Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Beta Tubulin
Beta Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody for FC (Intra), IF, WB
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Réactivité testée
Humain, namatode, poisson-zèbre, porc, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IF, FC (Intra)
Conjugaison
CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
1D4A4
N° de cat : CL488-66240
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
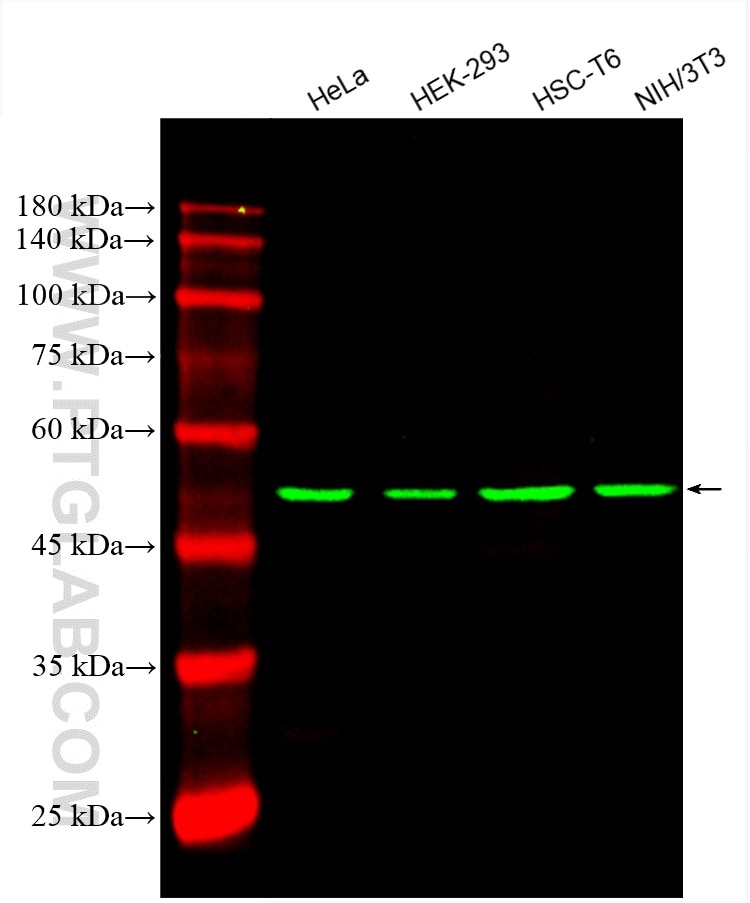
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HeLa, cellules HEK-293, cellules HSC-T6, cellules NIH/3T3 |
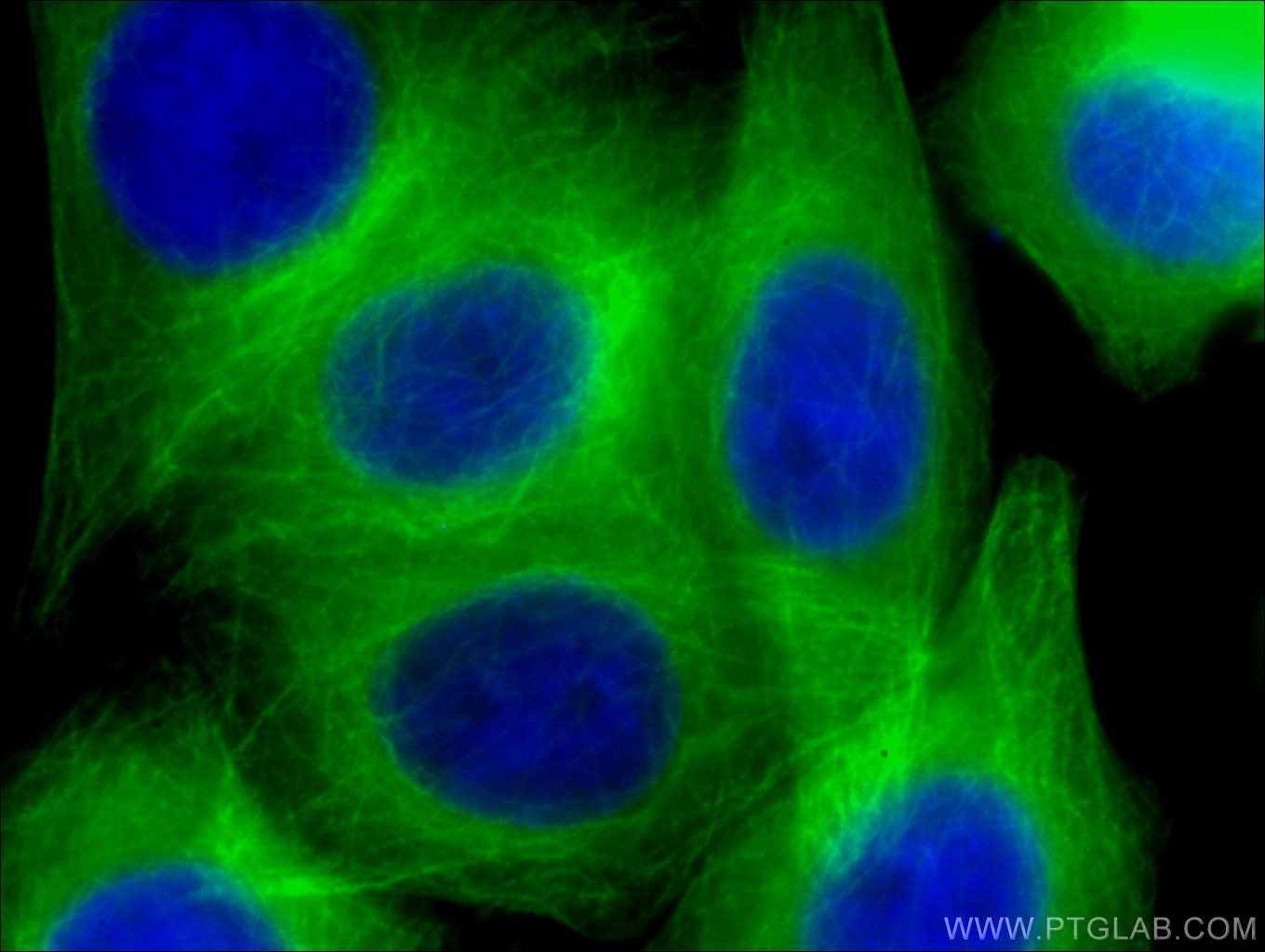
| Résultats positifs en IF | cellules HepG2, |
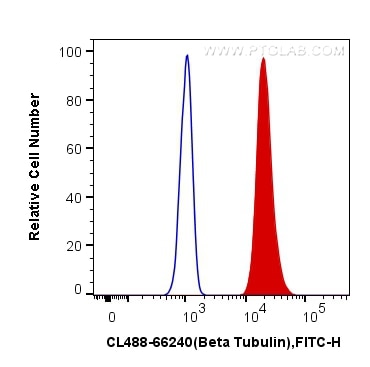
| Résultats positifs en cytométrie | cellules HeLa |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:50-1:500 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 7 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
CL488-66240 cible Beta Tubulin dans les applications de WB, IF, FC (Intra) et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, namatode, poisson-zèbre, porc, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, namatode, poisson-zèbre, porc, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Beta Tubulin Protéine recombinante Ag0117 |
| Nom complet | tubulin, beta 3 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 450 aa, 50 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC000748 |
| Symbole du gène | TUBB3 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 10381 |
| Conjugaison | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec glycérol à 50 %, Proclin300 à 0,05 % et BSA à 0,5 %, pH 7,3. |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20 °C. Éviter toute exposition à la lumière. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
There are five tubulins in human cells: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon. Tubulins are conserved across species. They form heterodimers, which multimerize to form a microtubule filament. An alpha and beta tubulin heterodimer is the basic structural unit of microtubules. The alpha and beta tubulins (+/- 55 kDa MW) are homologous but are not identical. Beta tubulins have been widely used as loading control.
What is the molecular weight of beta-tubulin? Are there any isoforms of beta-tubulin?
The molecular weight of tubulin is 50-52 kDa. Humans have eight beta-tubulin isotypes, encoded by different genes, that differ in their C-terminal sequences. They have different tissue expression profiles and can rise to microtubules of different properties (PMID: 20191564).
How to use beta-tubulin as a loading control
Beta-tubulin is one of the most commonly used references as a loading control for cell lysates in western blotting. It is abundantly expressed across various tissues and developmental stages and highly conserved across species. However, since some variability has been observed in the expression levels of commonly used housekeeping genes (PMID: 15627964), it is recommended that more than one loading control antibody is used while developing new assays. More information can be found here: https://www.ptglab.com/news/blog/loading-control-antibodies-for-western-blotting/.
What drugs can influence beta-tubulin and organization of microtubules?
Many drugs that affect microtubule dynamics target beta-tubulin, mainly by interfering with the GTP hydrolysis (PMID: 21381049). Paclitaxel (Taxol) is used to stabilize microtubules by slowing down their depolymerization, while colchicine and vinca alkaloids (vinblastine) destabilize microtubules. They are used in research and also in the clinic as anti-cancer agents.
Is beta-tubulin post-translationally modified?
Yes, tubulins are subject to extensive post-translational modifications (PTMs) that affect the organization of microtubules and their dynamics. The most common modifications include polyglutamylation, polyglycylation, polyamination, glycososylation, glycation, phosphorylation, and acetylation (PMID: 24801181 and 25468068).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CL Plus 488 Beta Tubulin antibody CL488-66240 | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 Beta Tubulin antibody CL488-66240 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Chem Biol S1PR3-G12-biased agonist ALESIA targets cancer metabolism and promotes glucose starvation. | ||
Elife A novel mechanism of bulk cytoplasmic transport by cortical dynein in Drosophila ovary. | ||
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids Non-targeting control for MISSION shRNA library silences SNRPD3 leading to cell death or permanent growth arrest. | ||
Front Cell Dev Biol Caffeine Induces Autophagy and Apoptosis in Auditory Hair Cells via the SGK1/HIF-1α Pathway. | ||
iScience The vesicular transporter STX11 governs ATGL-mediated hepatic lipolysis and lipophagy. |