Anticorps Monoclonal anti-NOX4
NOX4 Monoclonal Antibody for IF, IHC, WB,ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
4E5F1
N° de cat : 67681-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
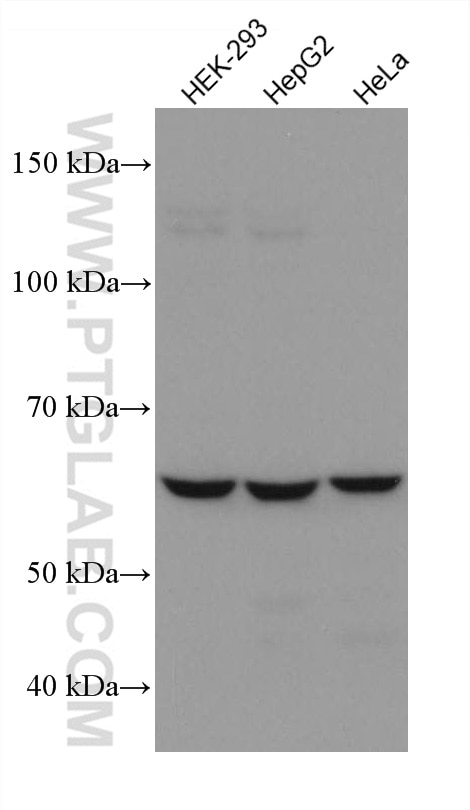
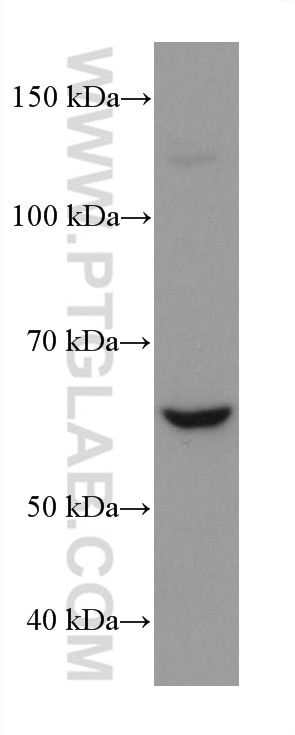
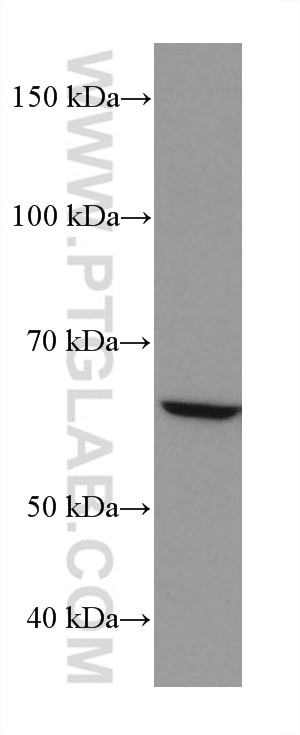
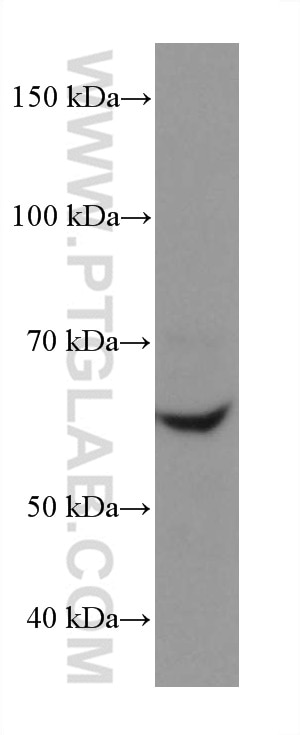
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules HeLa, cellules HepG2, cellules HSC-T6, cellules Jurkat, cellules MG U-87 |
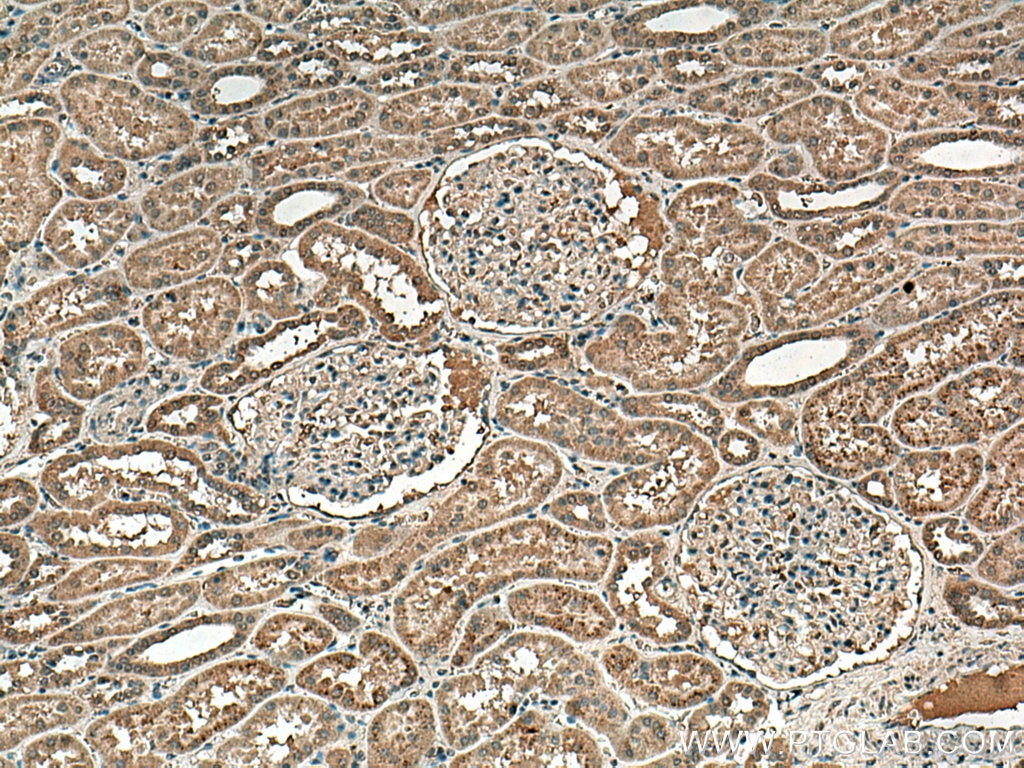
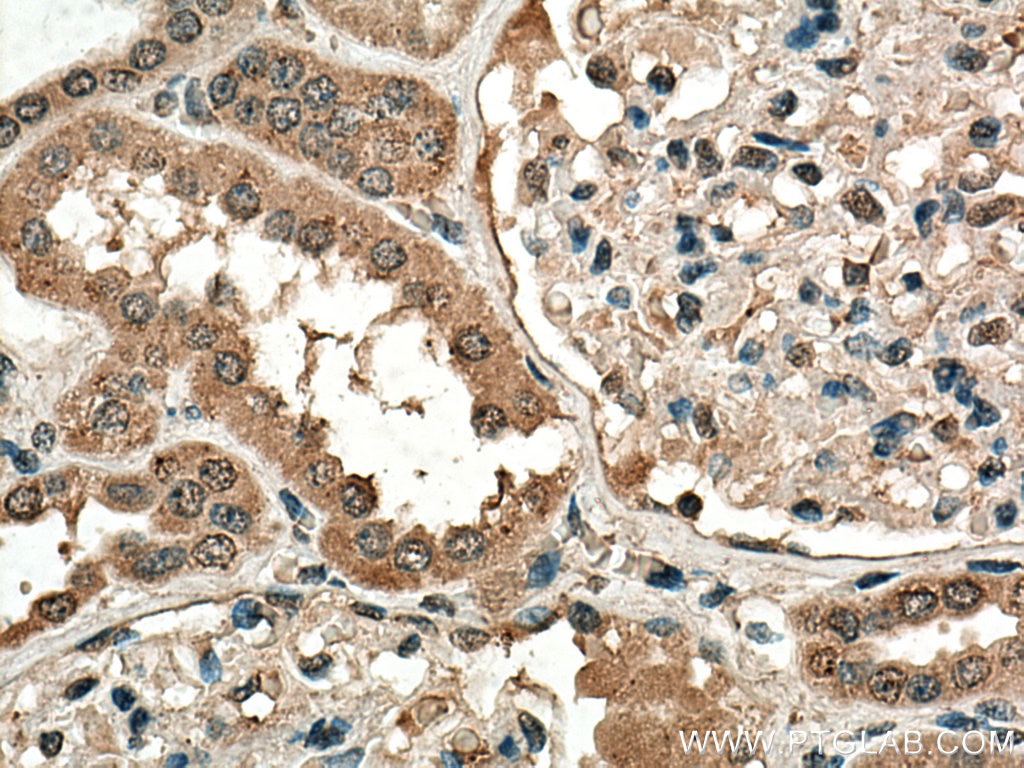
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu rénal humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
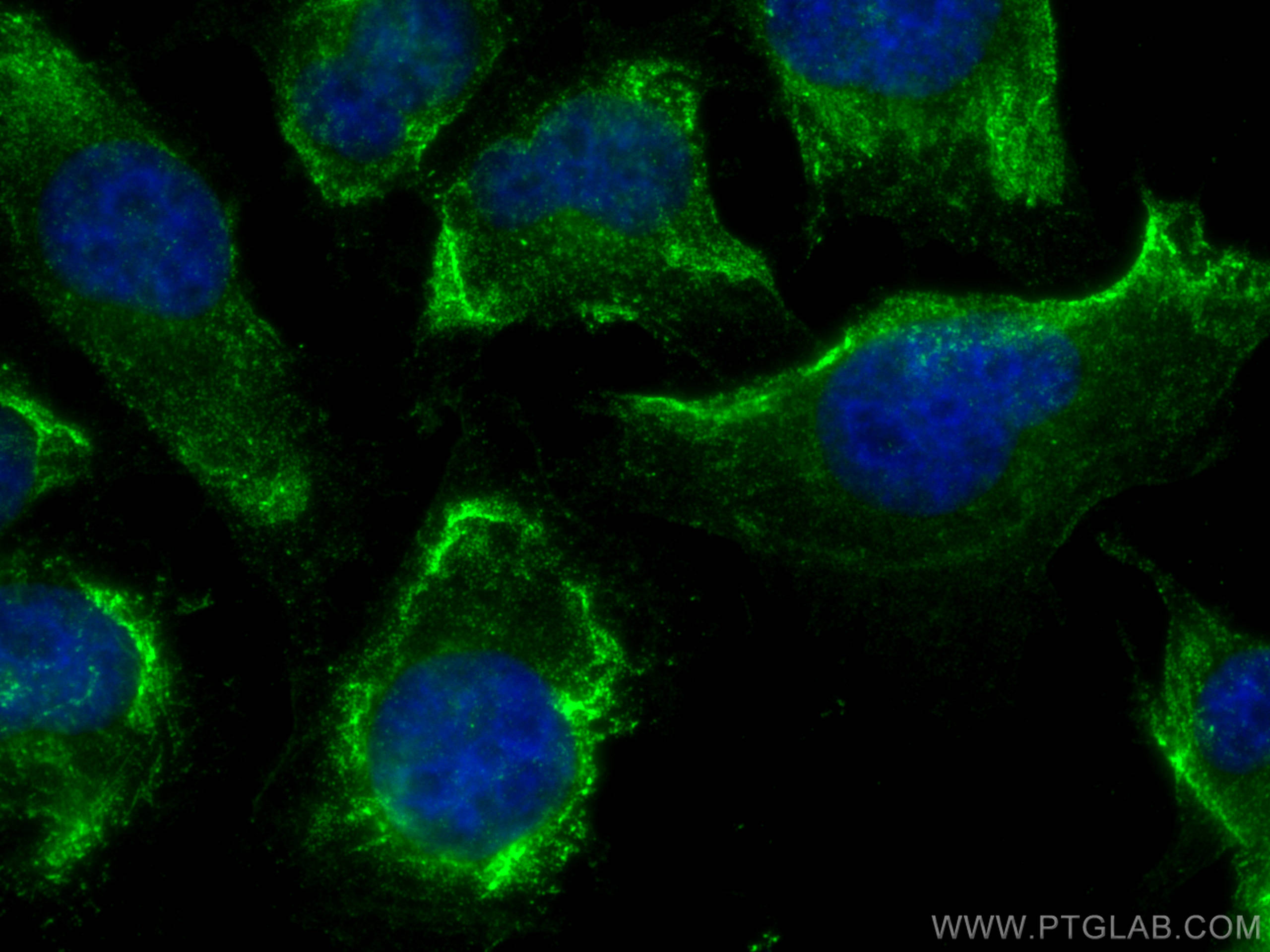
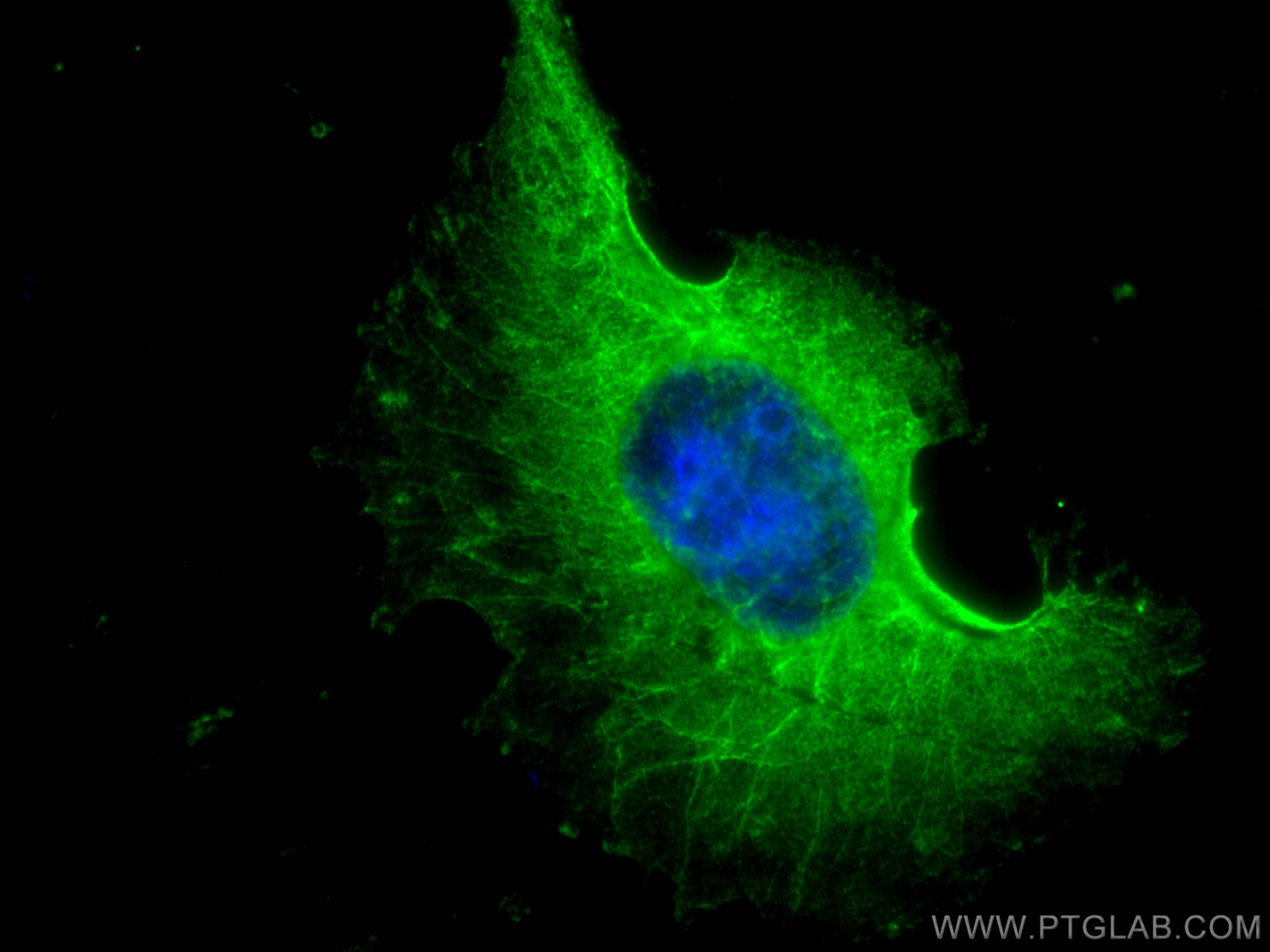
| Résultats positifs en IF | cellules HUVEC, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
67681-1-Ig cible NOX4 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat
| Réactivité | Humain, rat |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | NOX4 Protéine recombinante Ag6176 |
| Nom complet | NADPH oxidase 4 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 67 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 67 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC040105 |
| Symbole du gène | NOX4 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 50507 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20 ℃. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
NOX4 (NADPH oxidase 4) is a phagocyte-type oxidase, similar to that responsible for the production of large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in neutrophil granulocytes with resultant antimicrobial activity and it has been postulated to function in the kidney as an oxygen sensor that regulates the synthesis of erythropoietin in the renal cortex. Studies have reported molecular masses of Nox4 protein by western blot analysis ranging from 55 to 80 kDa. The truncated NOX4 splice variant D (28 kDa) lacks the majority of the transmembrane domain and has been shown to produce higher levels of ROS and DNA damage compared to its prototype. NOX4D has previously been shown to localise to the nucleus and nucleolus in various cell types and is implicated in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damage (PMID: 11728818, PMID: 29285262, PMID: 14670934). Nox4 in cardiac myocytes is primarily expressed in mitochondria, and upregulation of Nox4 induced by hypertrophic stimuli elicits mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiac failure. In breast or ovarian tumor cells, mitochondrial Nox4 contributes to oncogenesis. In vascular endothelial cells, however, Nox4 is expressed in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and plays a specific role in redox-mediated ER signaling (PMID: 24259511).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NOX4 antibody 67681-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for NOX4 antibody 67681-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for NOX4 antibody 67681-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Biomedicines Identification of NOX4 as a New Biomarker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Effect on Sorafenib Therapy | ||
Antioxidants (Basel) Sirtuin1 Mediates the Protective Effects of Echinacoside against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Regulating the NOX4-Nrf2 Axis | ||
Antioxidants (Basel) The Effect of Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid (TUDCA) Treatment on Pregnancy Outcomes and Vascular Function in a Rat Model of Advanced Maternal Age |