Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-STAT3
STAT3 Polyclonal Antibody for IHC, IP, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 51076-2-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
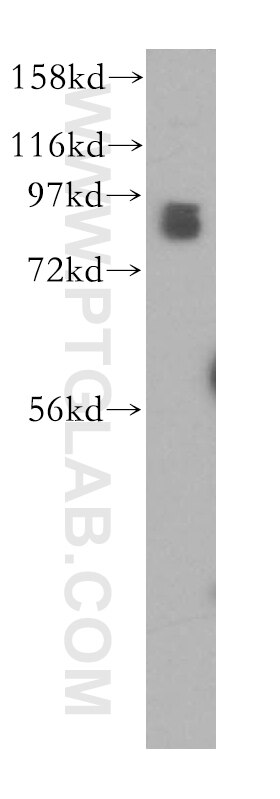
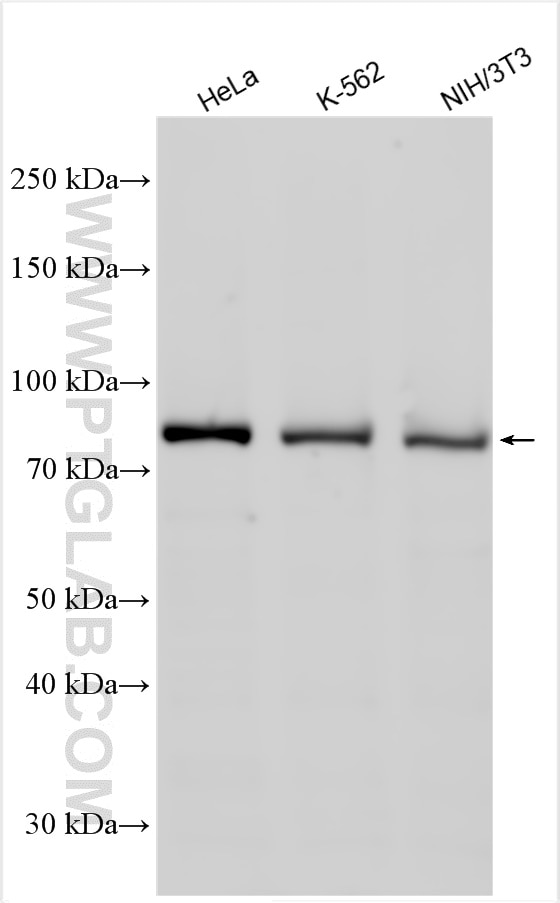
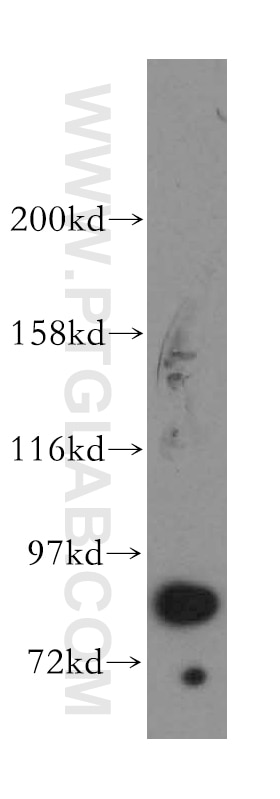
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules K-562, cellules HeLa, cellules NIH/3T3 |
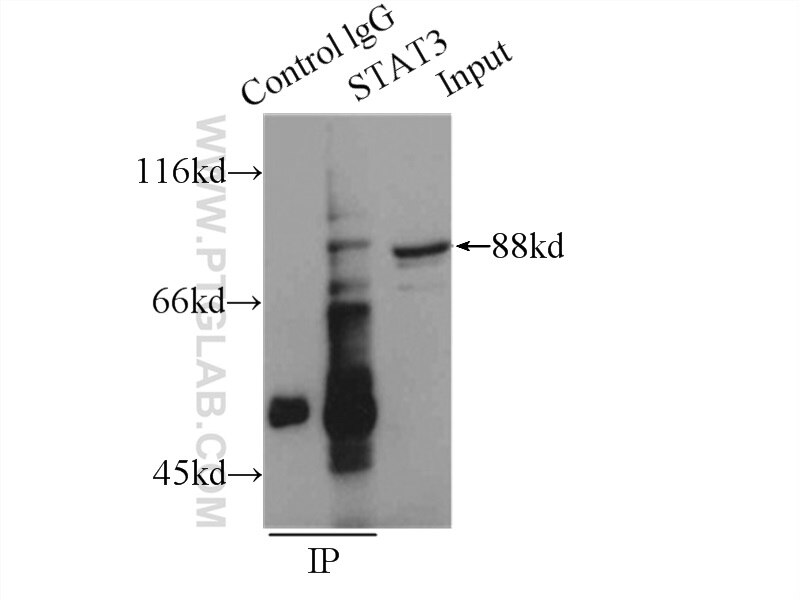
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HeLa |
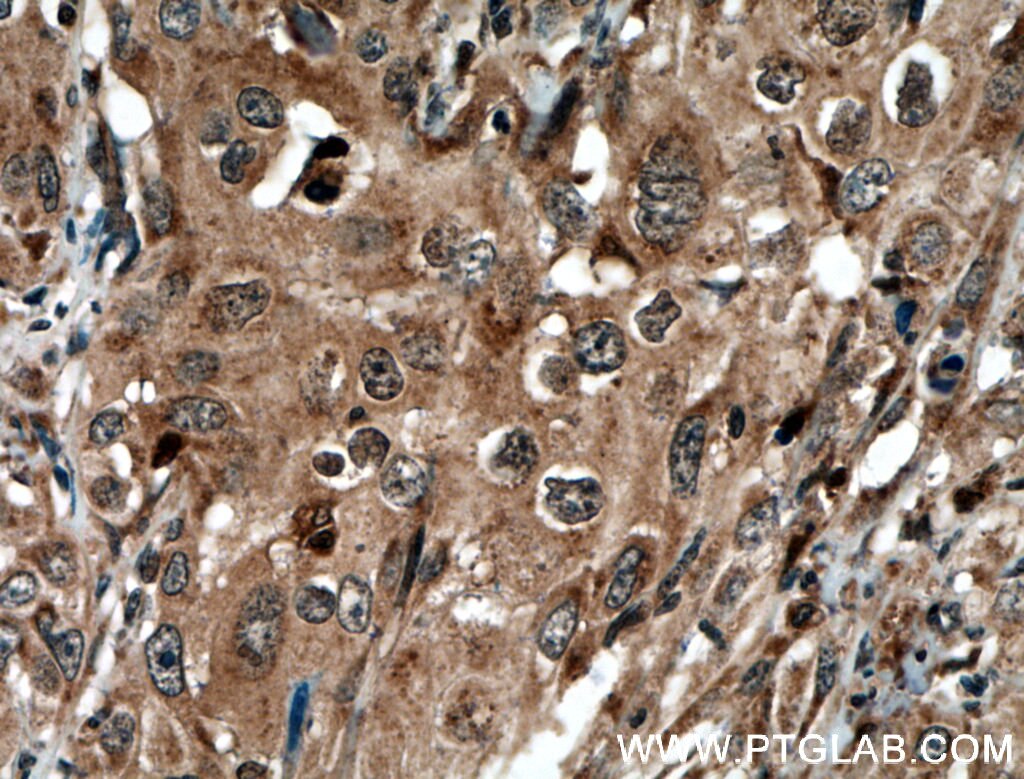
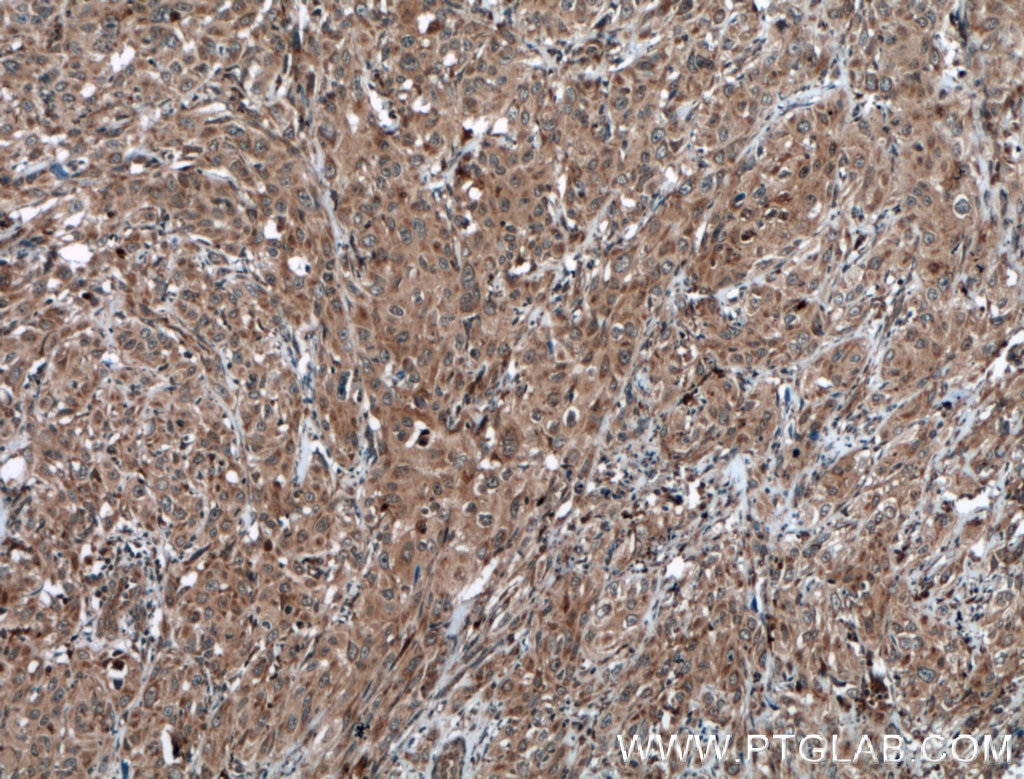
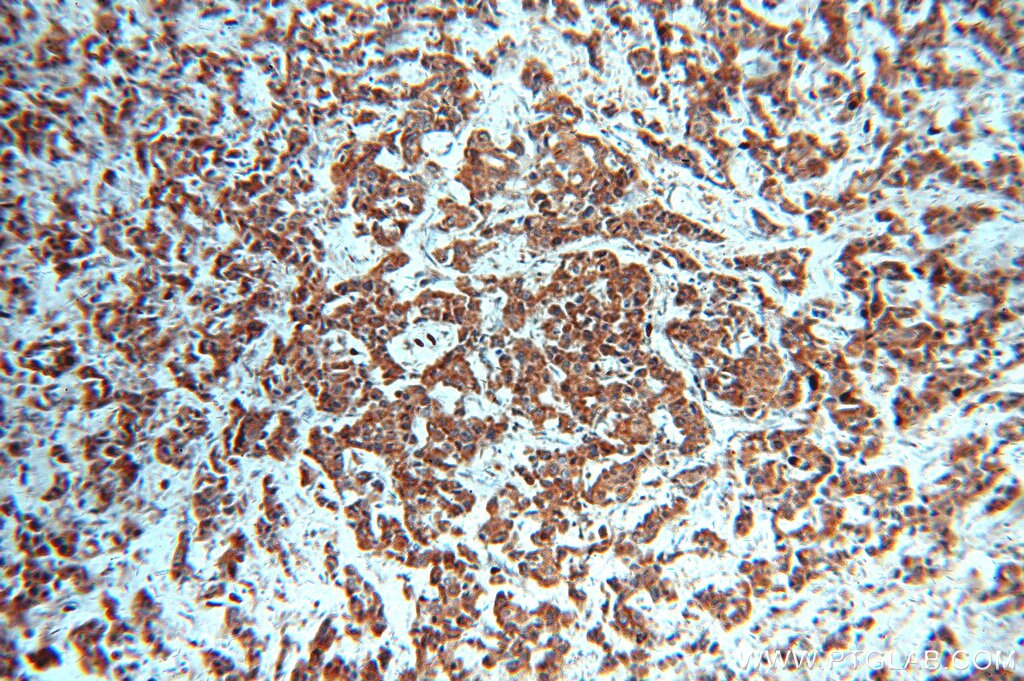
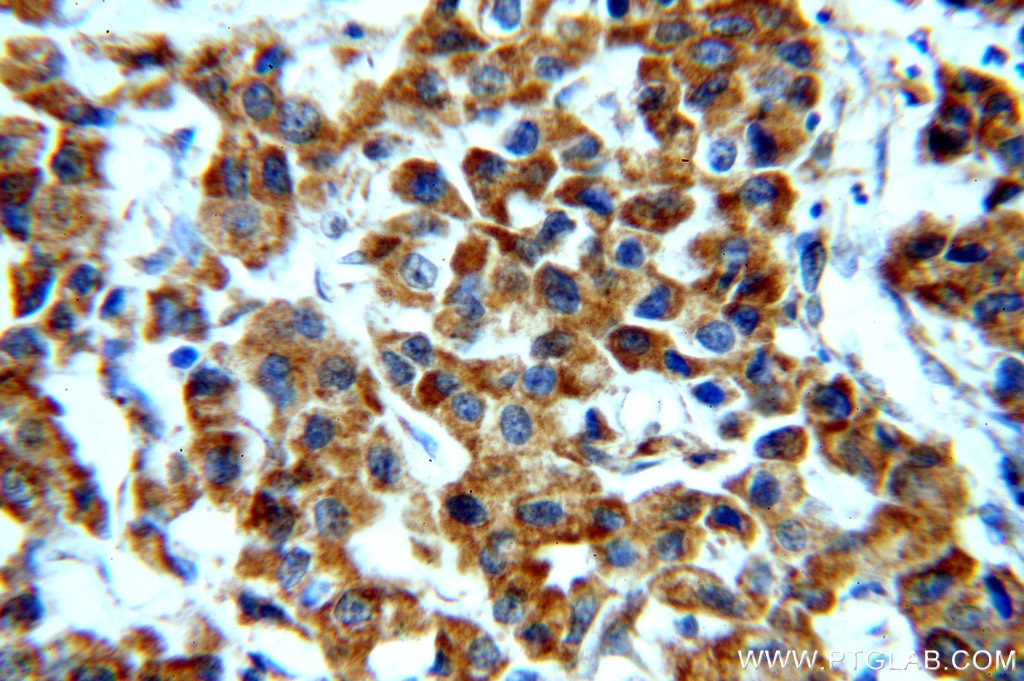
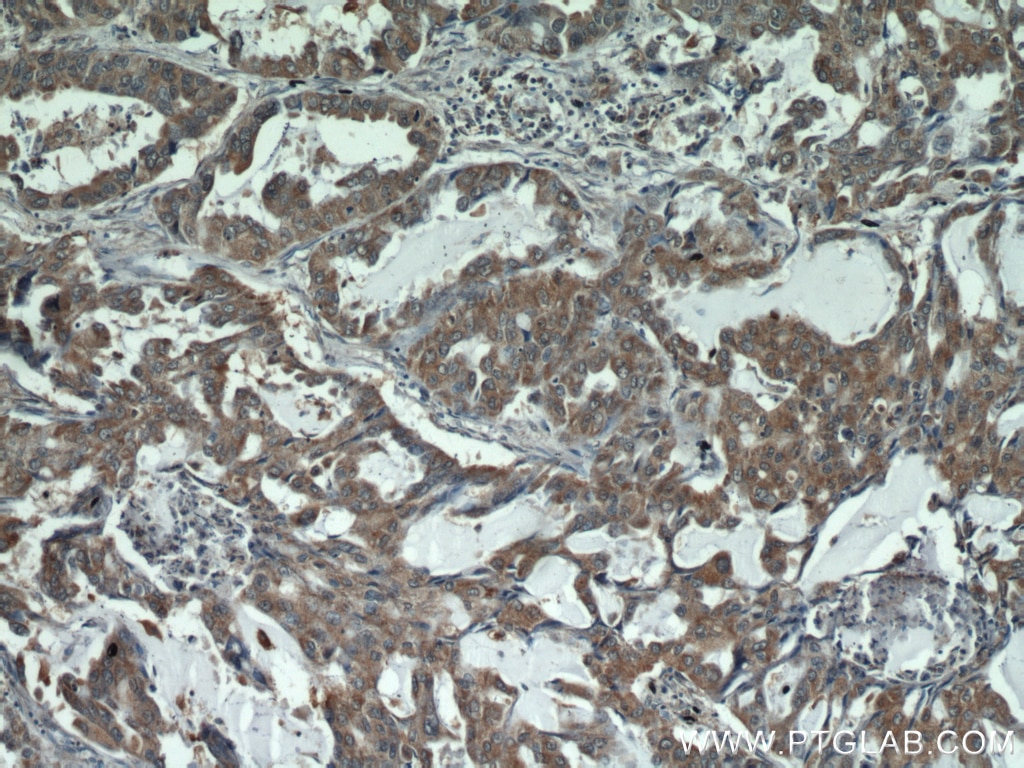
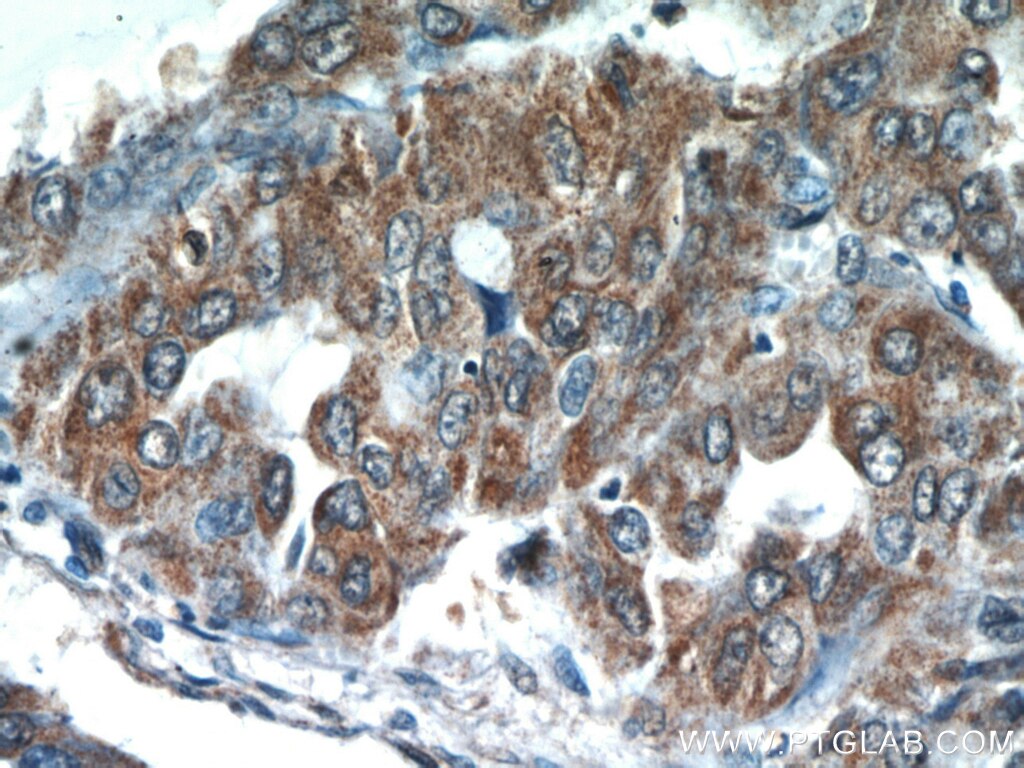
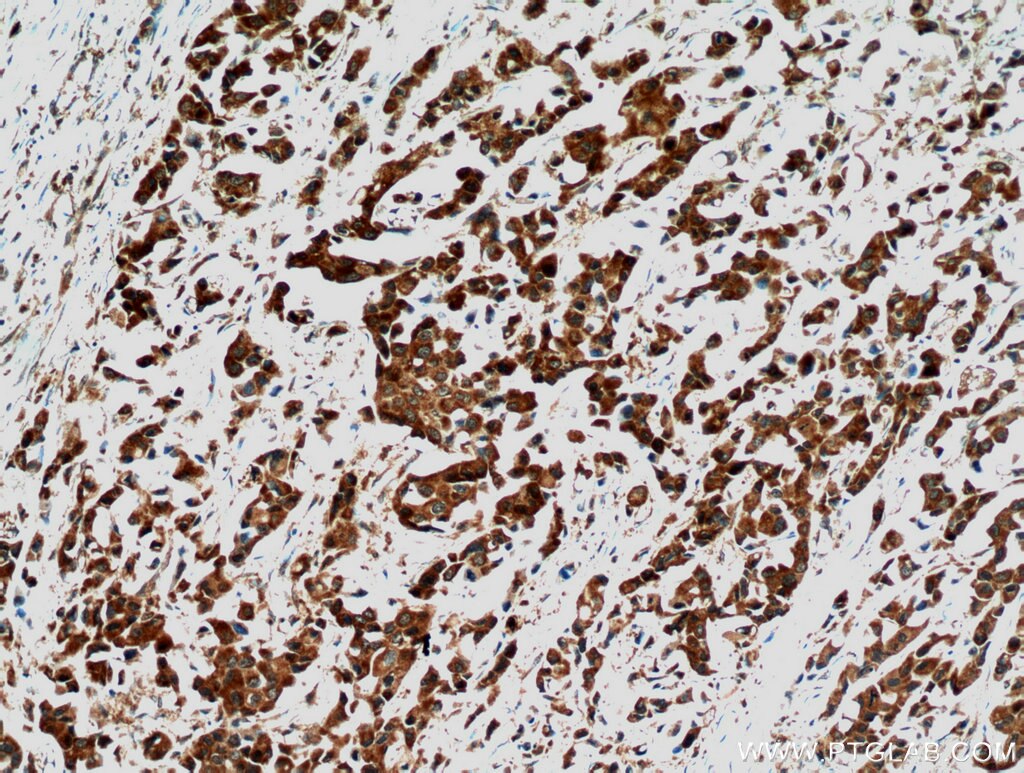
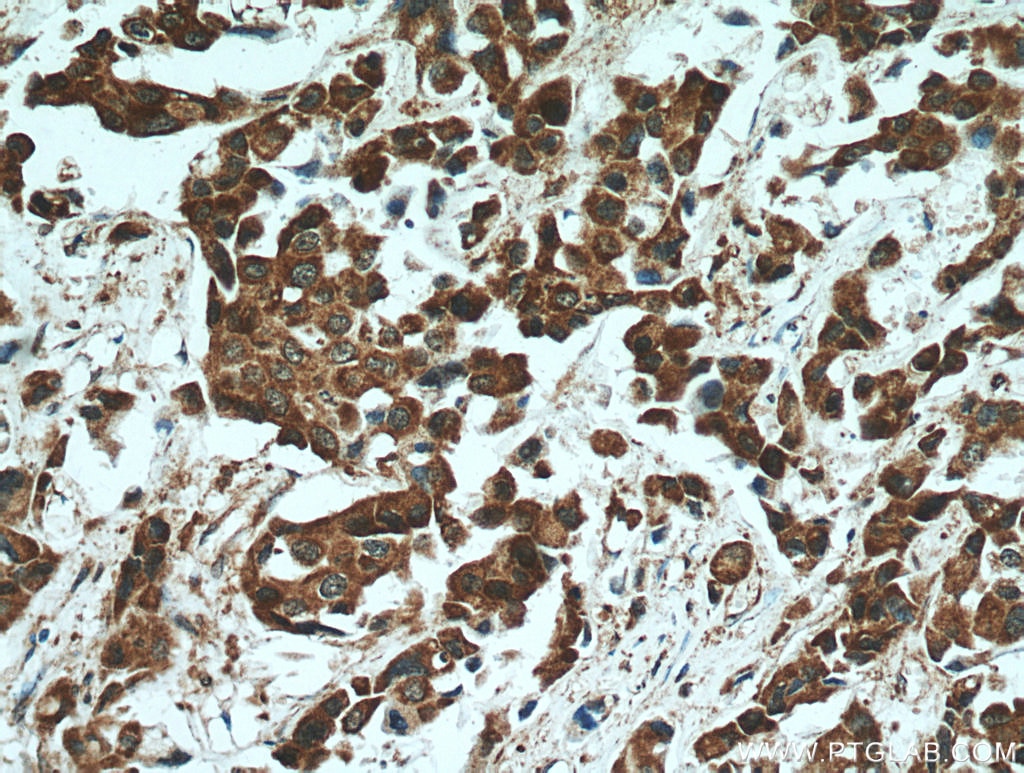
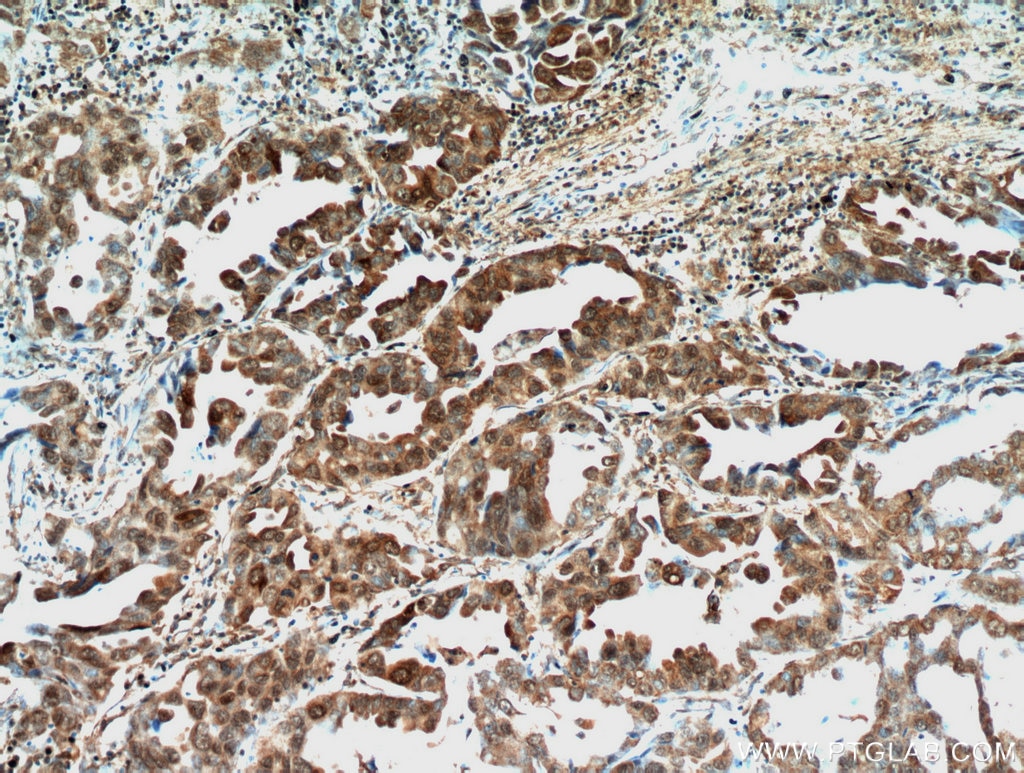
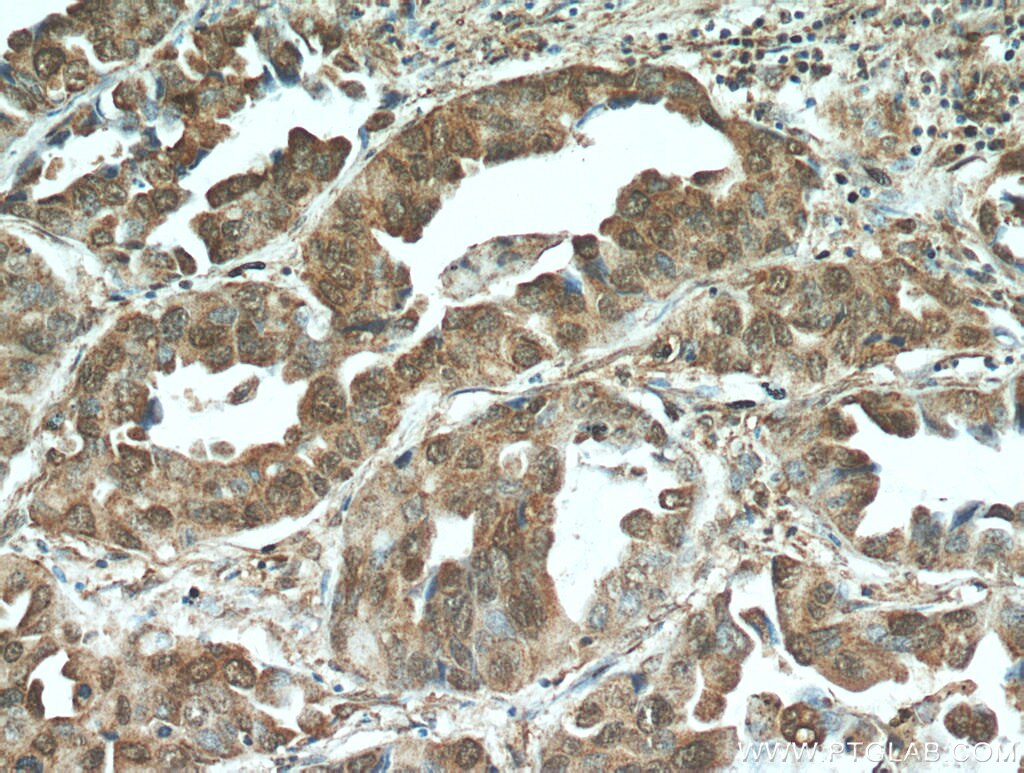
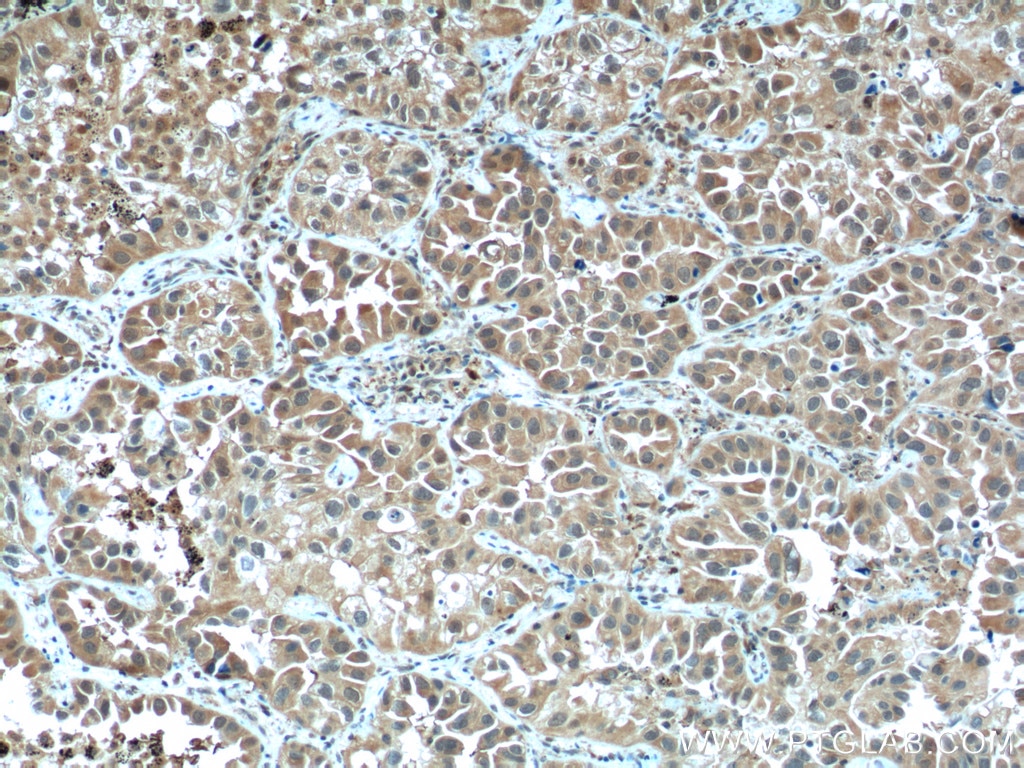
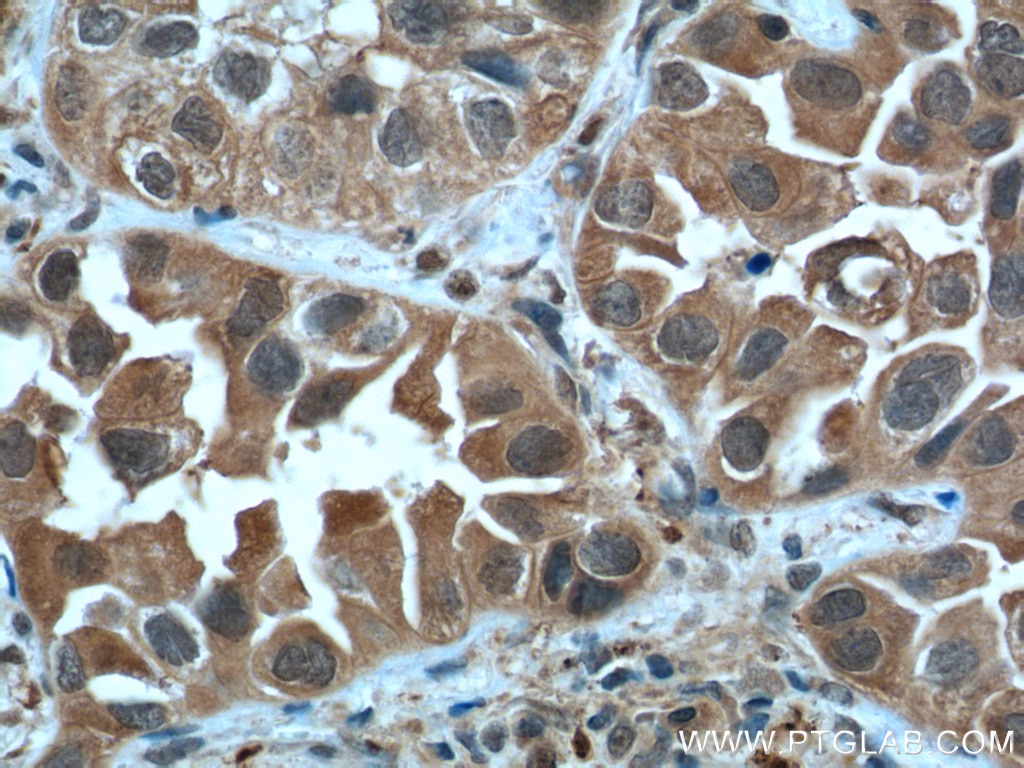
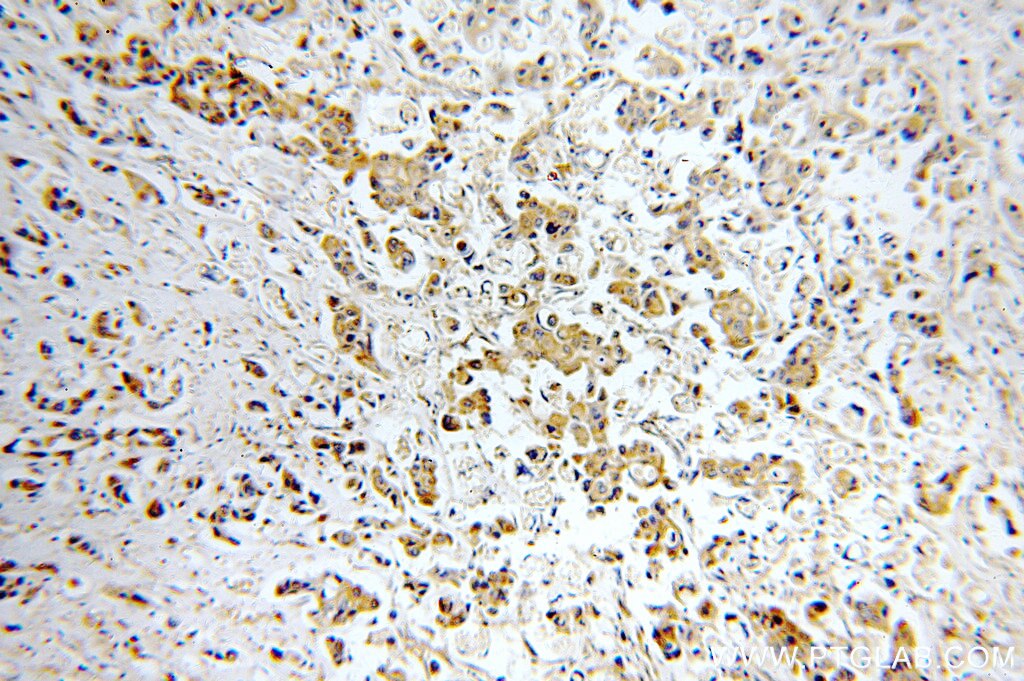
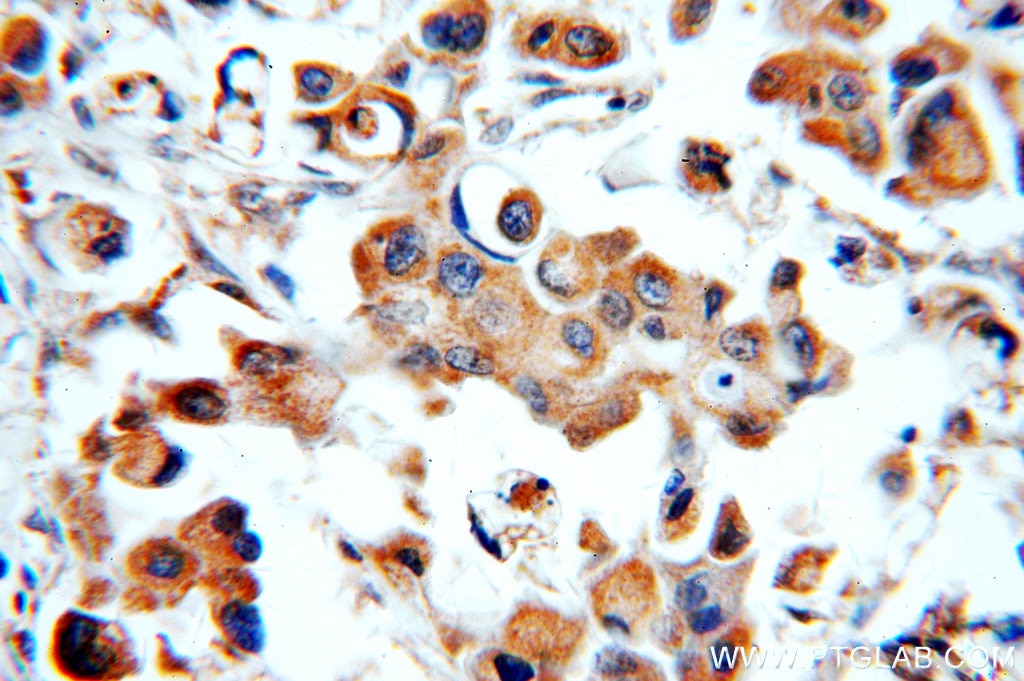
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du col de l'utérus humain, tissu de cancer du poumon humain, tissu de cancer du sein humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 3 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
51076-2-AP cible STAT3 dans les applications de WB, IP, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 770 aa, 88 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 88 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC000627 |
| Symbole du gène | STAT3 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 6774 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor) (STAT3, synonyms: APRF, FLJ20882, MGC16063) is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. STAT3 is activated through phosphorylation in response to various cytokines and growth factors including IFNs, EGF, IL5, IL6, HGF, LIF and BMP2. STAT3 mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. The small GTPase Rac1 has been shown to bind and regulate the activity of STAT3. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against a peptide mapping within human STAT3. STAT3 exists three isoforms and the molecular weight of each isoform respectively is 83 kDa, 87 kDa and 88 kDa.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for STAT3 antibody 51076-2-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for STAT3 antibody 51076-2-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for STAT3 antibody 51076-2-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
FASEB J Lmo4-resistin signaling contributes to adipose tissue-liver crosstalk upon weight cycling. | ||
Neurotox Res Hispidulin Inhibits Neuroinflammation in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated BV2 Microglia and Attenuates the Activation of Akt, NF-κB, and STAT3 Pathway. | ||
Oncol Lett ST8SIA1 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by blocking the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. | ||
Cell Biol Int Identification and analysis of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta1 interactome. | ||
Mol Med Rep A small GTPase?like protein fragment of Mycoplasma promotes tumor cell migration and proliferation in?vitro via interaction with Rac1 and Stat3. |