Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-TRAF5
TRAF5 Polyclonal Antibody for WB,ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
WB,ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 26917-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
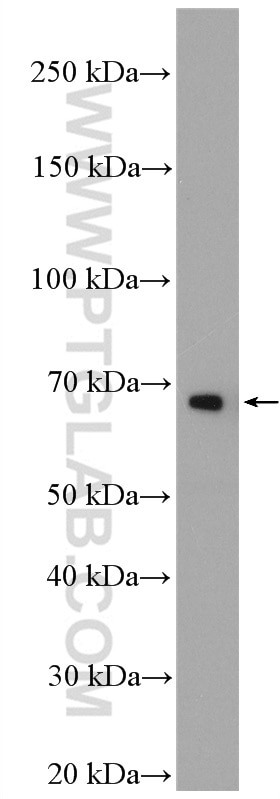
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules Jurkat, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
26917-1-AP cible TRAF5 dans les applications de WB,ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | TRAF5 Protéine recombinante Ag25284 |
| Nom complet | TNF receptor-associated factor 5 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 557 aa, 64 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 64 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC029600 |
| Symbole du gène | TRAF5 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 7188 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
TRAF5 (also known as TNF receptor-associated factor 5, Ring finger protein 84, RNF8, MGC:39780) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated (TRAF) family of proteins that are characterized by the presence of a meprin and TRAF homology (MATH) domain, a RING-type zinc finger domain, and two TRAF-type zinc finger domains (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O00463). TRAF5 is a scaffold protein that associates with and mediates signal transduction by cell surface receptors belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily, including CD27, CD30, CD40, and lymphotoxin-β receptor, positively regulating activation of the canonical NF-κB pathway and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation by these receptors (PMIDs: 8999898, 9582383, 8790348, 8663299).
The RING-type zinc finger domain of TRAF5 exhibits ubiquitin protein ligase activity and is responsible for Lys-63-linked polyubiquitination of protein targets (PMIDs:23758787, 29176576). This domain has been demonstrated to be required for TRAF5-mediated activation of NF-κB (PMID:8663299).
What is the molecular weight of TRAF5?
TRAF5 is a 557 amino acid protein that has a predicted molecular weight of 64 kDa.
What is the subcellular localization of TRAF-5?
TRAF5 is a cytoplasmic protein (PMID:11607847).
What is the tissue specificity of TRAF5?
TRAF5 is broadly expressed in the spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, ovary, small intestine, colon, and peripheral blood. The highest level of expression is observed in Peyer's patches in the small intestine (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O00463).
What is the role of TRAF5 and immune cell function?
Studies in traf5-/- mice have shown that TRAF5 plays a key role in CD40-mediated signaling in B-cells and CD27-mediated signaling in T-cells. In B-cells, deletion of the traf5 gene results in defects in cell proliferation and upregulation of various cell surface molecules, including CD23, CD54, CD80, CD86, and Fas, in response to CD40 stimulation. Similarly, upregulation of CD27-mediated costimulatory signals is also impaired in traf5−/− T cells. These effects lead to impairments in lymphocyte activation in vivo (PMID:10449775).
TRAF5 also plays a critical role in in vitro signaling and in vivo function in B-cells by the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-encoded oncogenic mimic of CD40, latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1), which is encoded by the virus and is essential for transformation of B lymphocytes (PMID:19805155).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for TRAF5 antibody 26917-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |