Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Villin
Villin Monoclonal Antibody for IF, IHC, IP, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2B7B9
N° de cat : 66096-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
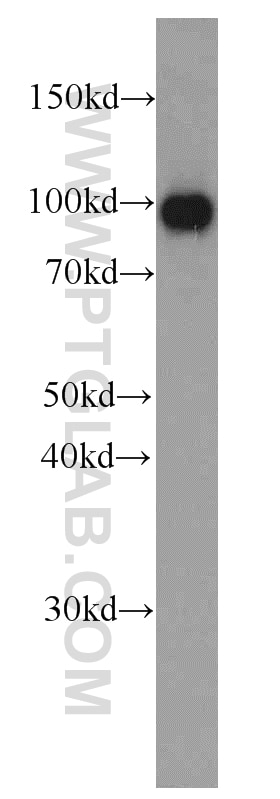
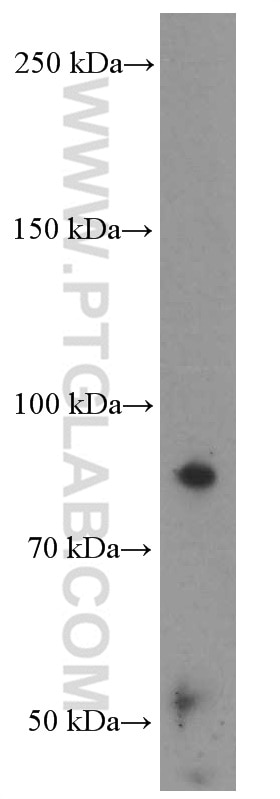
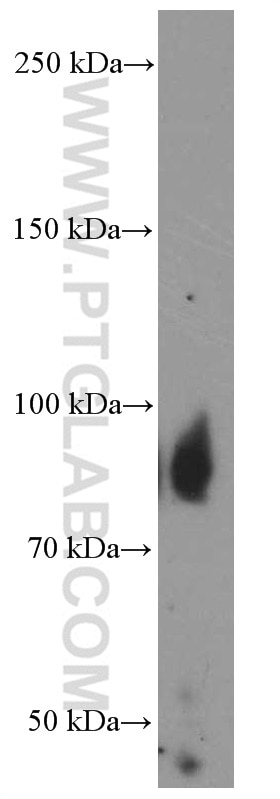
| Résultats positifs en WB | Rein humain, tissu |
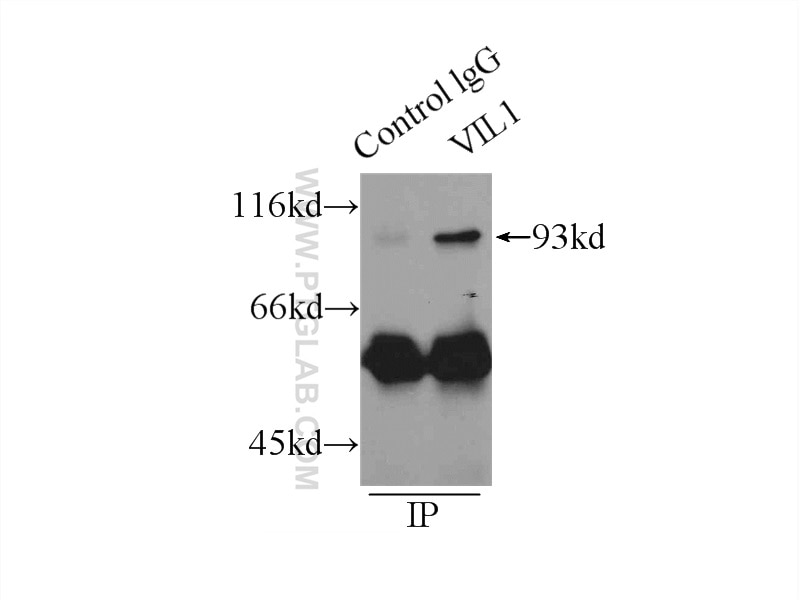
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu rénal de souris |
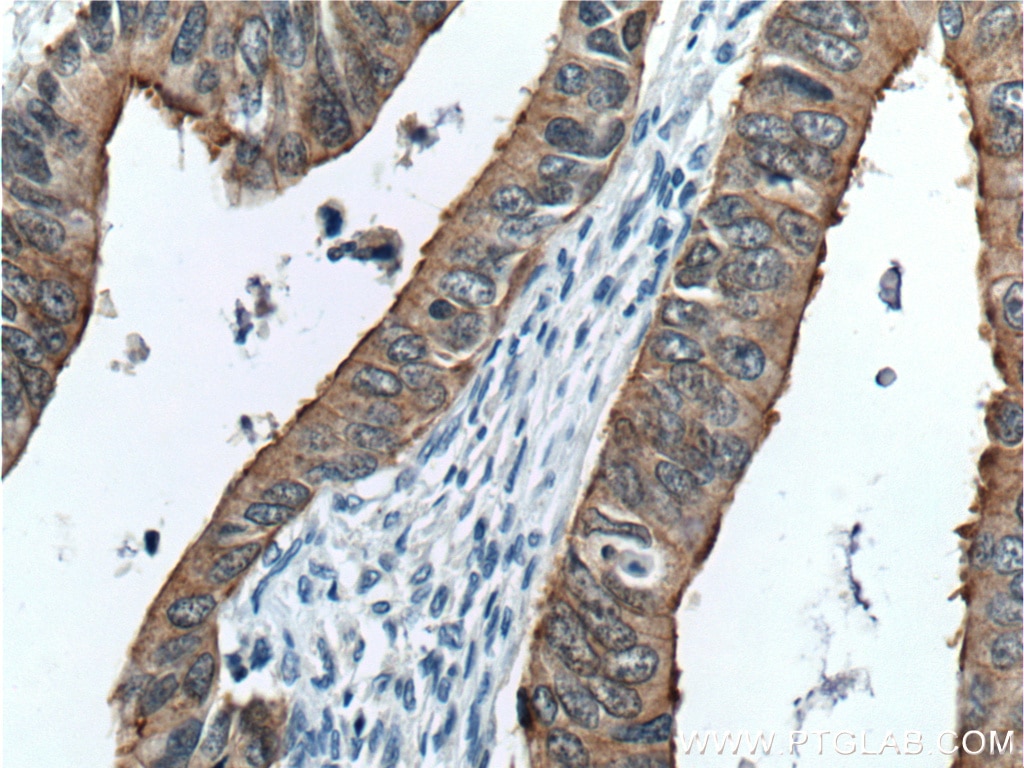
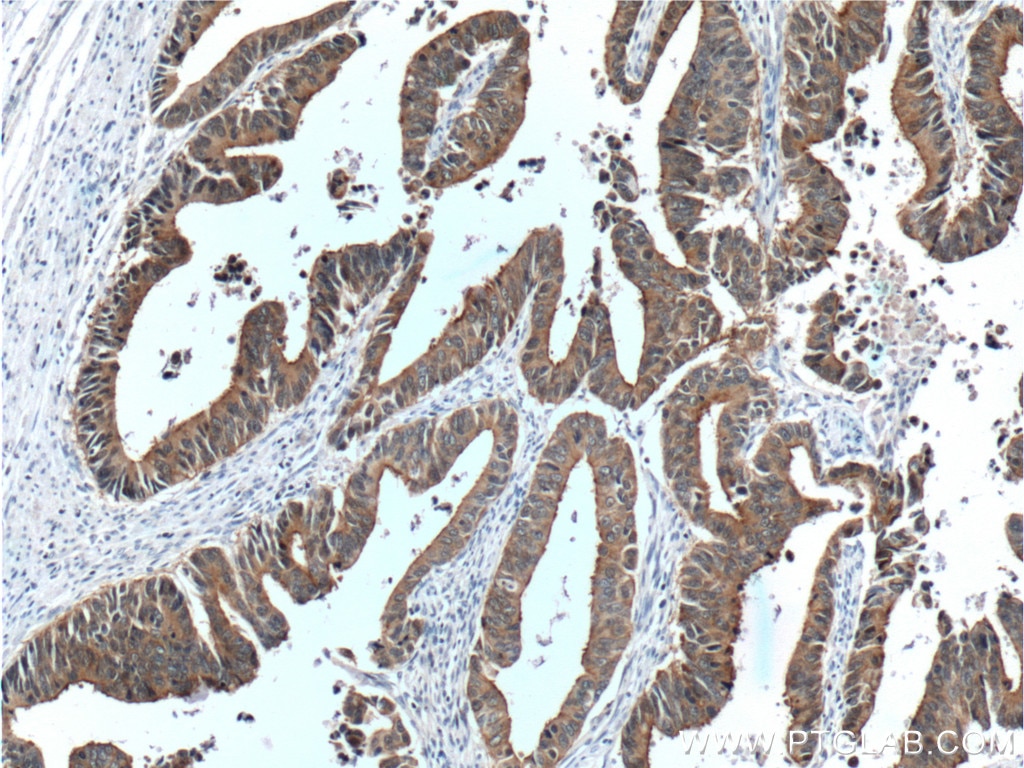
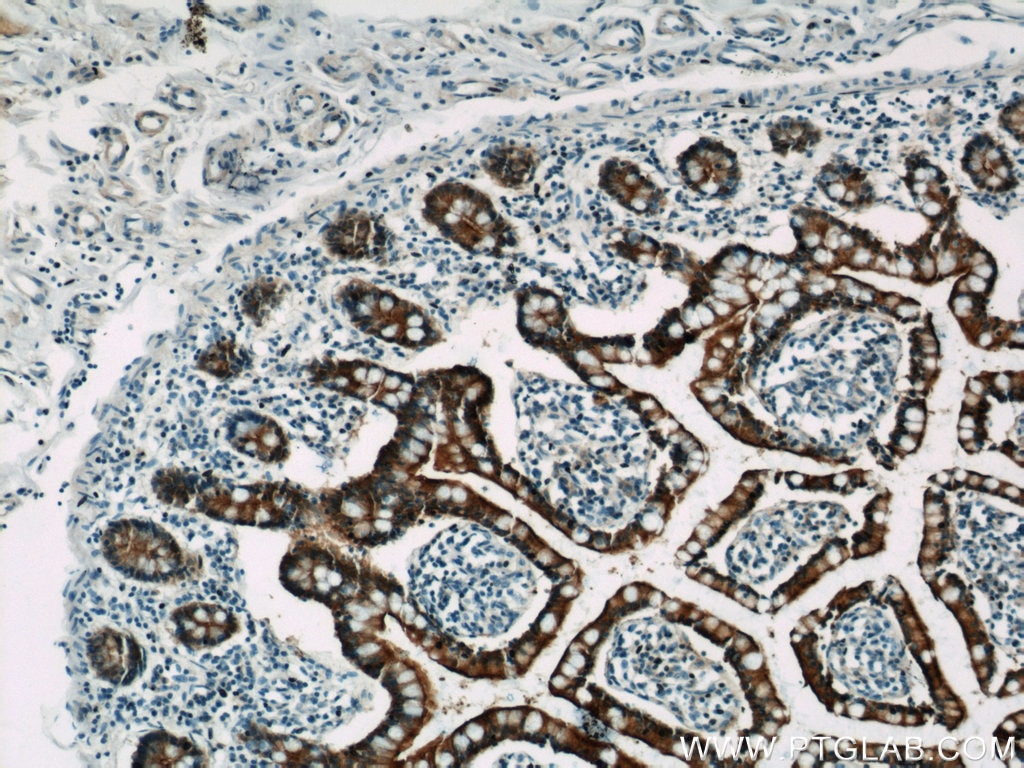
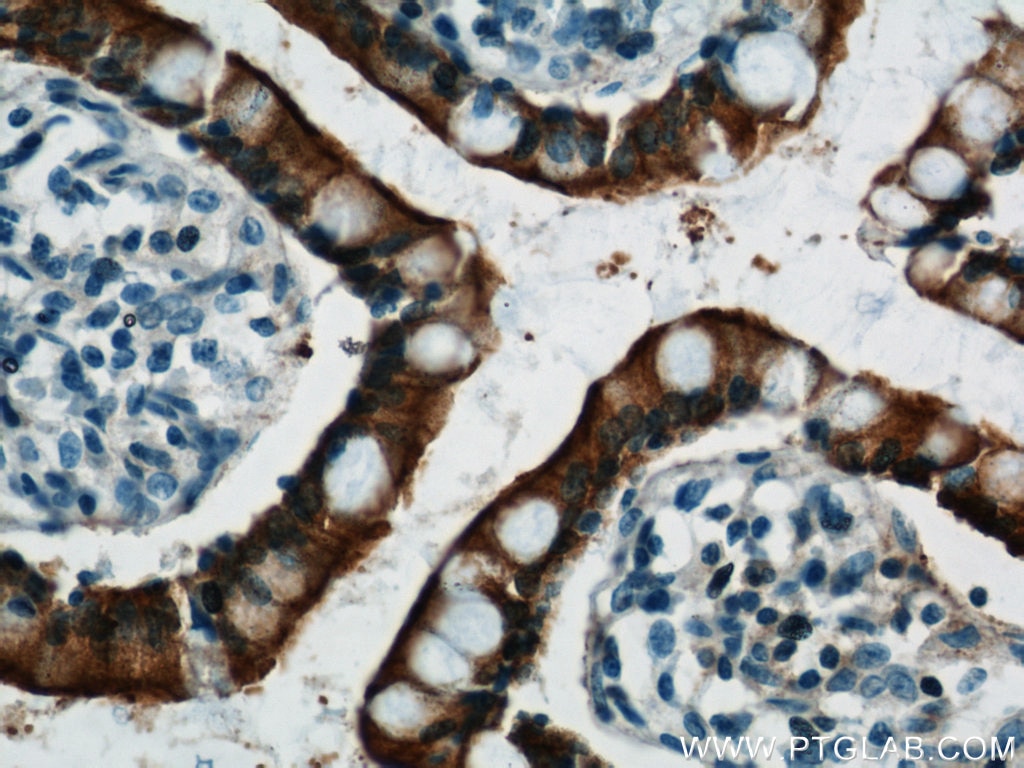
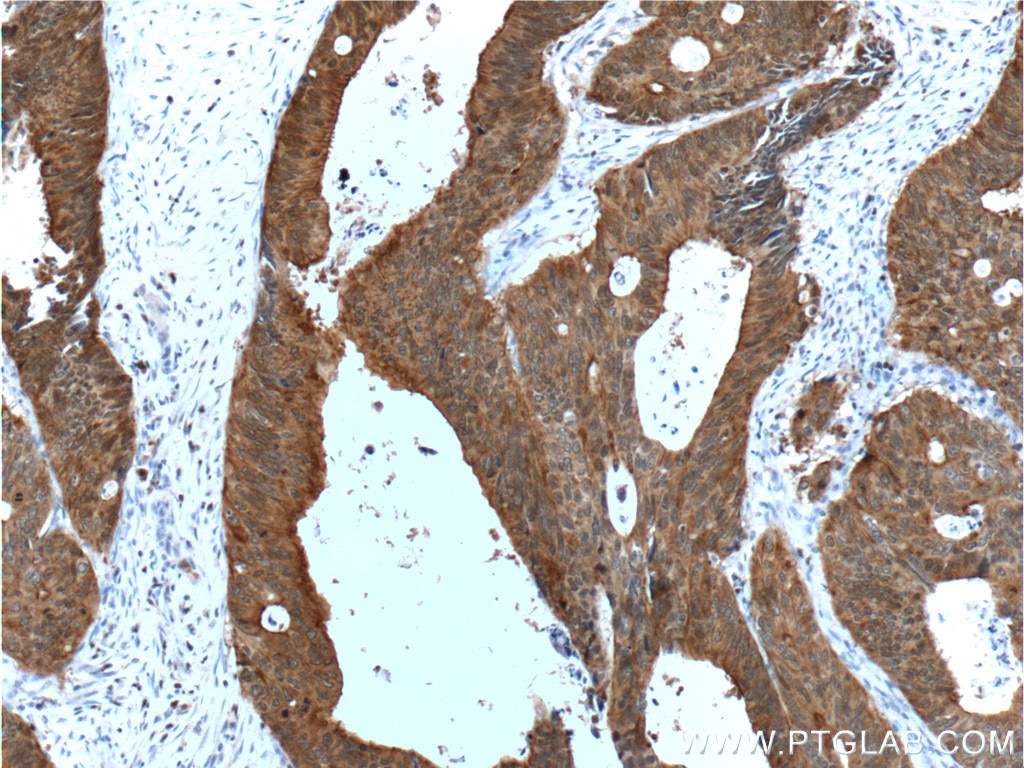
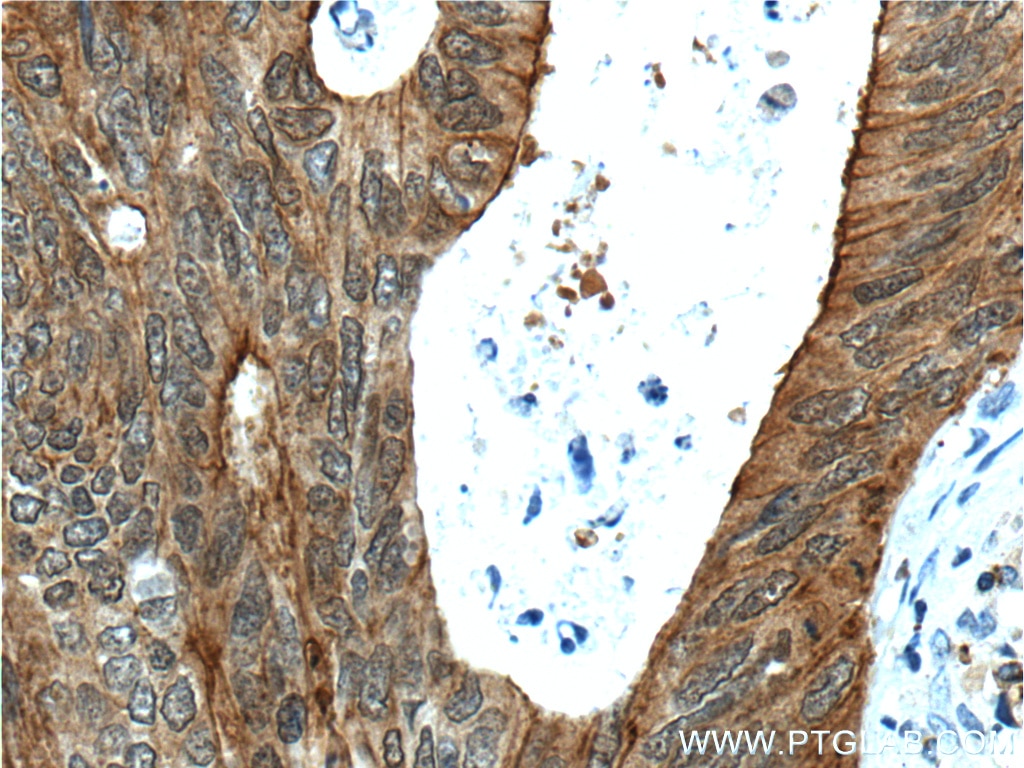
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du côlon humain, tissu d'intestin grêle humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
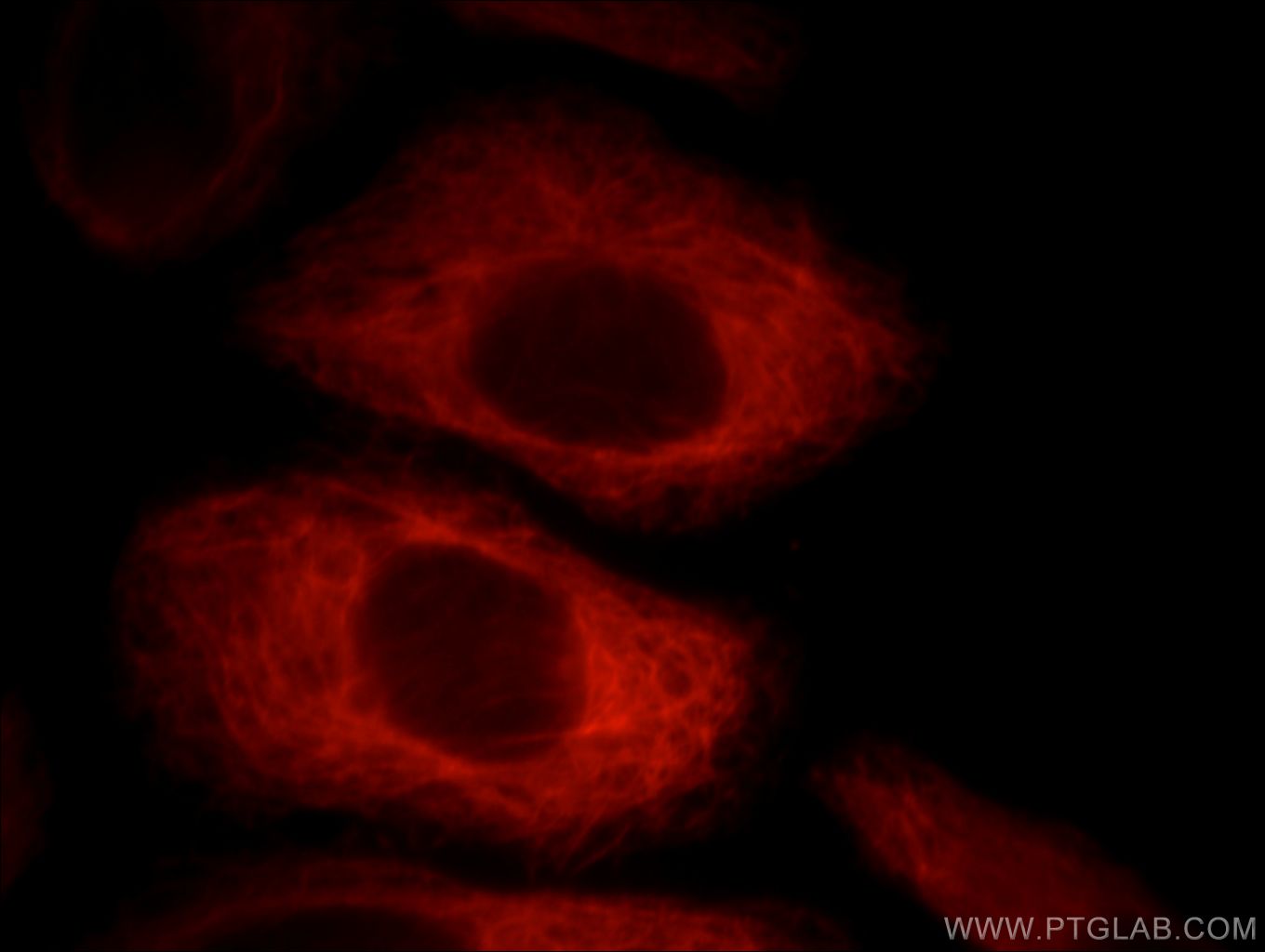
| Résultats positifs en IF | cellules HepG2 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66096-1-Ig cible Villin dans les applications de WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Villin Protéine recombinante Ag9637 |
| Nom complet | villin 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 827aa,93 kDa; 826aa,93 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 93-95 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC017303 |
| Symbole du gène | VIL1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 7429 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Villin 1 (VIL1) is a 95-kDa F-actin bundling and severing protein and its expression is restricted to epithelial cells with a brush border, like epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa, gall bladder, renal proximal tubules and ductuli efferentes of the testis. VIL1 has been reported to be an epithelial cell-specific anti-apoptotic protein, and to have an important function in regulating actin dynamics, cell morphology, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions, cell migration and cell survival. In addition, VIL1 is a useful diagnostic marker for of various cancer, like cervical and endometrial adenocarcinomas, renal cell carcinoma. VIL1 was recently identified as a novel biomarker predictive for postoperative recurrence and poorer prognosis of high serum AFP associated HCC.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Villin antibody 66096-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Villin antibody 66096-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Villin antibody 66096-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for Villin antibody 66096-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Gastroenterology Stiffness Restricts the Stemness of the Intestinal Stem Cells and Skews Their Differentiation Towards Goblet Cells | ||
Theranostics The Circadian Clock Gene Bmal1 Controls Intestinal Exporter MRP2 and Drug Disposition. | ||
Oxid Med Cell Longev Sitagliptin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury by Activating NRF2-Antioxidant Axis, Mitigating NLRP3 Inf--lammasome Activation, and Reversing Gut Microbiota Disorder. | ||
Inflamm Bowel Dis Excessive Mitochondrial Fission Suppresses Mucosal Repair by Impairing Butyrate Metabolism in Colonocytes | ||
J Pharmacol Sci Syntaxin 3 interacts with serotonin transporter and regulates its function. | ||
Int J Clin Exp Pathol A four actin-binding protein signature model for poor prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. |