- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
Chk1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
Chk1 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10362-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
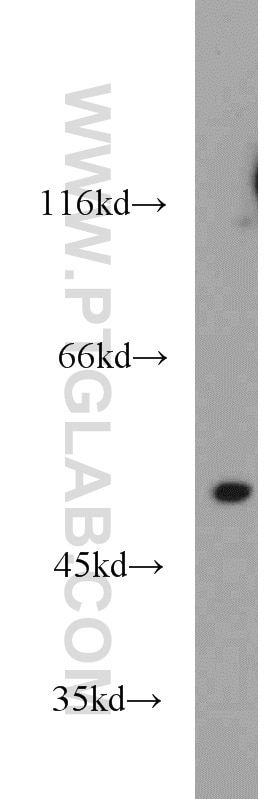
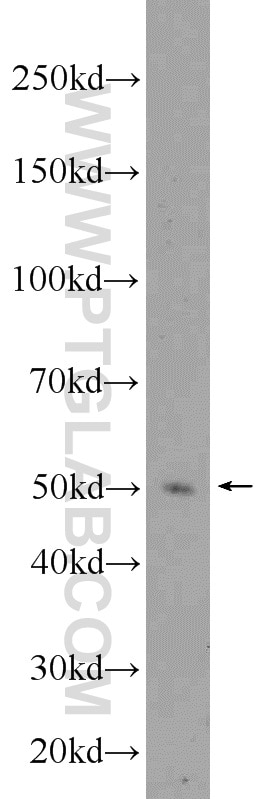
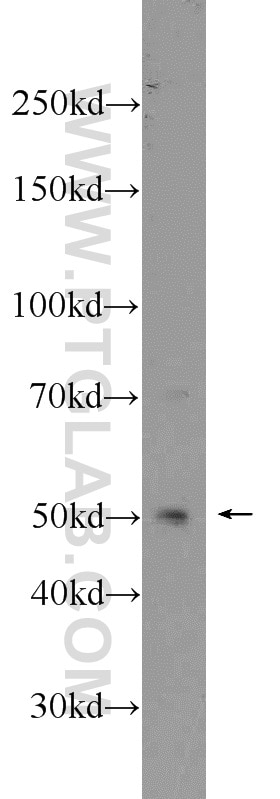
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Maus-Thymusgewebe, HeLa-Zellen, K-562-Zellen |
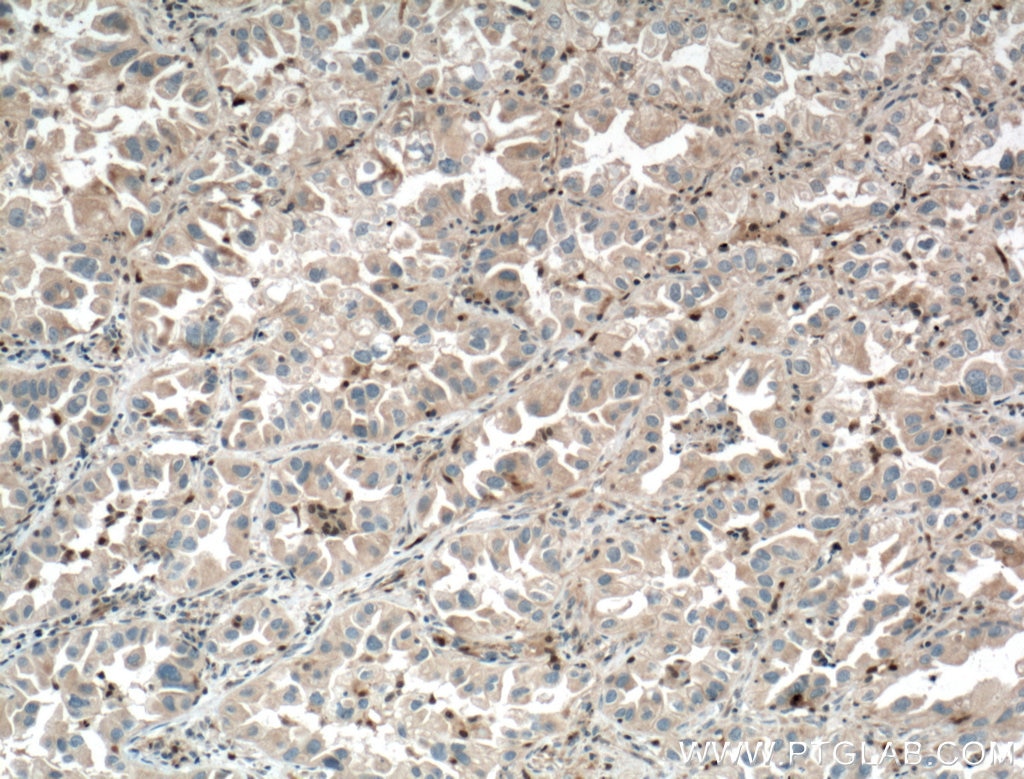
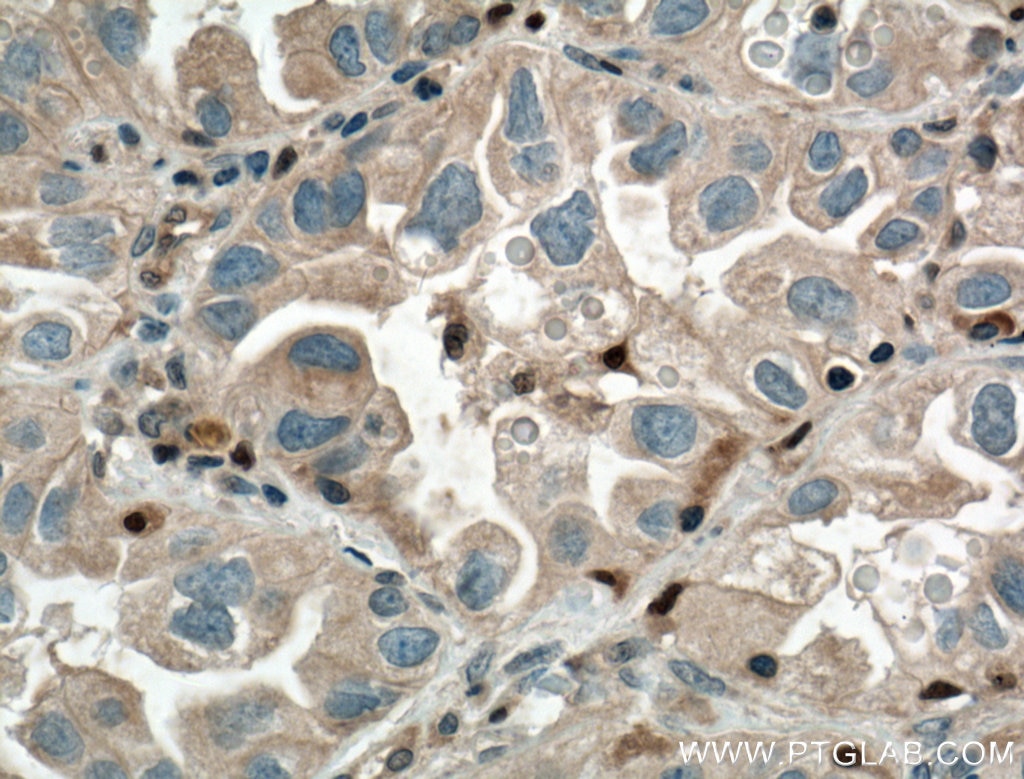
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Lungenkarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
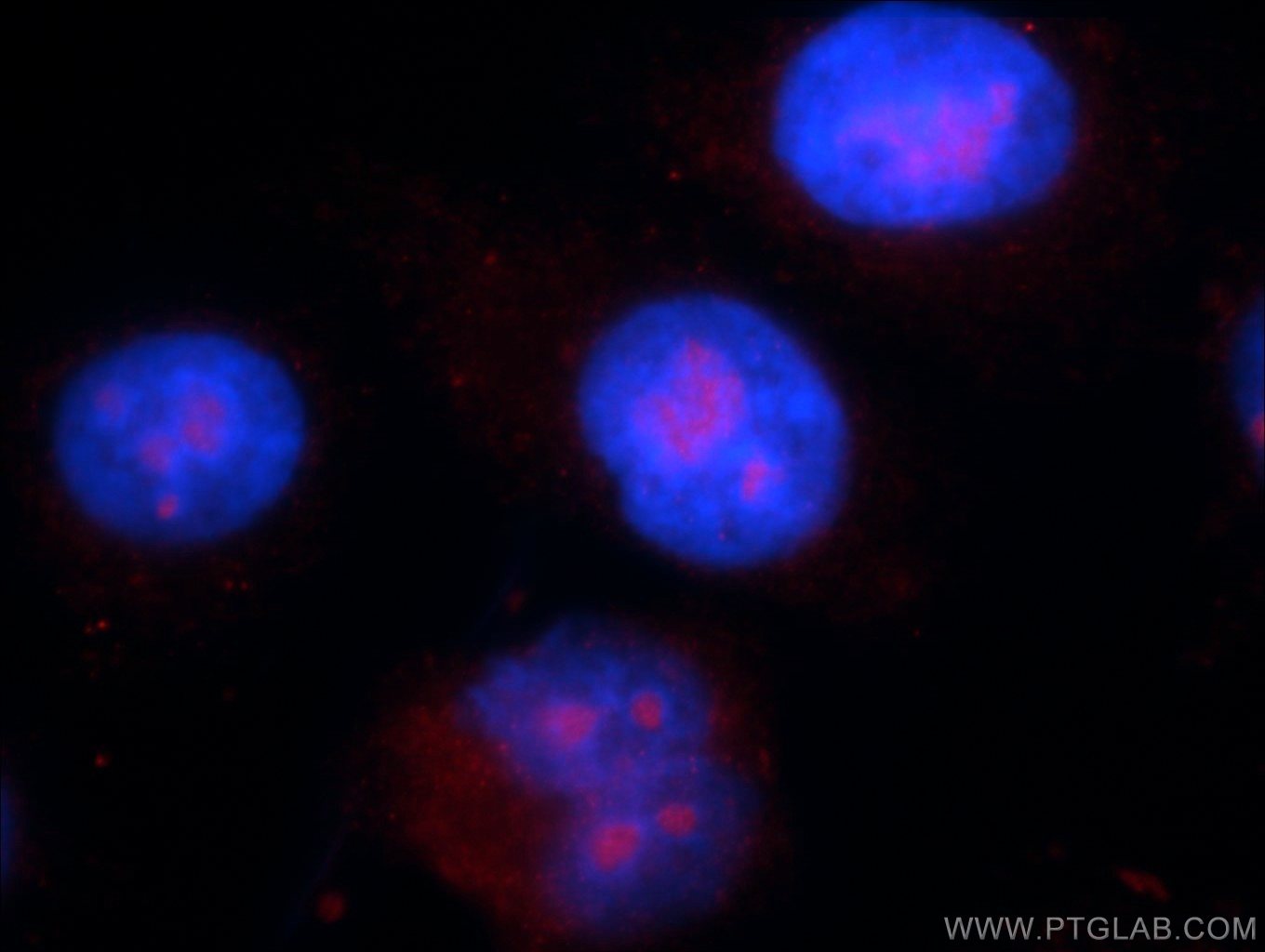
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HepG2-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 16 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
10362-1-AP bindet in WB, IF, IHC, ELISA Chk1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Chk1 fusion protein Ag0409 |
| Vollständiger Name | CHK1 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 54 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC004202 |
| Gene symbol | Chk1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1111 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
In response to DNA damage, mammalian cells prevent cell cycle progression through the control of critical cell cycle regulators. CHK1 (synonym: CHEK1), a homolog of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Chk1 protein kinase, is required for the DNA damage checkpoint. Human Chk1 protein is modified in response to DNA damage. In vitro Chk1 binds to and phosphorylate the dual-specificity protein phosphatases Cdc25A, Cdc25B, and Cdc25C, which control cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating cyclin-dependent kinases. CHK1 can be autophosphorylated(PMID:22941630) and ubiquitinated (PMID:19276361). It has 3 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 54 kDa, 44 kDa and 50 kDa.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| FC protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun Human Tra2 proteins jointly control a CHEK1 splicing switch among alternative and constitutive target exons.
| ||
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A Checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1)-short is a splice variant and endogenous inhibitor of Chk1 that regulates cell cycle and DNA damage checkpoints. | ||
Oncotarget UBE2D3 gene overexpression increases radiosensitivity of EC109 esophageal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. | ||
EBioMedicine High PARP-1 expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia and PARP-1 inhibitor and SAHA-bendamustine hybrid inhibitor combination treatment synergistically enhances anti-tumor effects. | ||
Cell Death Dis HBV infection potentiates resistance to S-phase arrest-inducing chemotherapeutics by inhibiting CHK2 pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. | ||
Cell Death Dis PFKFB3 blockade inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by impairing DNA repair through AKT. |