- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
B4GALT7 Polyklonaler Antikörper
B4GALT7 Polyklonal Antikörper für ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
WB, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10535-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
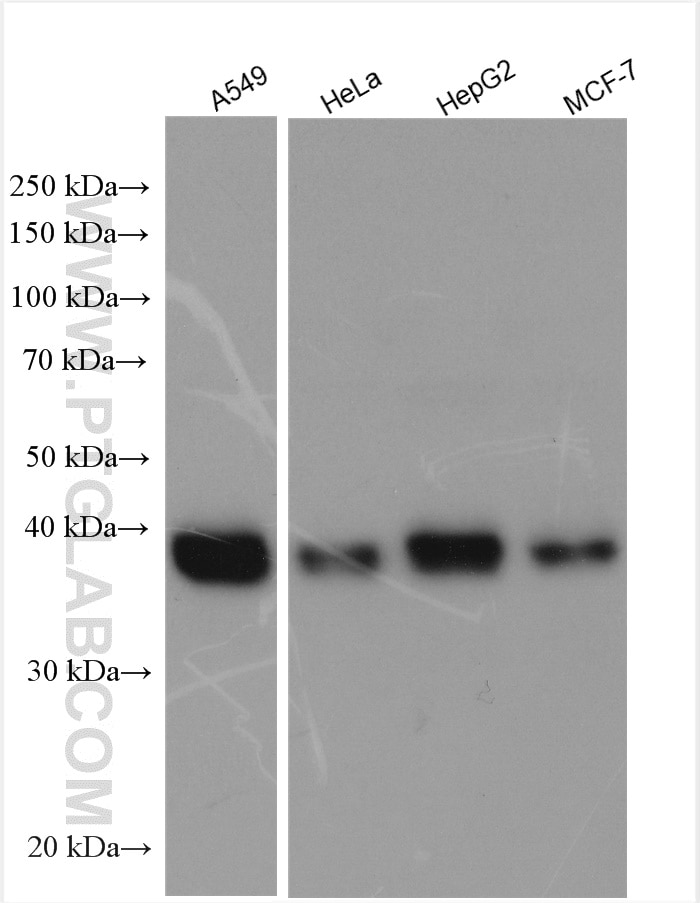
10535-1-AP bindet in WB, ELISA B4GALT7 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | B4GALT7 fusion protein Ag0793 |
| Vollständiger Name | xylosylprotein beta 1,4-galactosyltransferase, polypeptide 7 (galactosyltransferase I) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 37 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 37 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC007317 |
| Gene symbol | B4GALT7 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 11285 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
B4GALT7 (Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 7), also known as galactosyltransferase I, is involved in the formation of proteoglycans which are components of the extracellular matrix in connective tissues (PubMed: 10438455). The reduced activity of B4GALT7 results in delayed wound repair, altered migration, adhesion and contractility of patient fibroblasts (PMID: 16583246, PMID: 18158310). Mutations in B4GALT7 that also result in Spondylodysplastic (PMID: 24755949, PMID: 12417421).
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for B4GALT7 antibody 10535-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Eur J Hum Genet Impairment of glycosaminoglycan synthesis in mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA cells by using siRNA: a potential therapeutic approach for Sanfilippo disease.
|