- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-SURVIVIN
SURVIVIN Monoclonal Antibody for FC, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IF, FC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
3B9H7
N° de cat : 66495-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
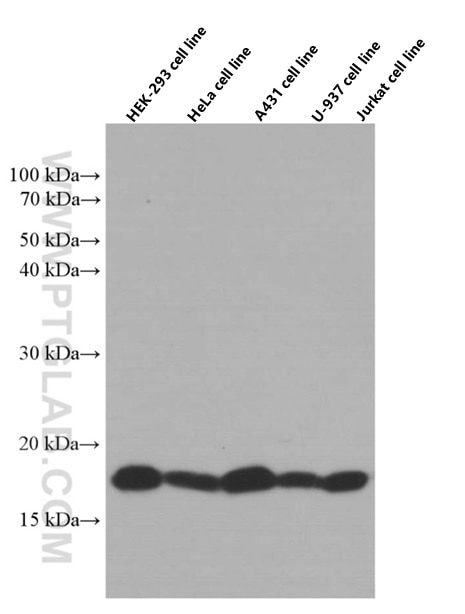
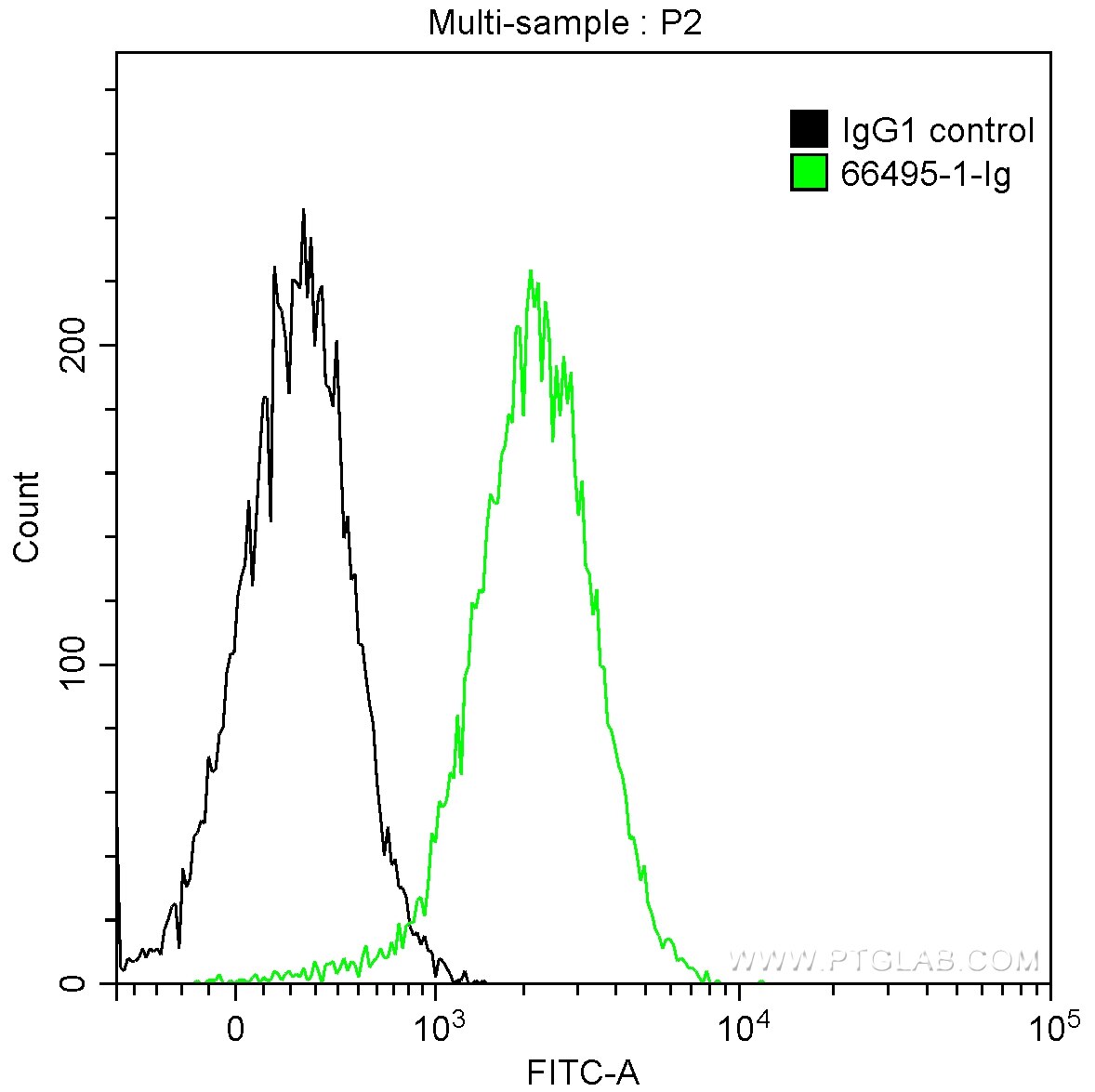
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules A431, cellules HeLa, cellules Jurkat, cellules K-562, cellules Raji, cellules U-937 |
| Résultats positifs en cytométrie | cellules Jurkat, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.50 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66495-1-Ig cible SURVIVIN dans les applications de WB, IF, FC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SURVIVIN Protéine recombinante Ag20958 |
| Nom complet | baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 16 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 18 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC008718 |
| Symbole du gène | BIRC5 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 332 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Survivin, also called BIRC5, is a unique member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein family. Survivin is a 16 kDa anti-apoptotic protein highly expressed during fetal development and cancer cell malignancy, but is completely absent in terminally differentiated cells. The differential expression of survivin in cancer versus normal tissues makes it a useful tool in cancer diagnosis and a promising therapeutic target. Survivin expression is also highly regulated by the cell cycle and is only expressed in the G2-M phase. It is known that survivin localizes to the mitotic spindle by interaction with tubulin during mitosis and may play a contributing role in regulating mitosis. Disruption of survivin-microtubule interactions results in loss of survivin's anti-apoptosis function and increased caspase-3 activity, a mechanism involved in cell death, during mitosis. It also is a direct target gene of the Wnt pathway and is upregulated by beta-catenin.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SURVIVIN antibody 66495-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| FC protocol for SURVIVIN antibody 66495-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Bioeng Transl Med Multistage targeting and dual inhibiting strategies based on bioengineered tumor matrix microenvironment-mediated protein nanocages for enhancing cancer biotherapy. | ||
Exp Mol Med m 6 A-mediated upregulation of AC008 promotes osteoarthritis progression through the miR-328-3p‒AQP1/ANKH axis | ||
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) Proliferation inhibition and apoptosis promotion by dual silencing of VEGF and Survivin in human osteosarcoma.
| ||
Front Oncol Synergistic effects of nab-PTX and anti-PD-1 antibody combination against lung cancer by regulating the Pi3K/AKT pathway through the Serpinc1 gene | ||
Front Pharmacol Analysis of regulating activities of 5'-epiequisetin on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo | ||
BMC Cancer The survivin-ran inhibitor LLP-3 decreases oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis and growth of neuroblastoma cells |