Anticorps Recombinant de lapin anti-iNOS
iNOS Recombinant Antibody for IHC, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
6O22
N° de cat : 80517-1-RR
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
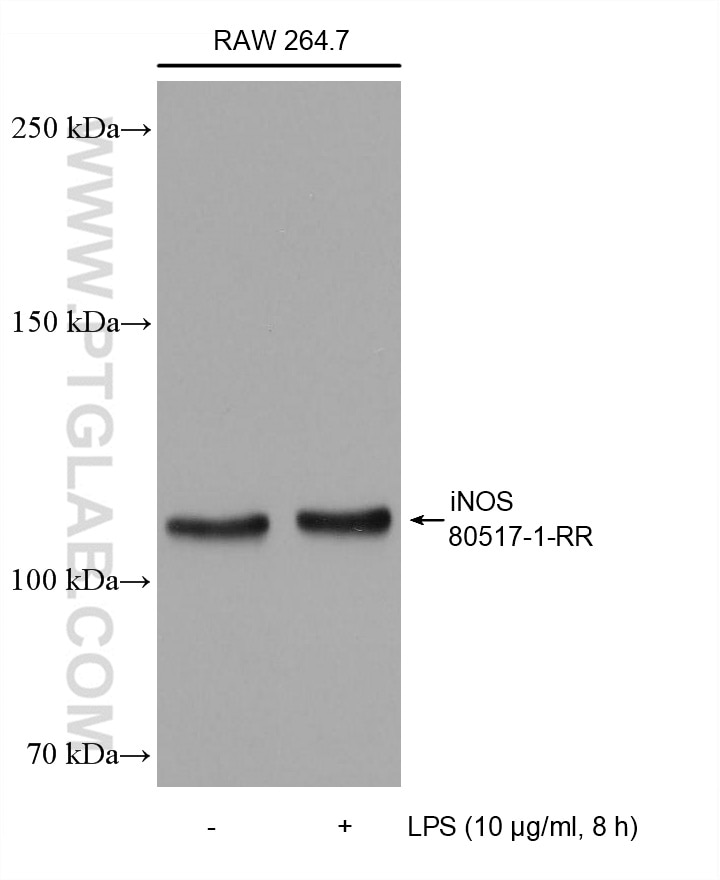
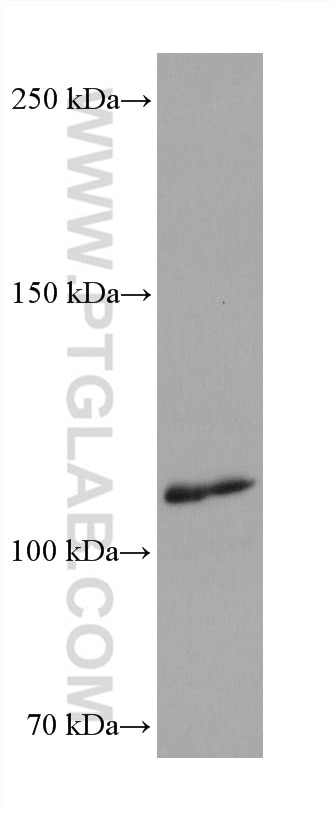
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules RAW 264.7, CMSP humaines traitées au LPS |
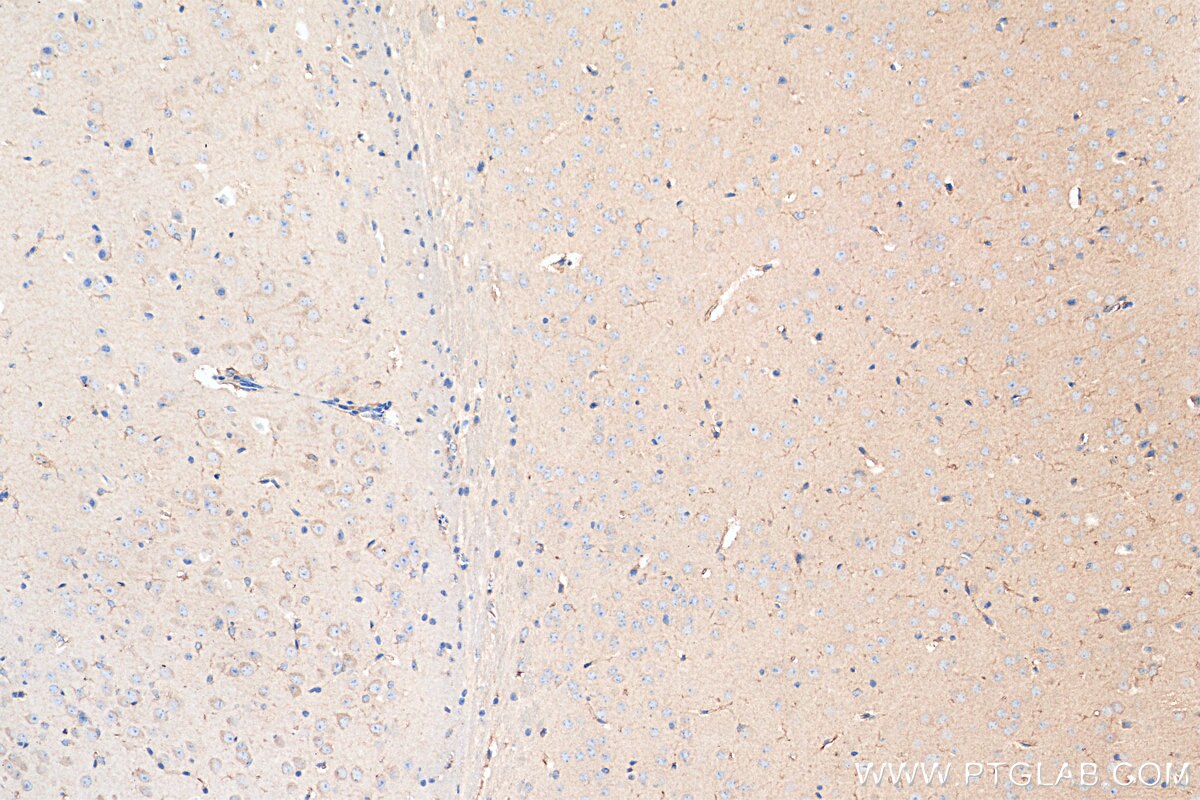
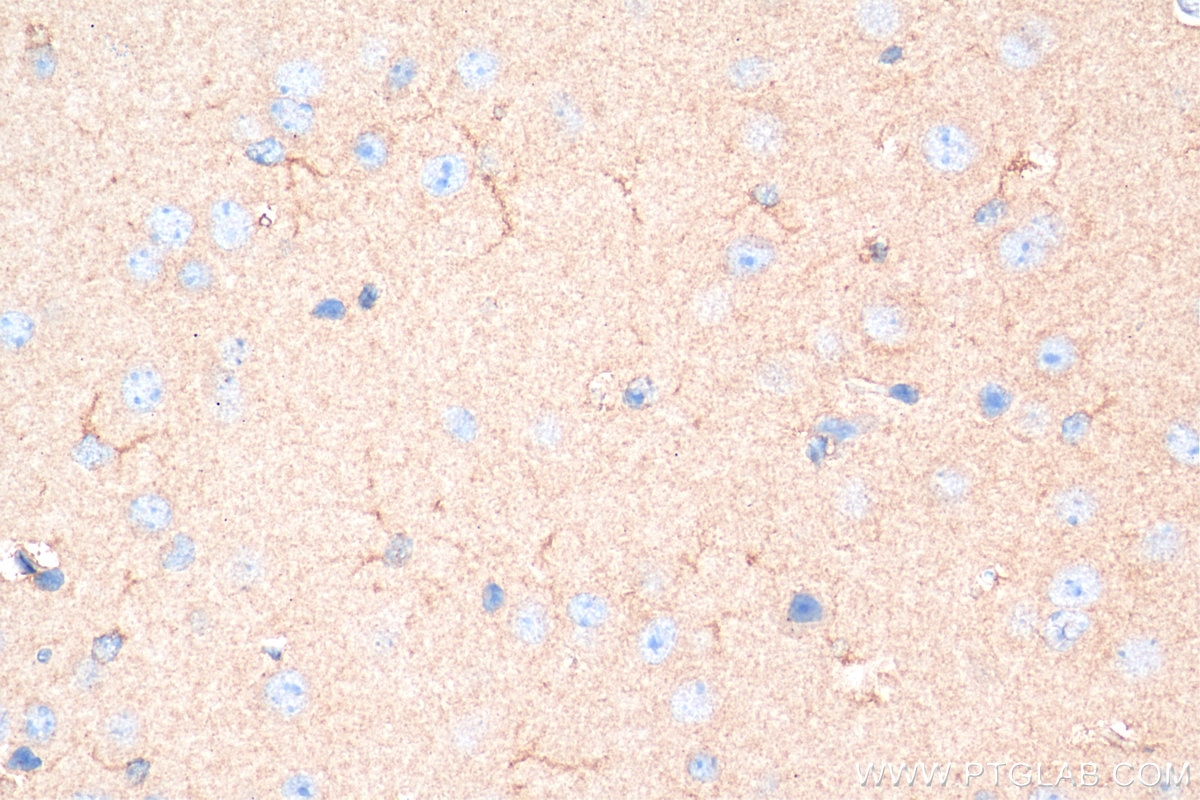
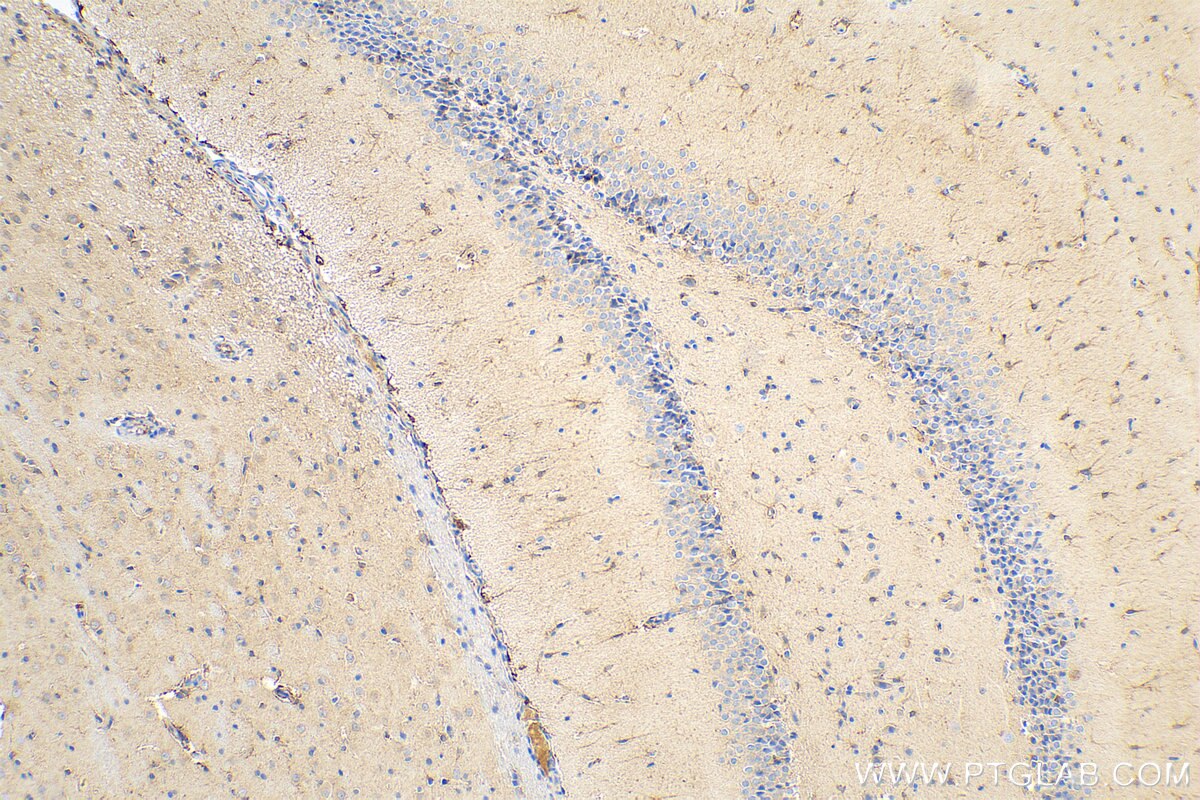
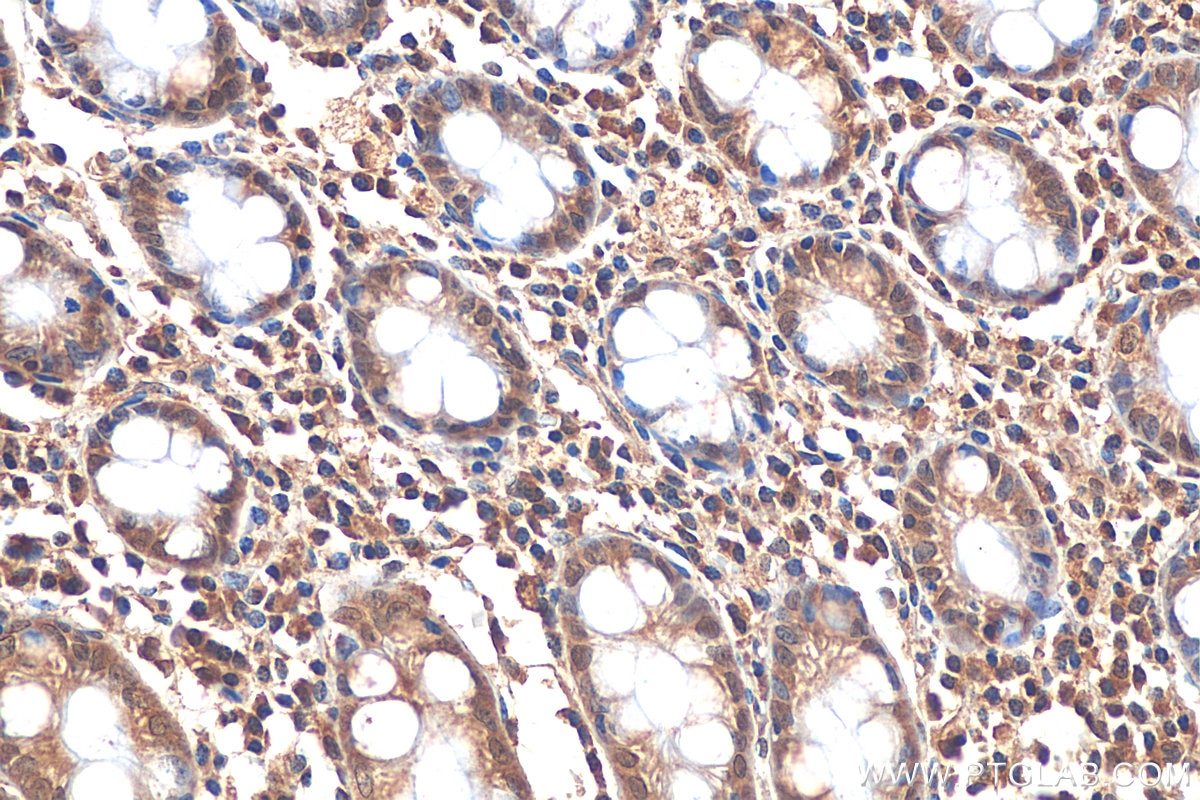
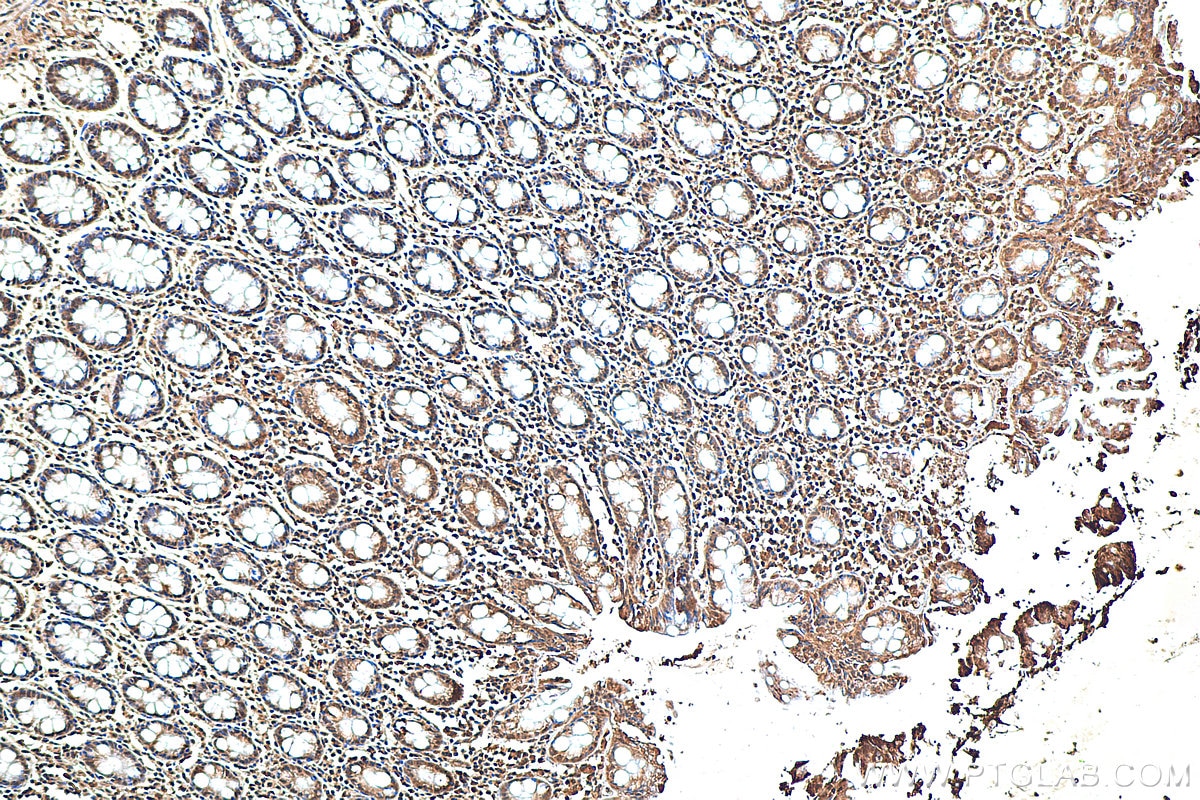
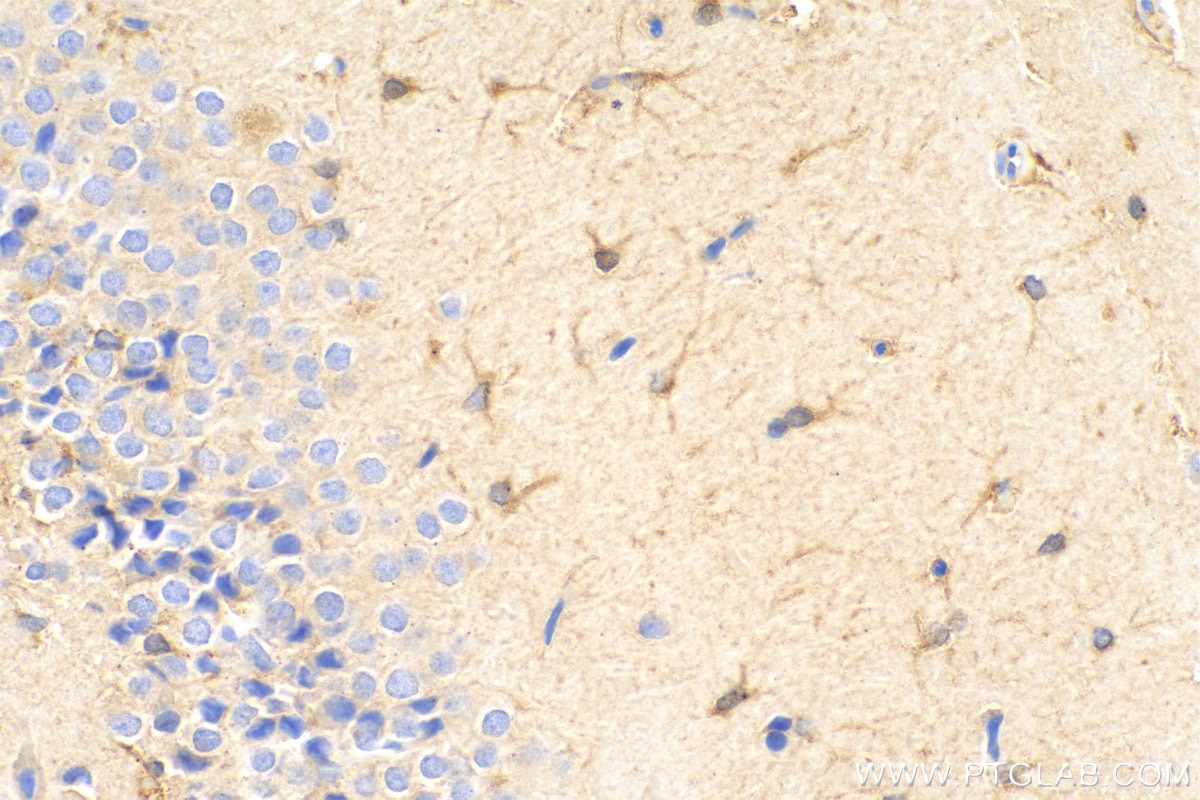
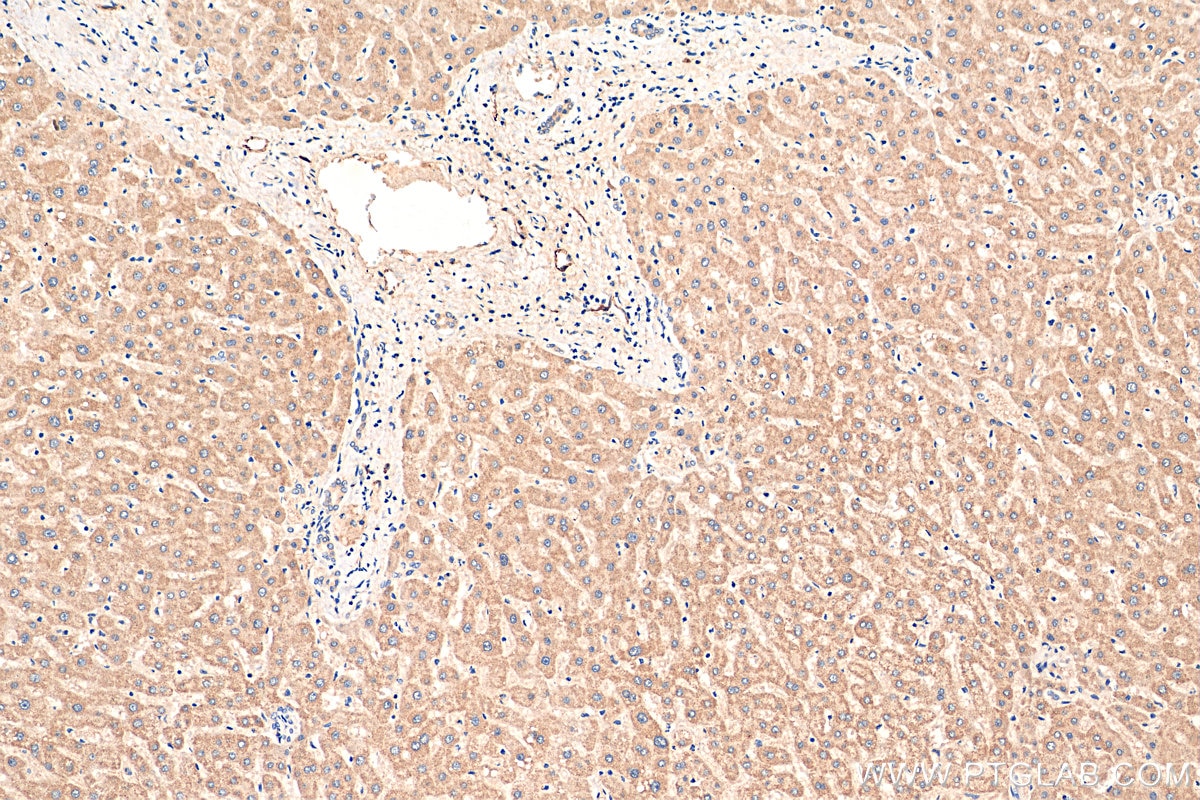
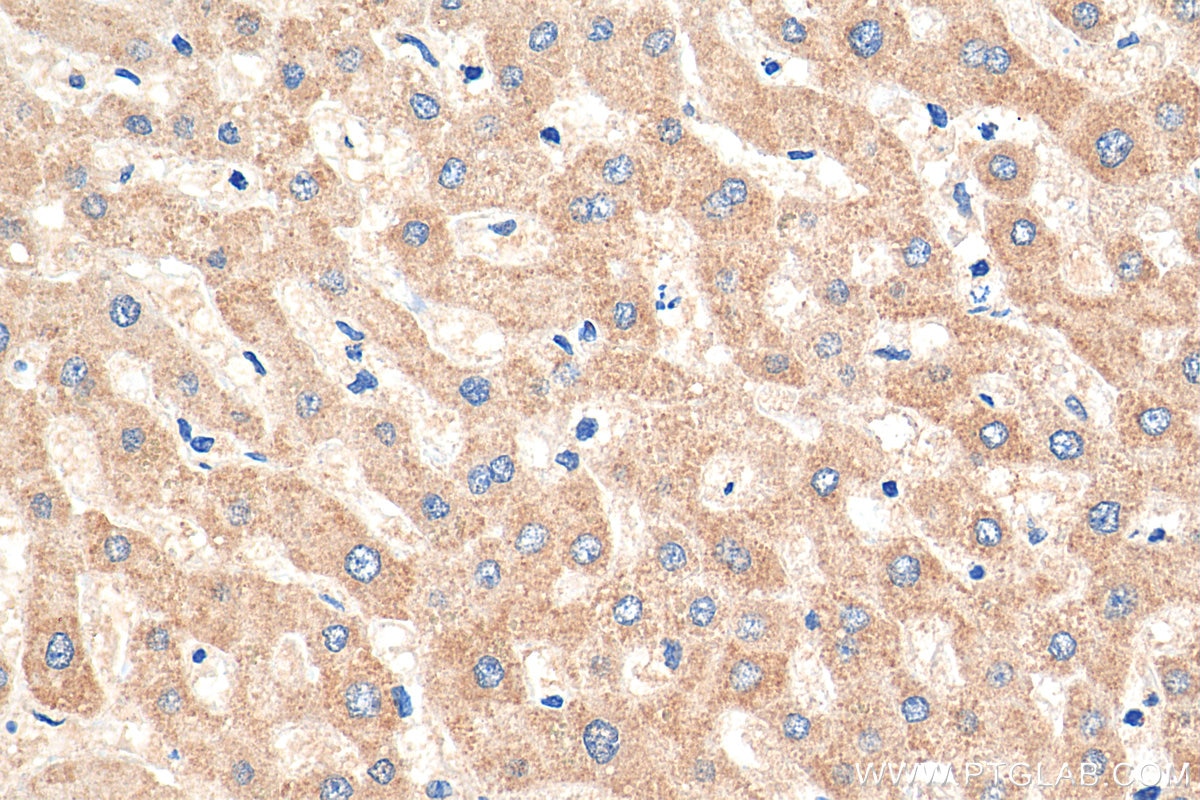
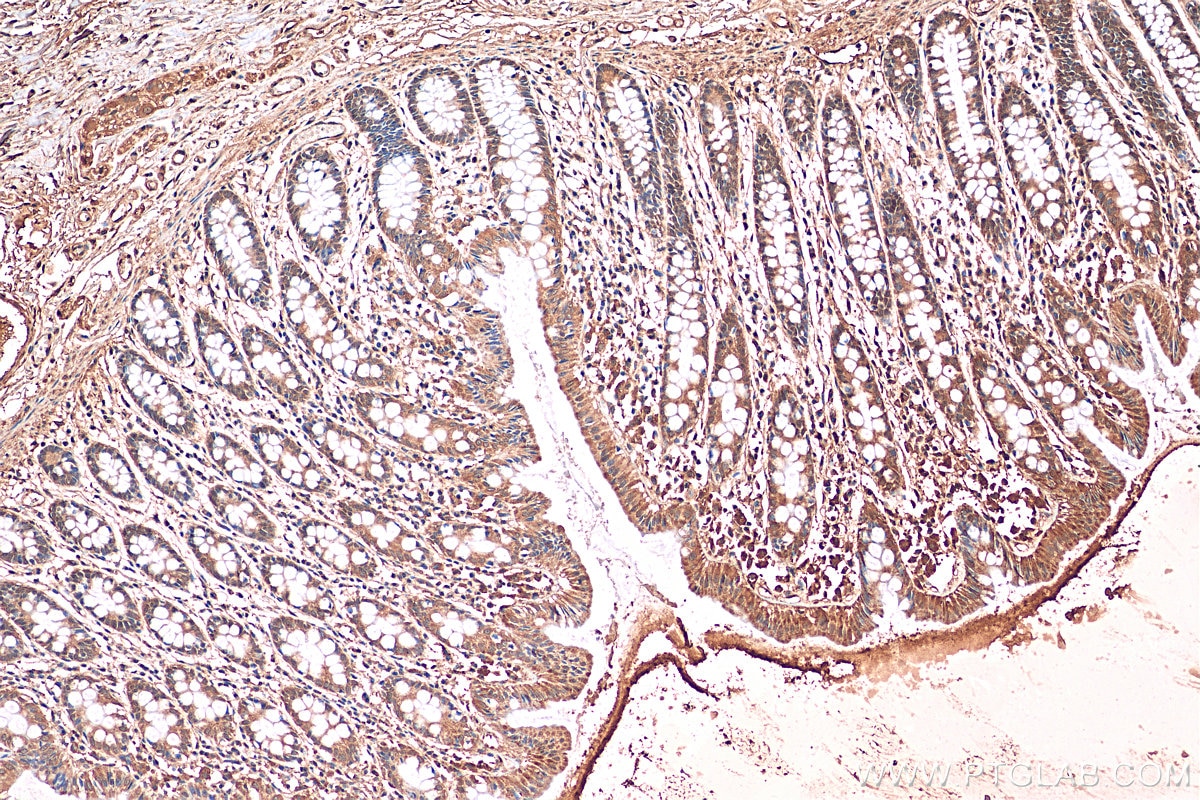
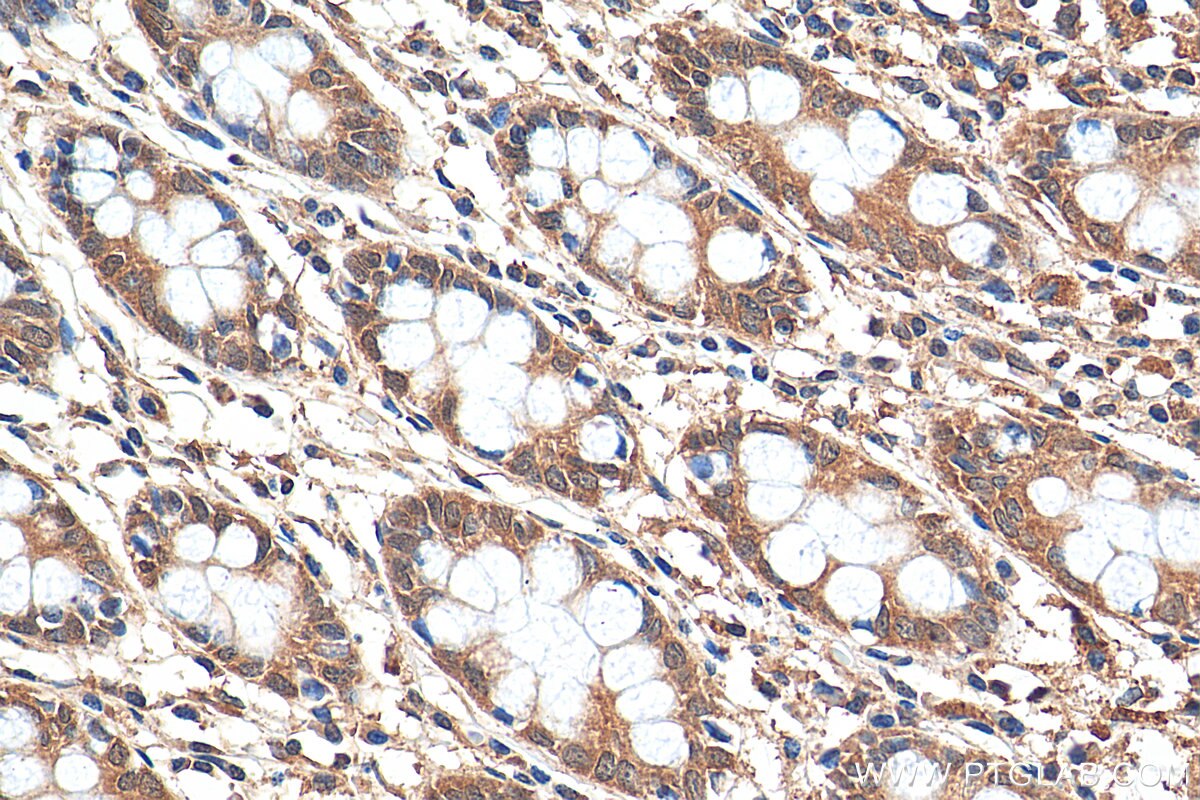
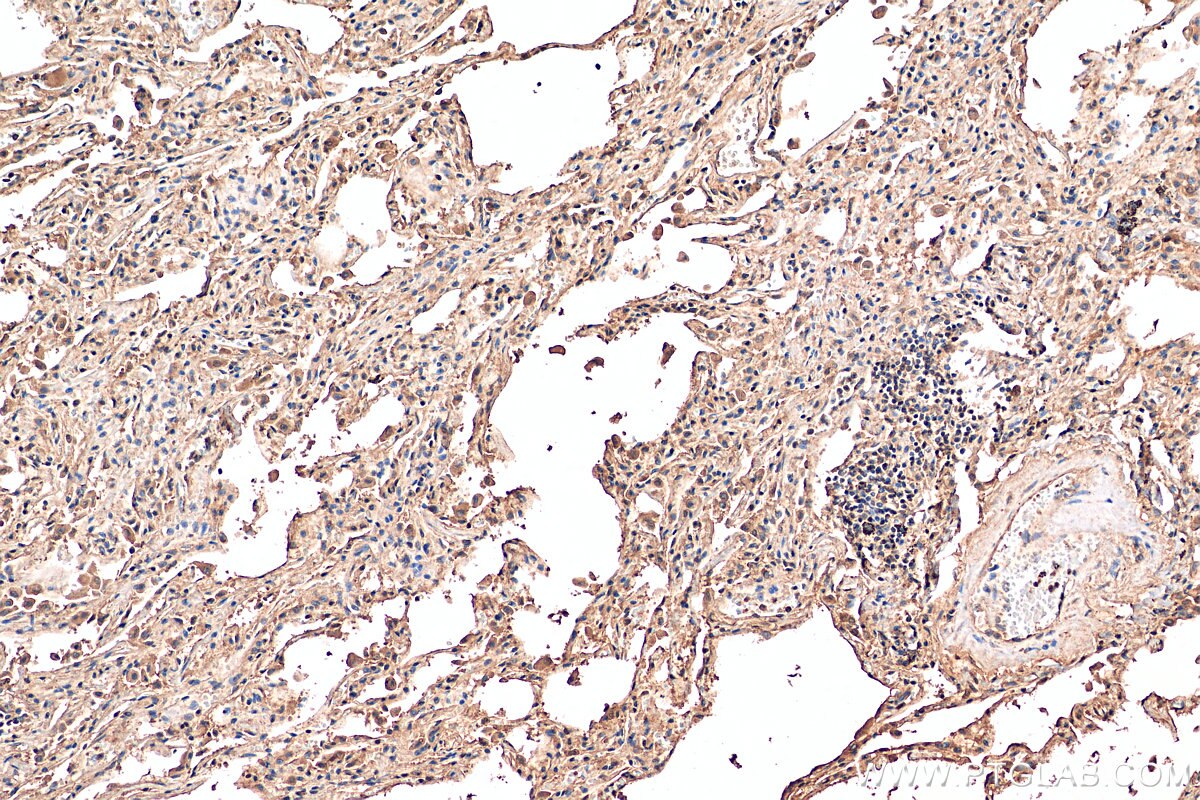
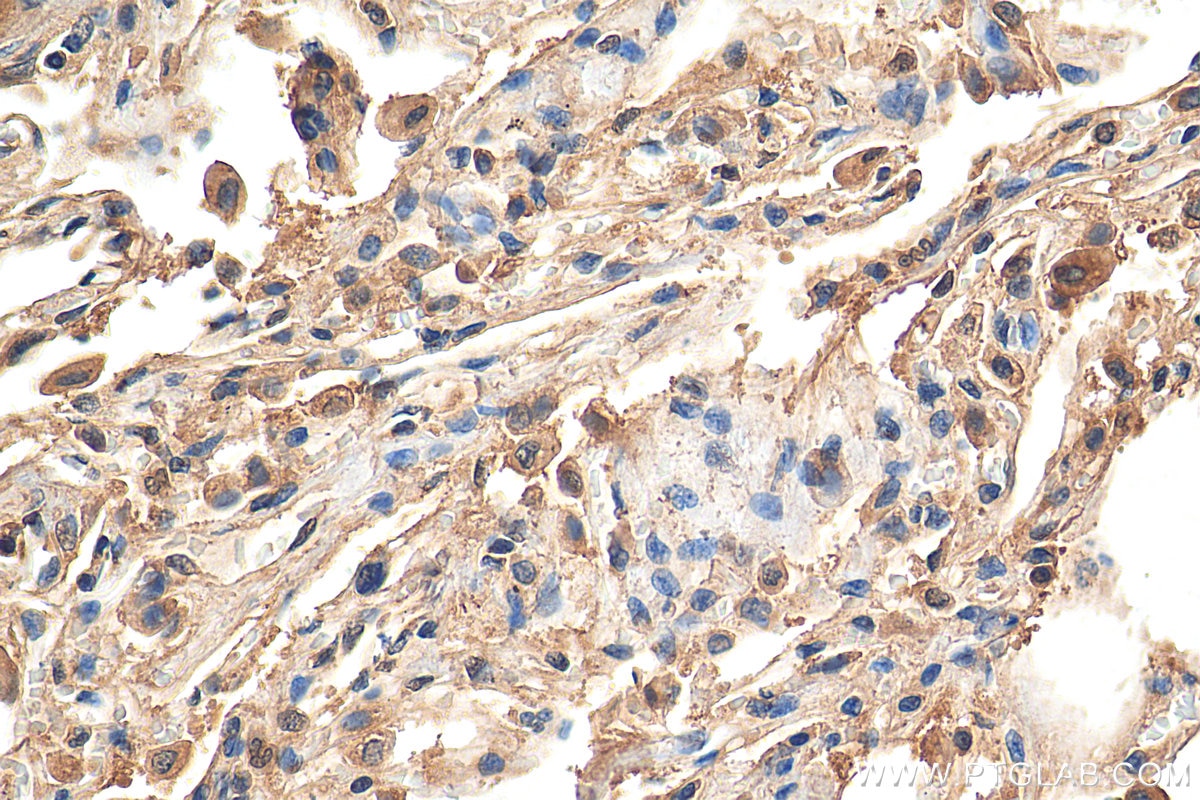
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cérébral de souris, tissu cérébral de rat, tissu de côlon humain, tissu hépatique humain, tissu pulmonaire humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 6 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
80517-1-RR cible iNOS dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Recombinant |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 131 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 110-130 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM_000625 |
| Symbole du gène | NOS2 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4843 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
NOS2, also named as iNOS and NOS2A, produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body. NO is a reactive free radical which acts as a biologic mediator in several processes, including neurotransmission, antimicrobial and antitumoral activities. NOS2 is a nitric oxide synthase which is expressed in liver and is inducible by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and certain cytokines. iNOS has a very short half-life due to rapid degradation by calpain. iNOS monomer is a direct substrate of calpain I and can be cleaved by calpain I at the canonical CaM-binding site(503-532aa) of iNOS, and then a ~70kD band can be detected by western (PMID:11786228). This antibody is specific to NOS2.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for iNOS antibody 80517-1-RR | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for iNOS antibody 80517-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Control Release Controlled extracellular vesicles release from aminoguanidine nanoparticle-loaded polylysine hydrogel for synergistic treatment of spinal cord injury | ||
Int J Mol Sci Ursolic Acid Alleviates Neuroinflammation after Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Mediating Microglial Pyroptosis via the NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD Pathway | ||
Int J Mol Sci C-X-C Motif Chemokine 3 Promotes the Inflammatory Response of Microglia after Escherichia coli-Induced Meningitis | ||
J Ethnopharmacol Extract of Astragali Radix and Solanum nigrum Linne regulates microglia and macrophage polarization and inhibits the growth and infiltration of C6 glioblastoma | ||
Mater Today Bio Treatment with FAP-targeted zinc ferrite nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial damage | ||
Free Radic Biol Med Exosomes derived from schwann cells alleviate mitochondrial dysfunction and necroptosis after spinal cord injury via AMPK signaling pathway-mediated mitophagy |