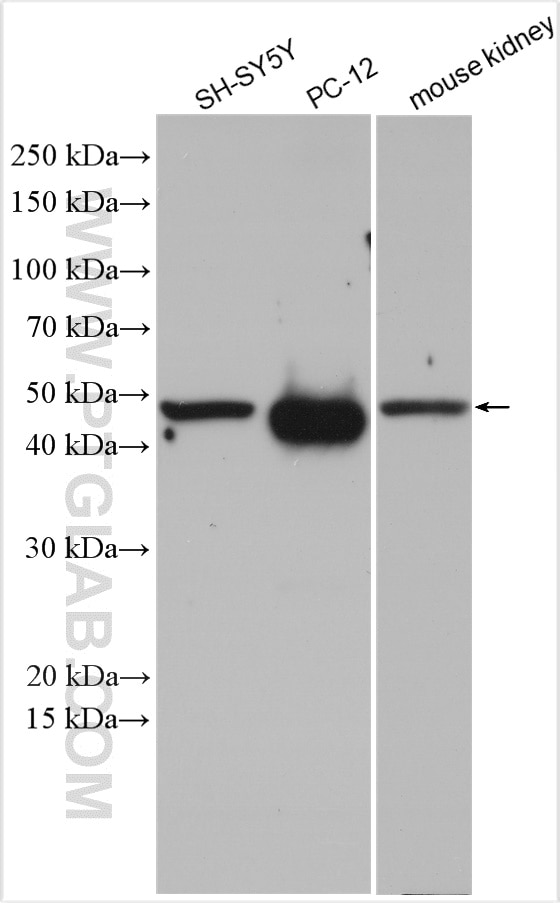
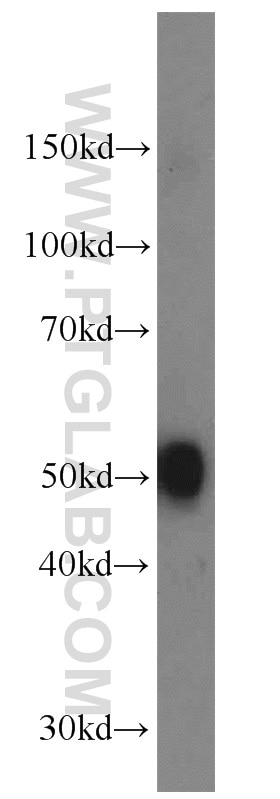
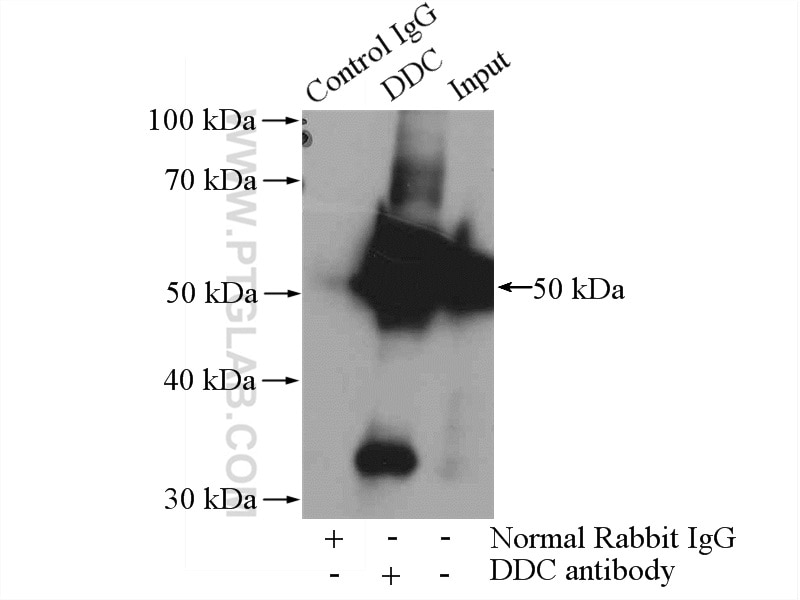
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | SH-SY5Y-Zellen, Maushirngewebe, Mausnierengewebe, PC-12-Zellen, Rattennierengewebe |
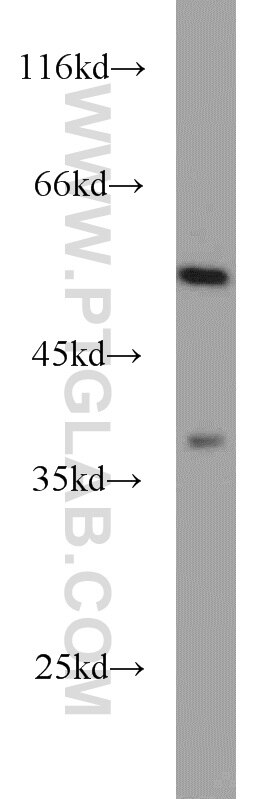
| Erfolgreiche IP | Maushirngewebe |
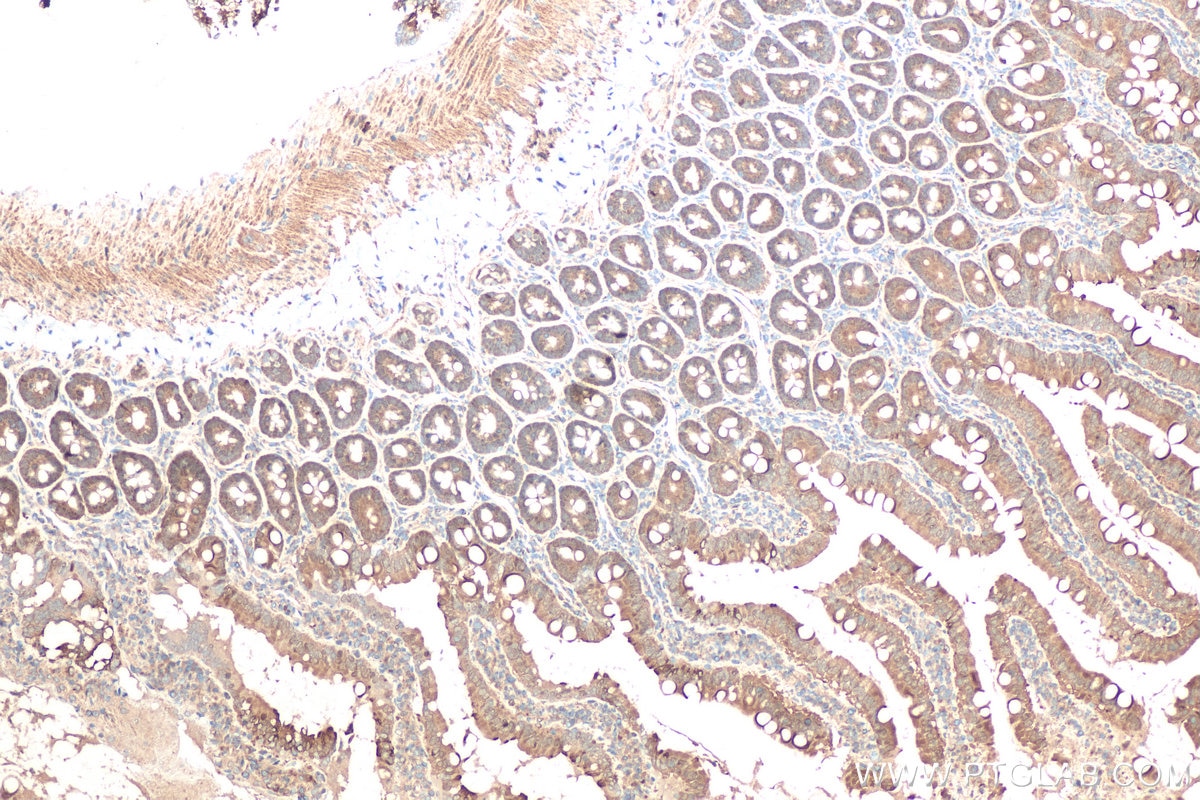
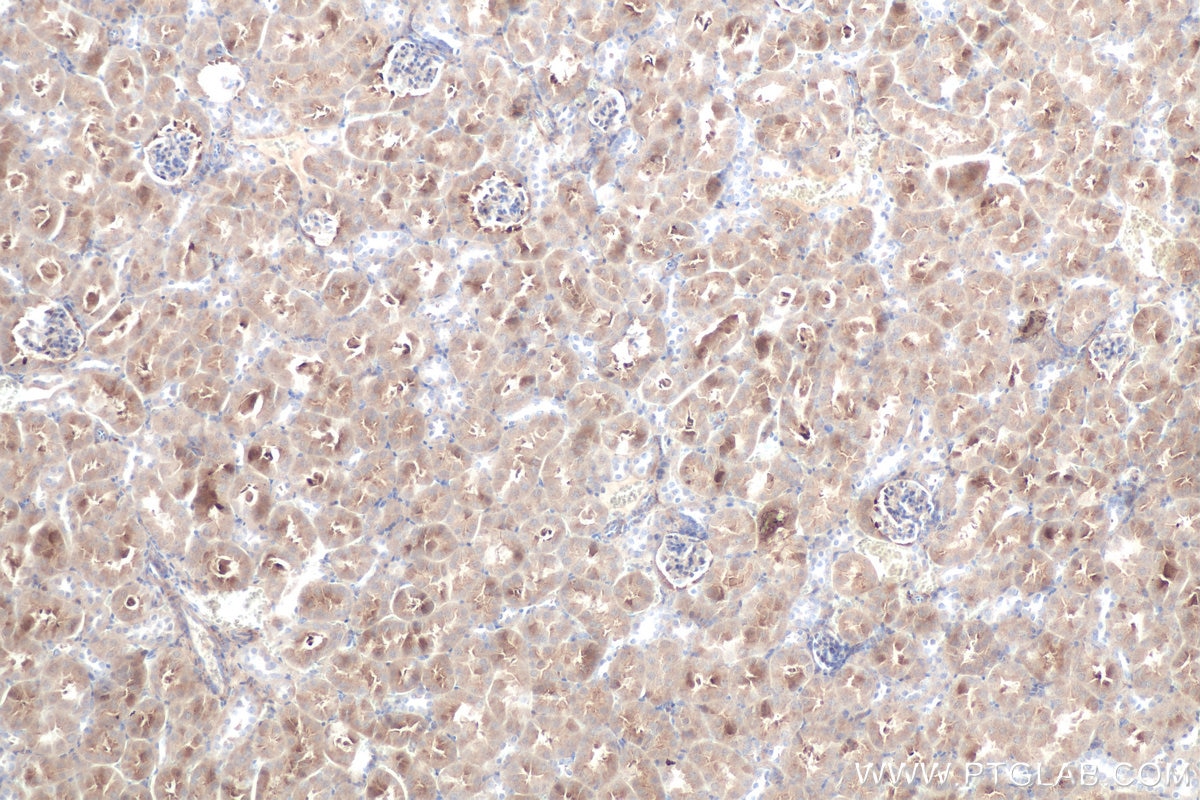
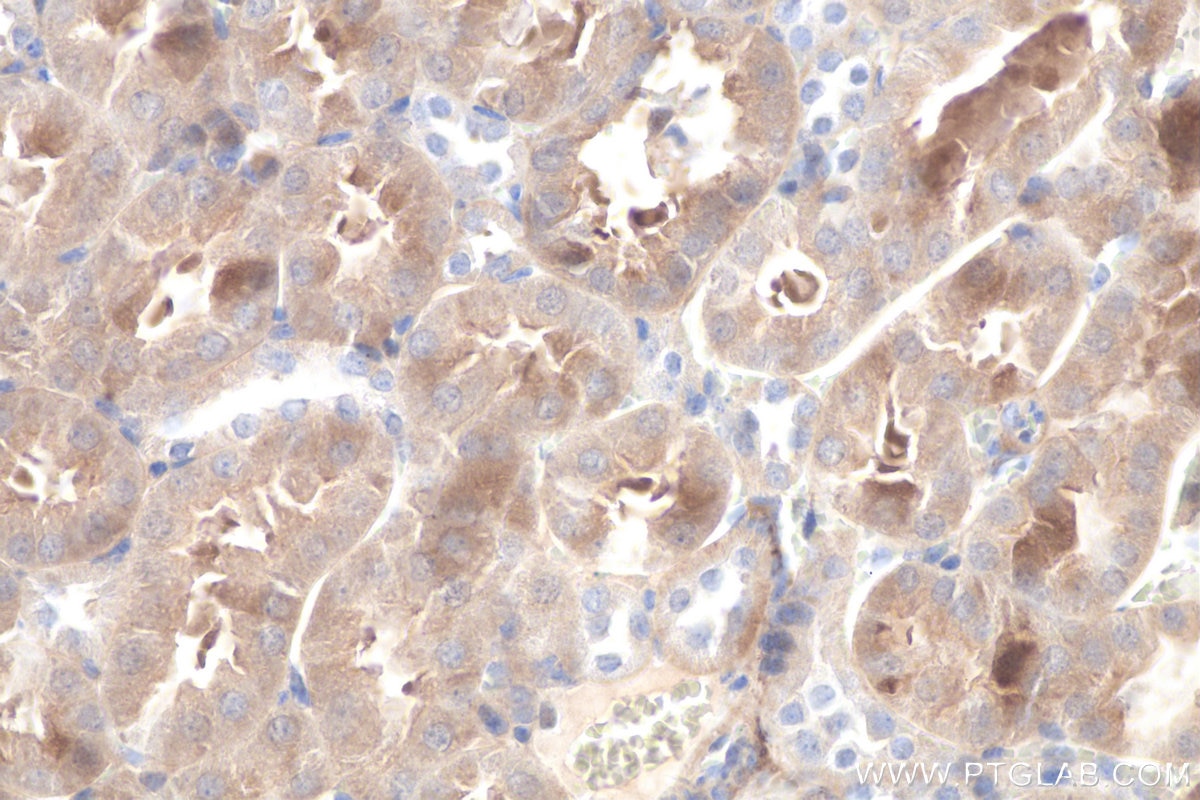
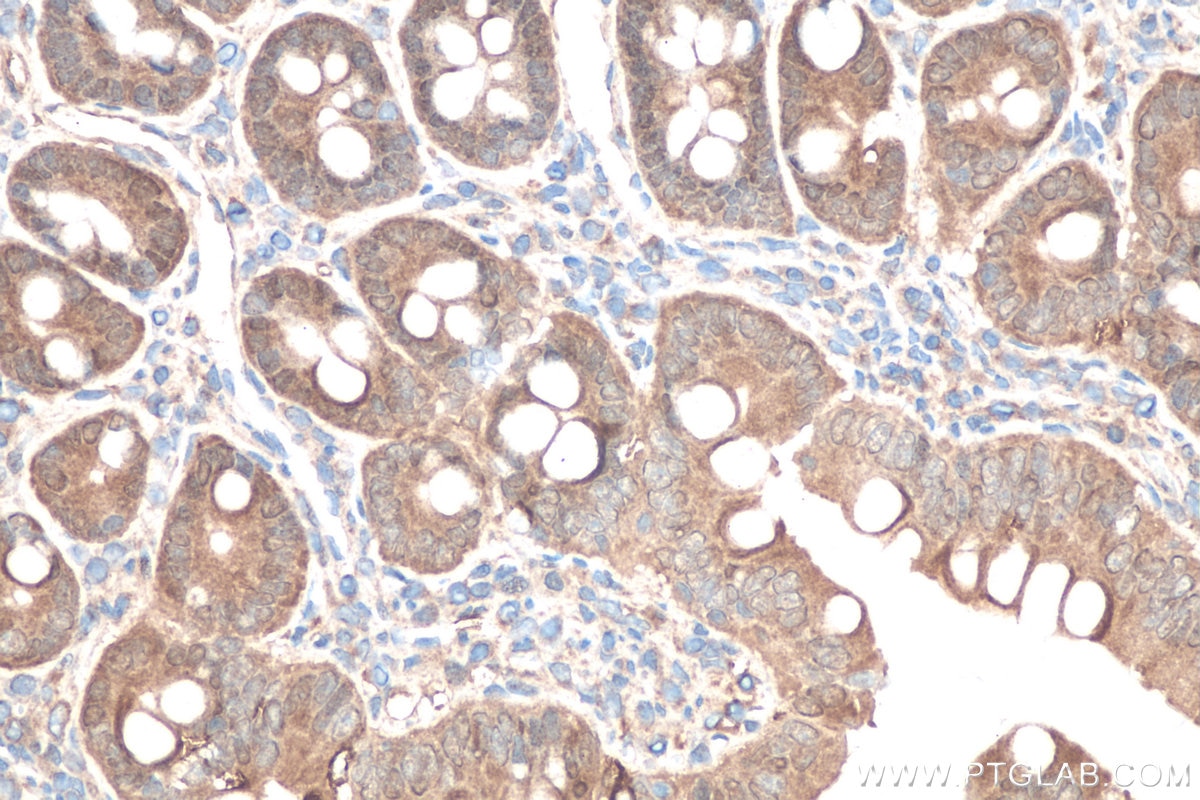
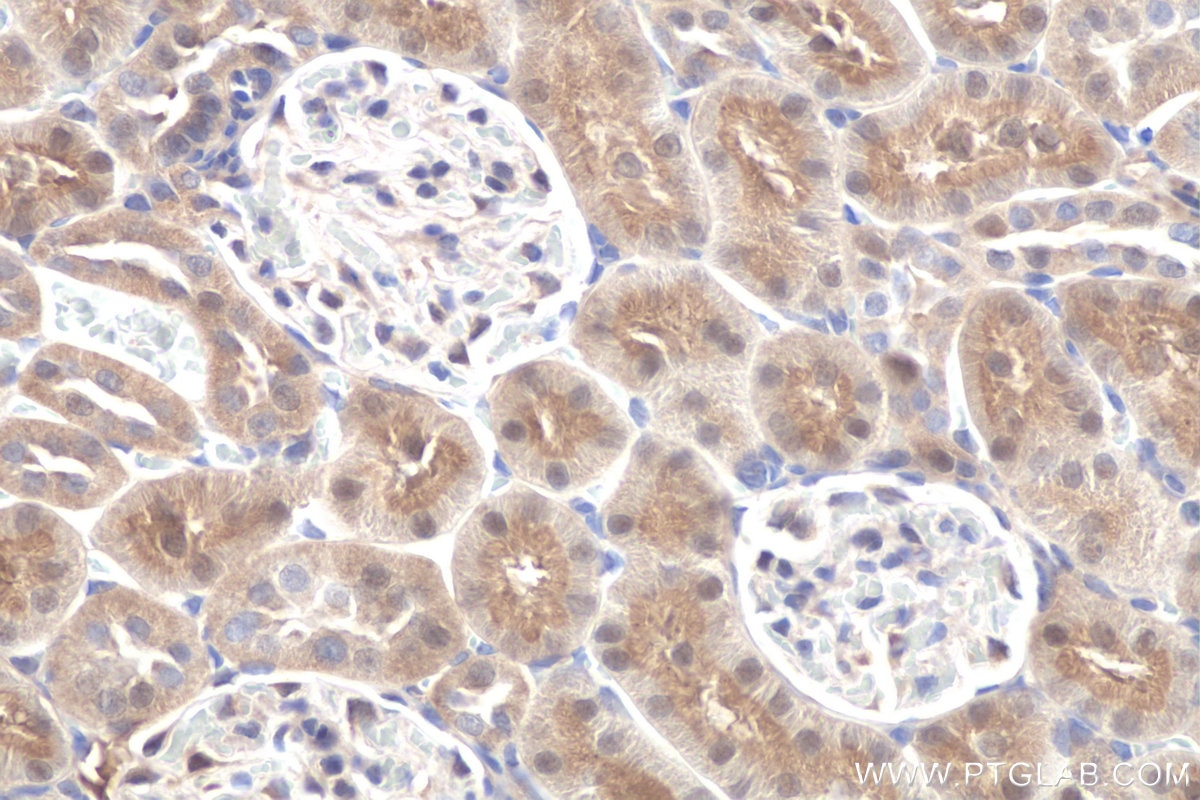
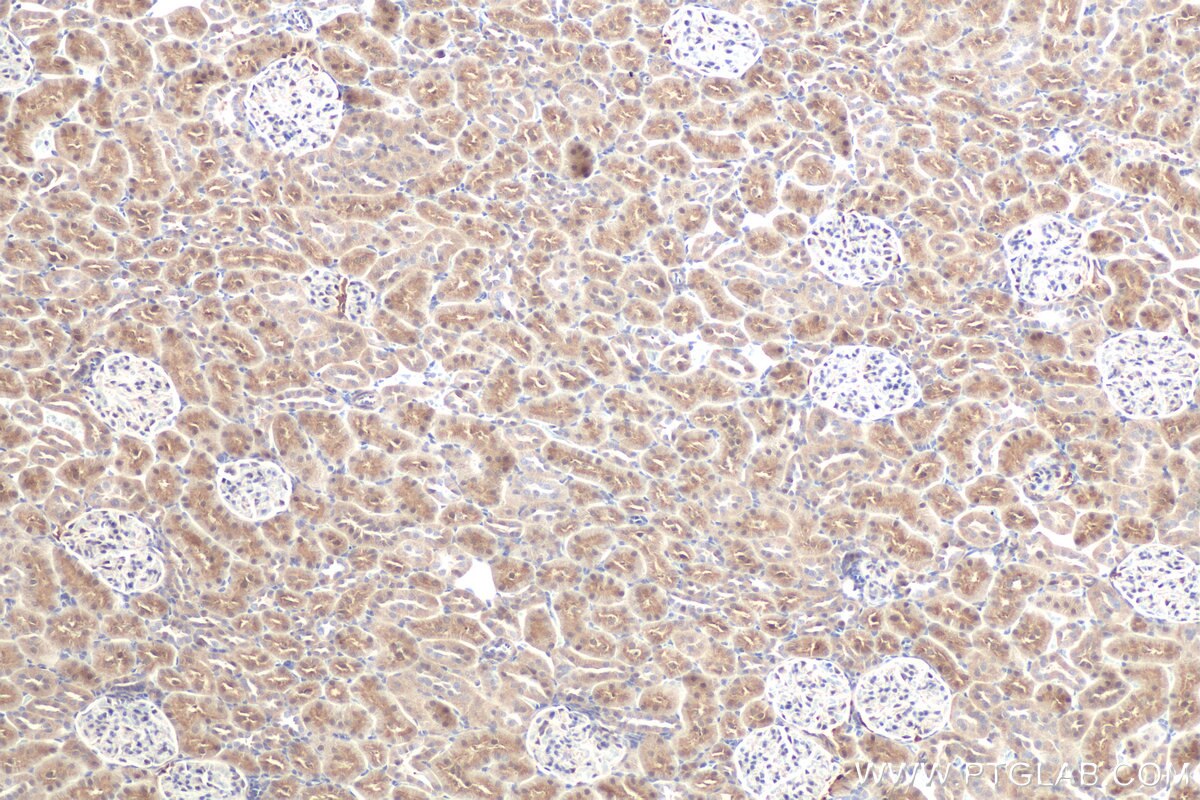
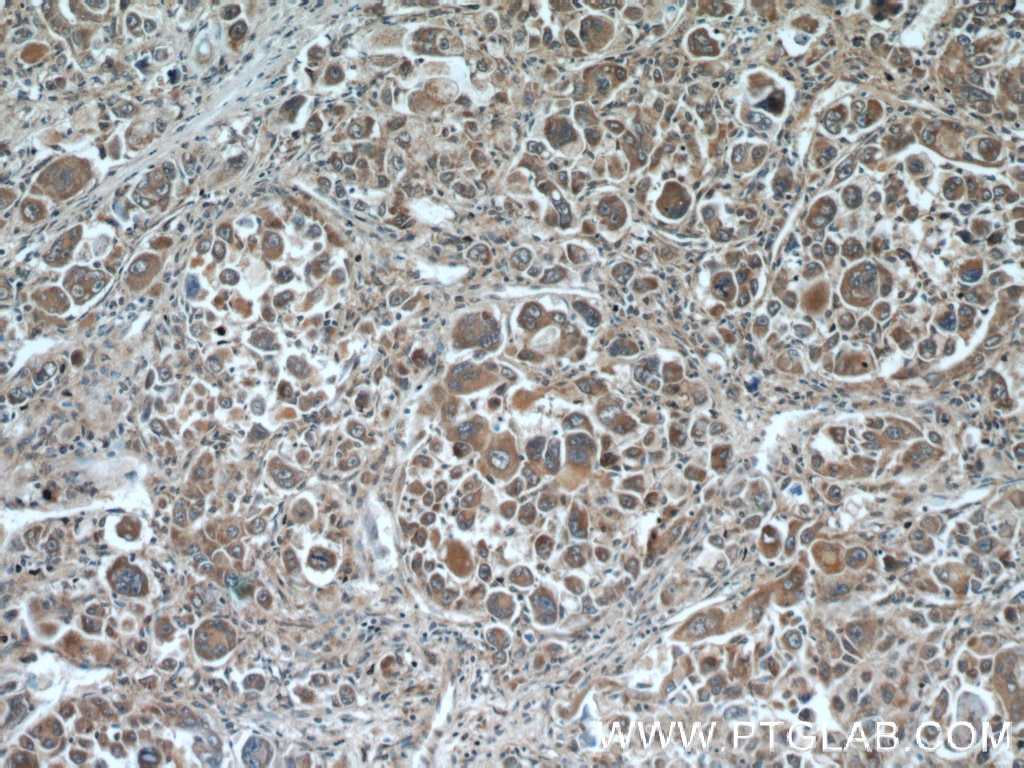
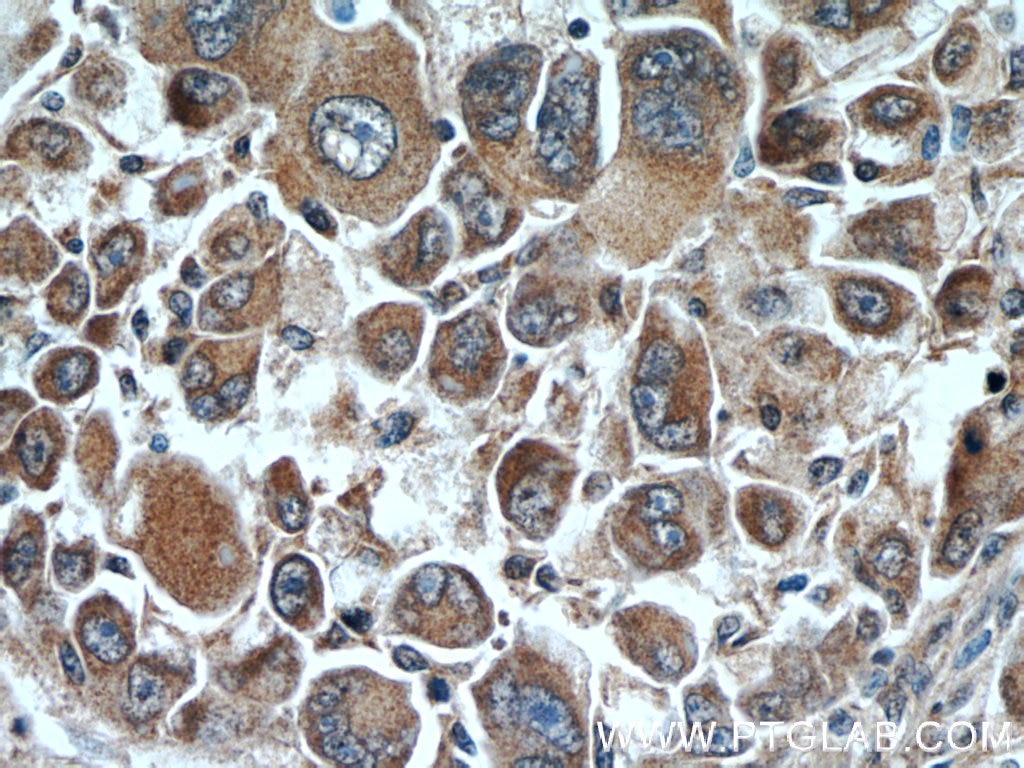
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | Mausnierengewebe, humanes Leberkarzinomgewebe, Ratten-Dünndarmgewebe, Rattennierengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
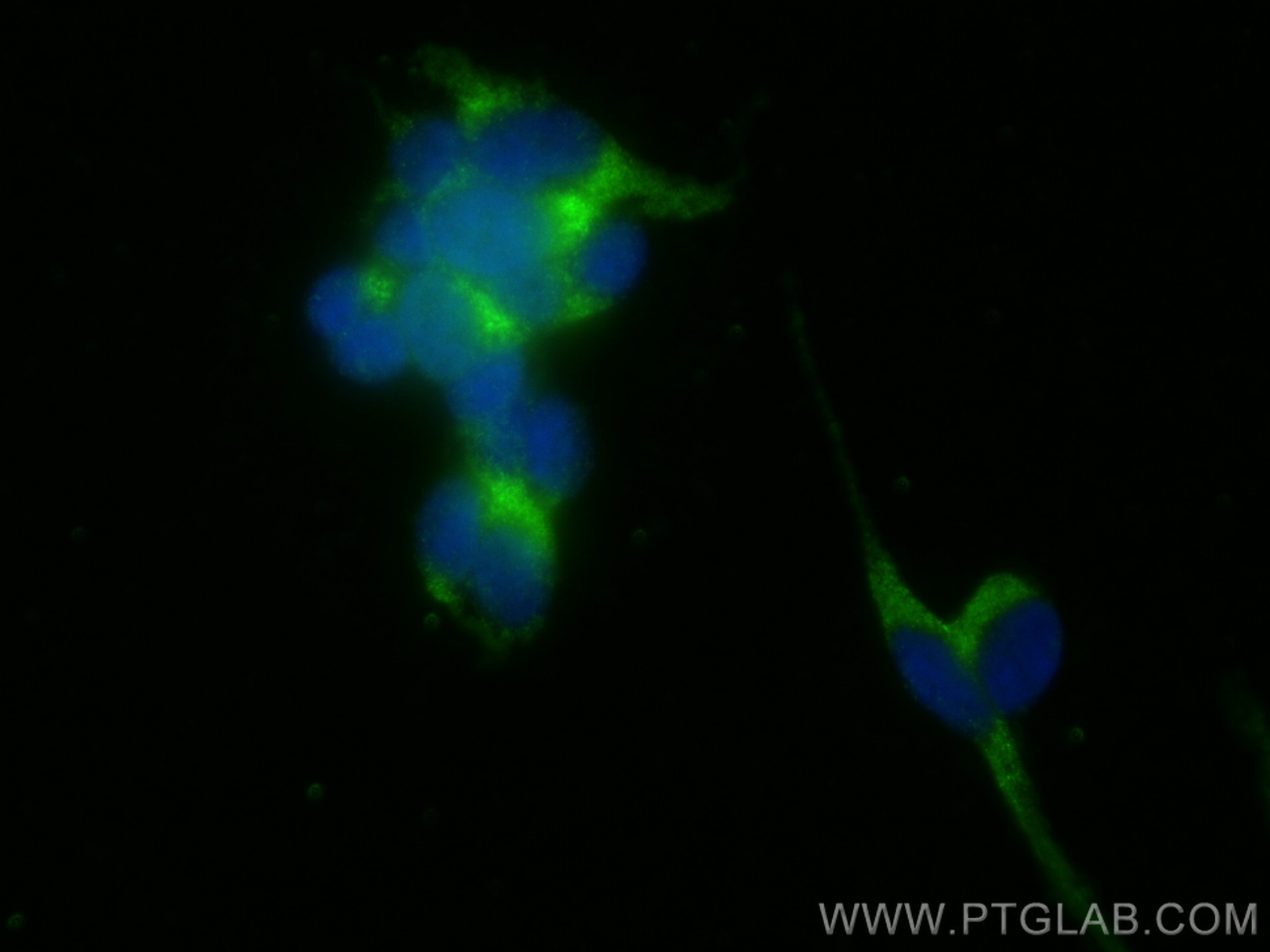
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | SH-SY5Y-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:3000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 5 publications below |
| IHC | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
10166-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA DOPA decarboxylase und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | DOPA decarboxylase fusion protein Ag0219 |
| Vollständiger Name | dopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 54 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 48-50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC008366 |
| Gene symbol | DOPA decarboxylase |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1644 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase belongs to the pyridoxal-dependent aminotransferase superfamily.DDC catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) to dopamine, L-5-hydroxytryptophan to serotonin and L-tryptophan to tryptamine.DDC is the cause of aromatic L-amino-acid decarboxylase deficiency (AADCD).Researches showed that Ddc is only one of the enzymes in the biosynthetic pathways for bioamines and catecholamines.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DOPA decarboxylase antibody 10166-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for DOPA decarboxylase antibody 10166-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for DOPA decarboxylase antibody 10166-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for DOPA decarboxylase antibody 10166-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Signal Profile of 5-HT2A receptor involved in signaling cascades associated to intracellular inflammation and apoptosis in hepatocytes and its role in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity | ||
Dis Model Mech A Matrigel-based 3D construct of SH-SY5Y cells models the α-synuclein pathologies of Parkinson's disease. | ||
J Transl Med Retinal pigment epithelial cells secrete neurotrophic factors and synthesize dopamine: possible contribution to therapeutic effects of RPE cell transplantation in Parkinson's disease. | ||
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol Carbon tetrachloride induced mitochondrial division, respiratory chain damage, abnormal intracellular [H+] and apoptosis are due to the activation of 5-HT degradation system in hepatocytes. |