Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Cytokeratin 14
Cytokeratin 14 Monoclonal Antibody for IF, IHC, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, porc, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2G1E2
N° de cat : 60320-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
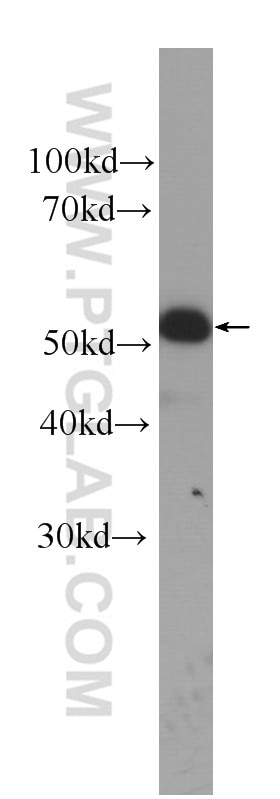
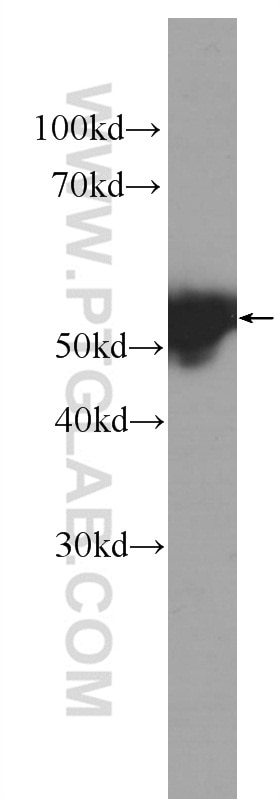
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules A431, tissu cutané de souris |
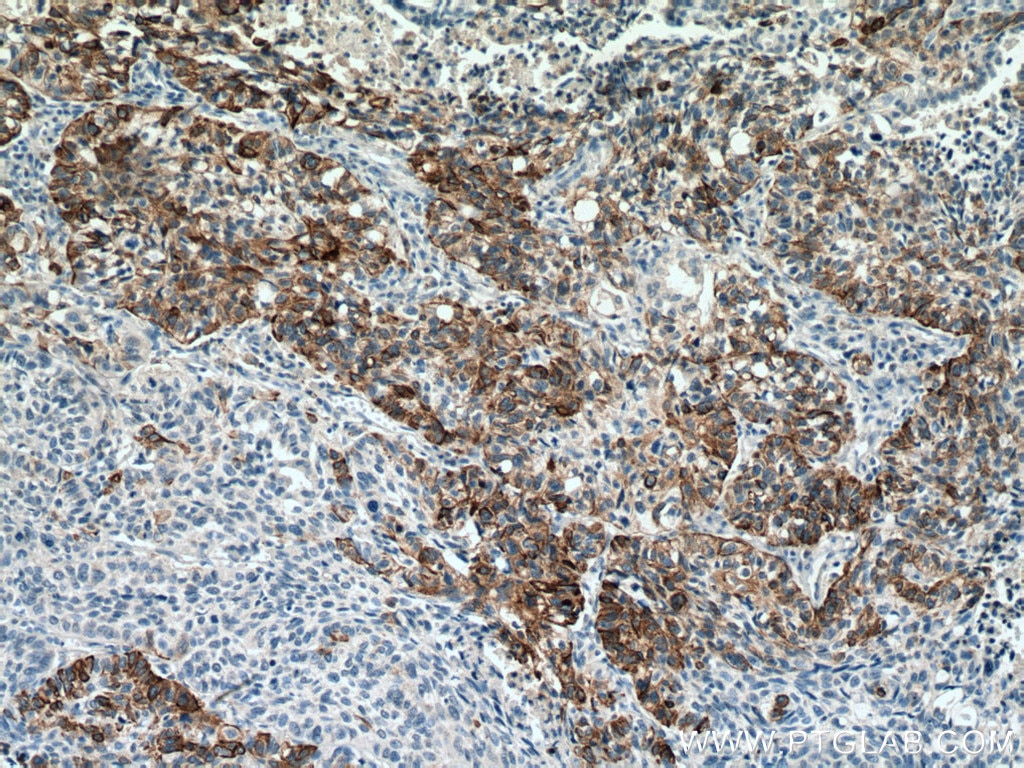
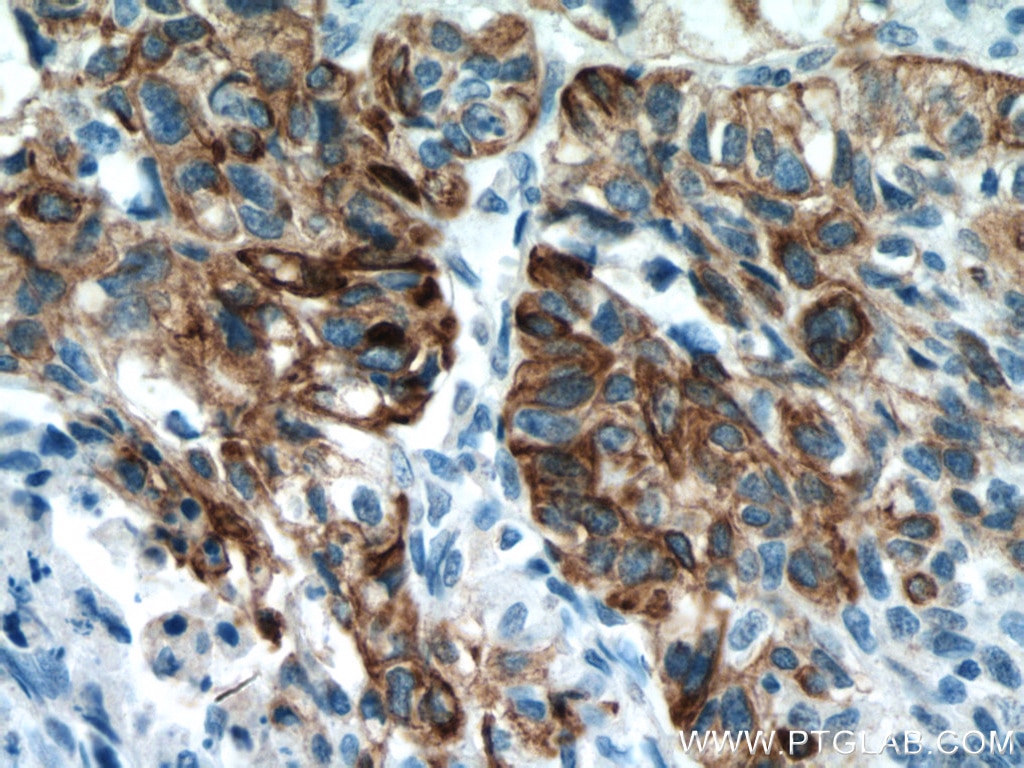
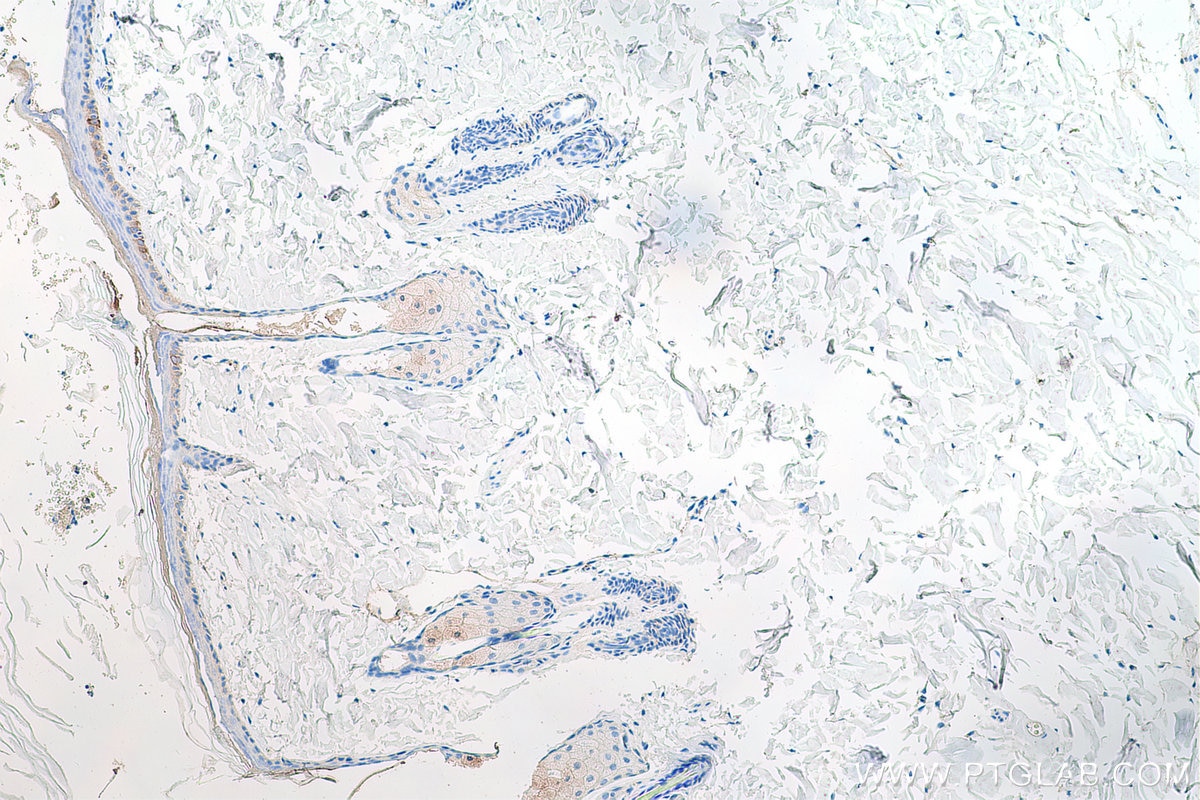
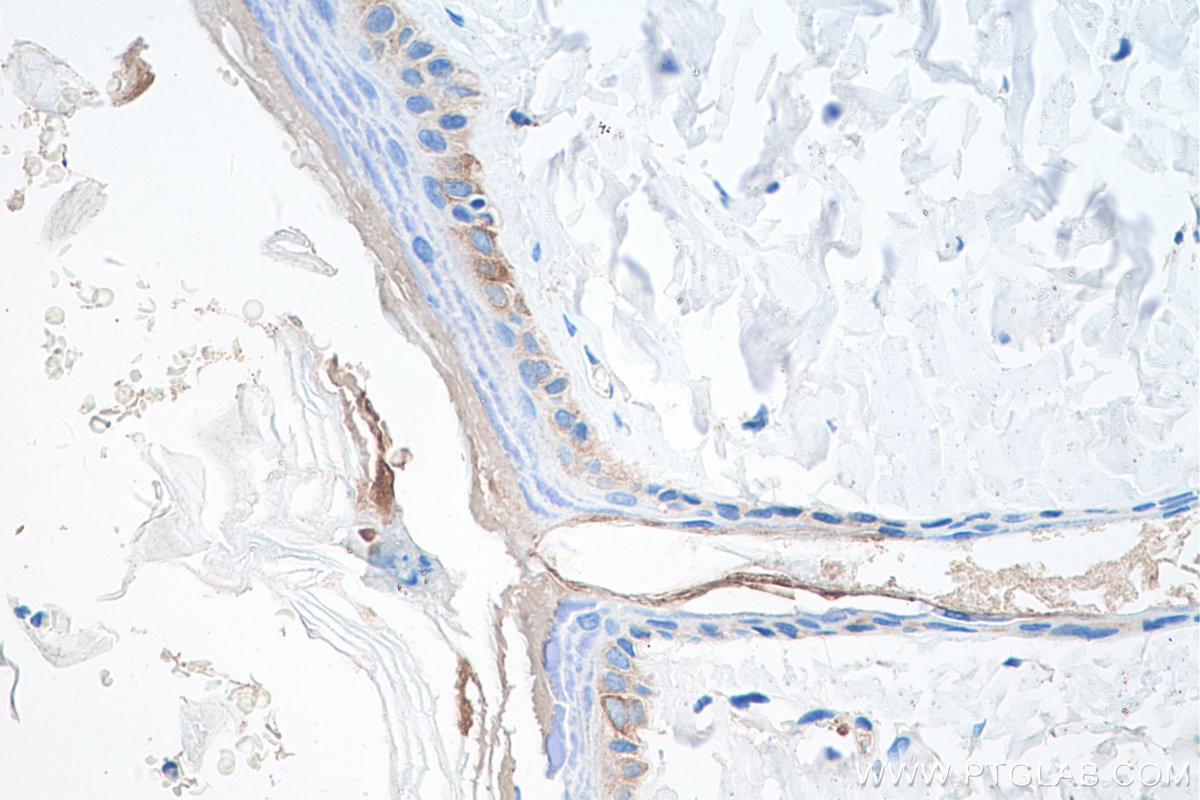
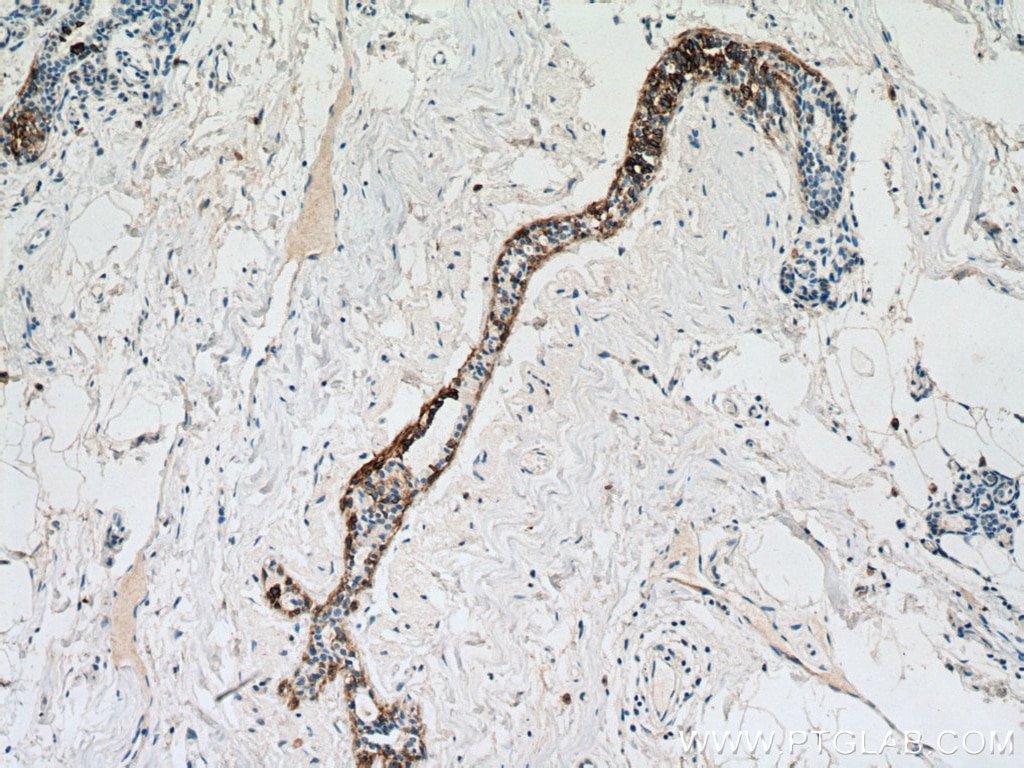
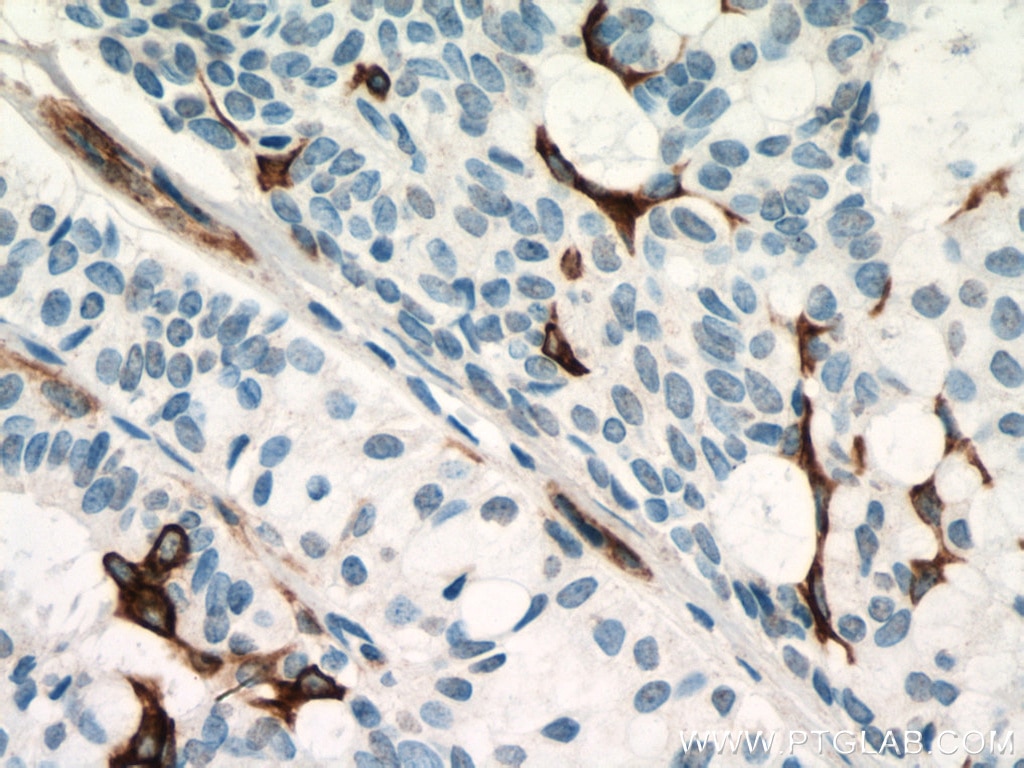
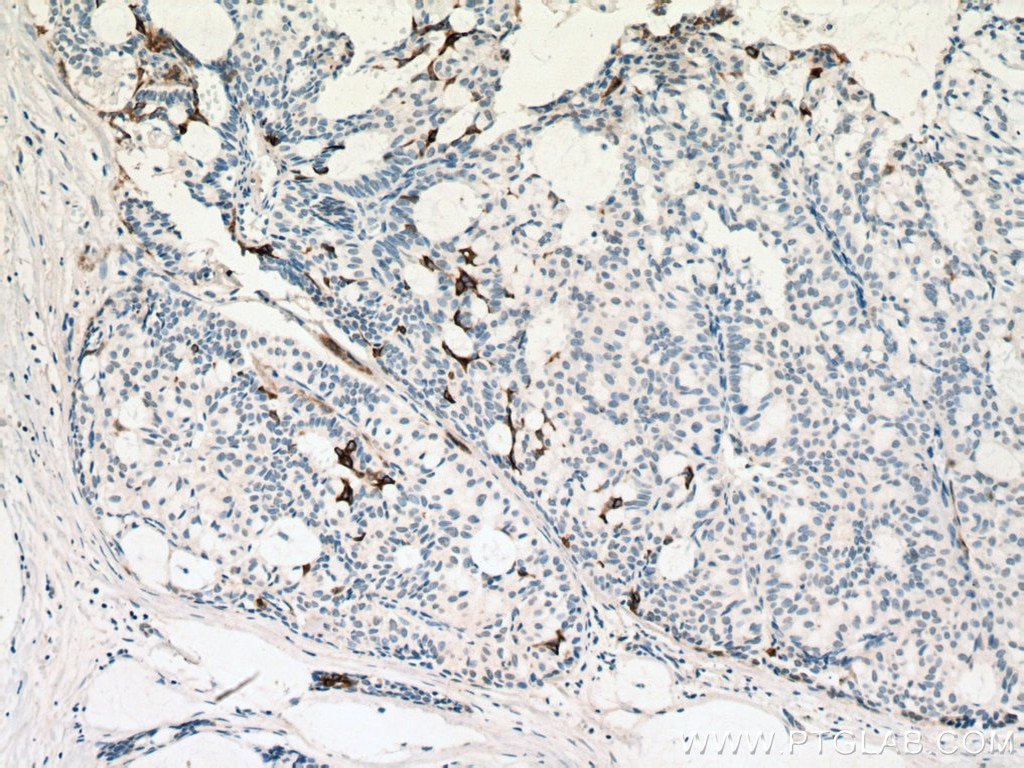
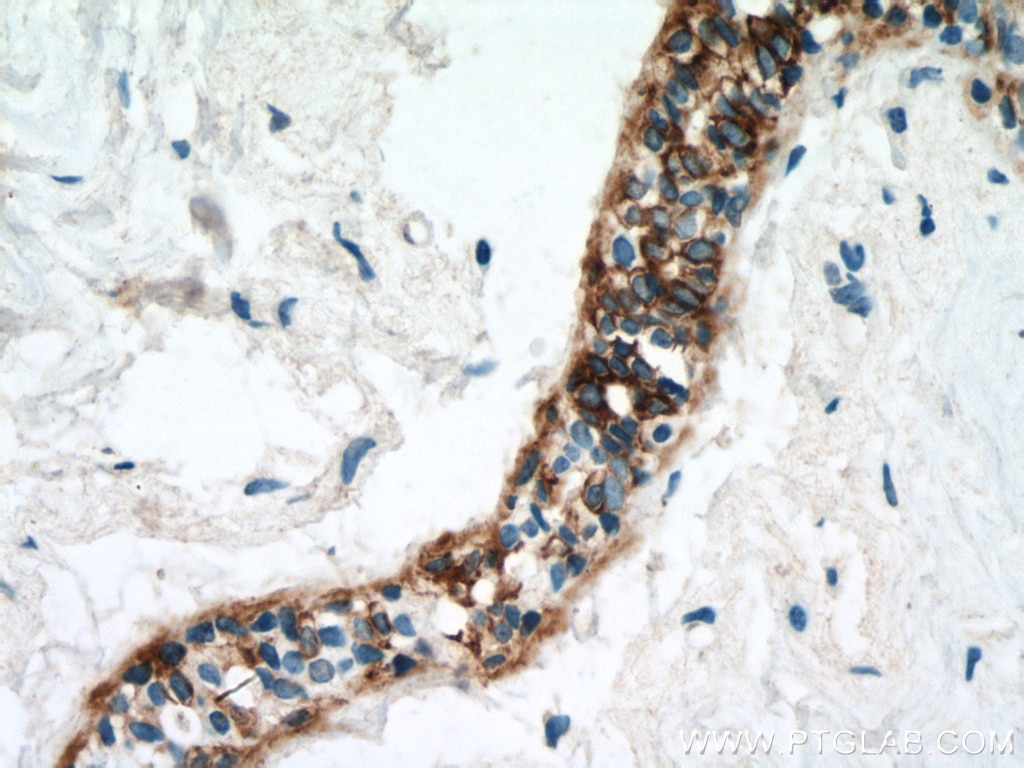
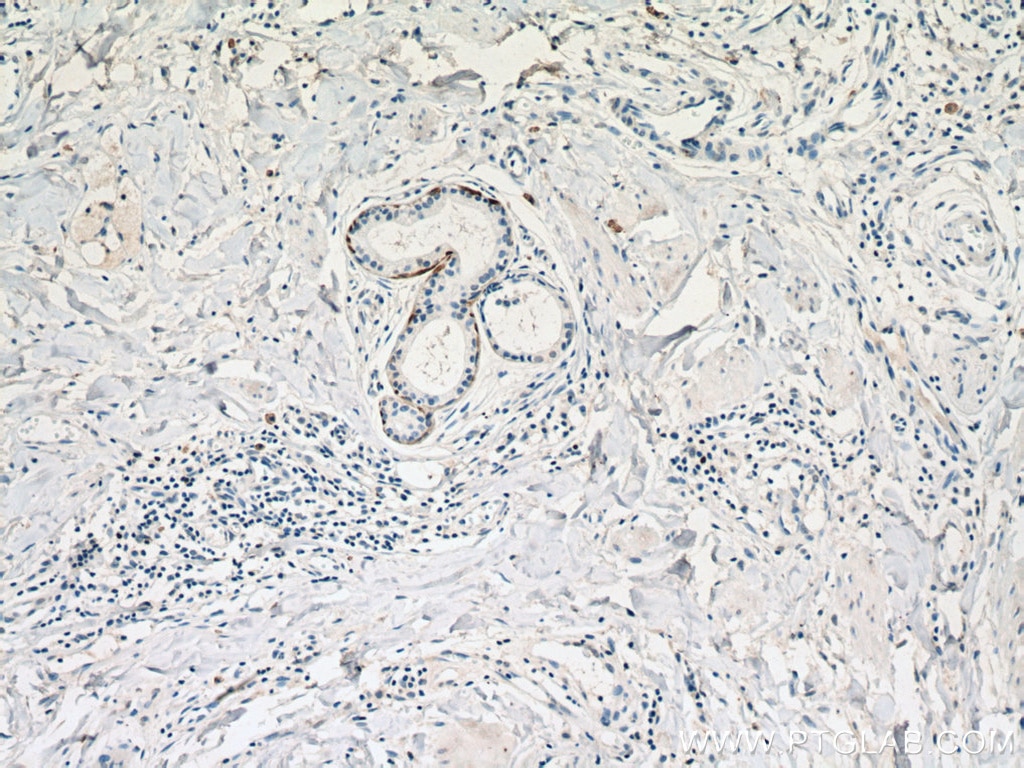
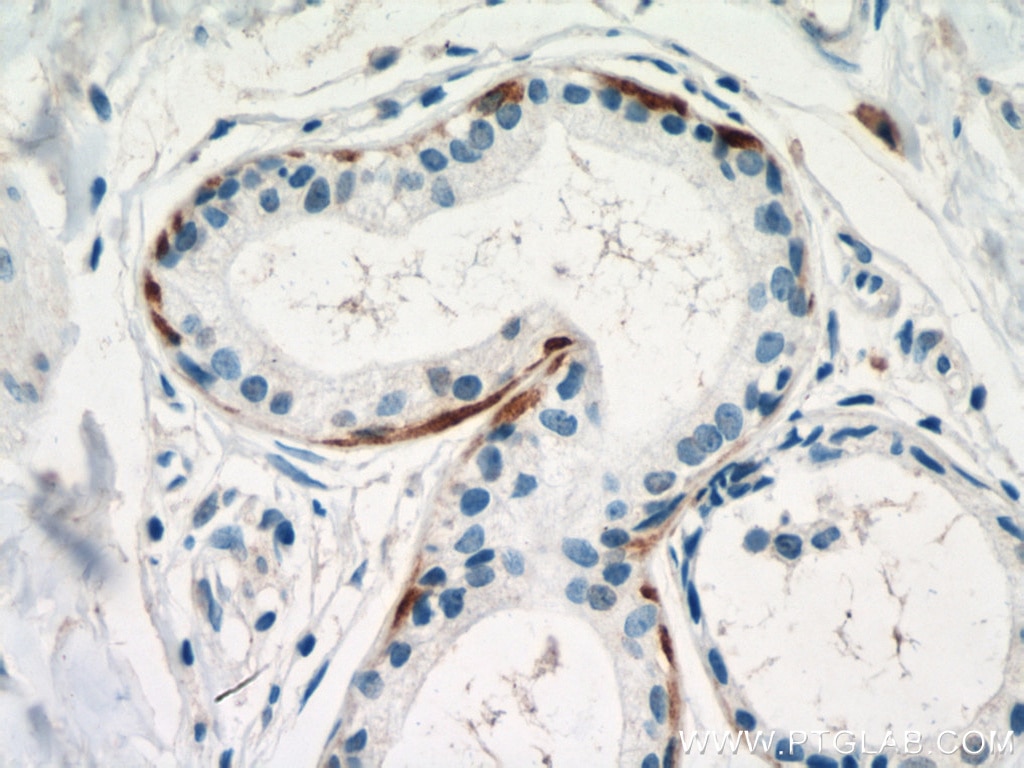
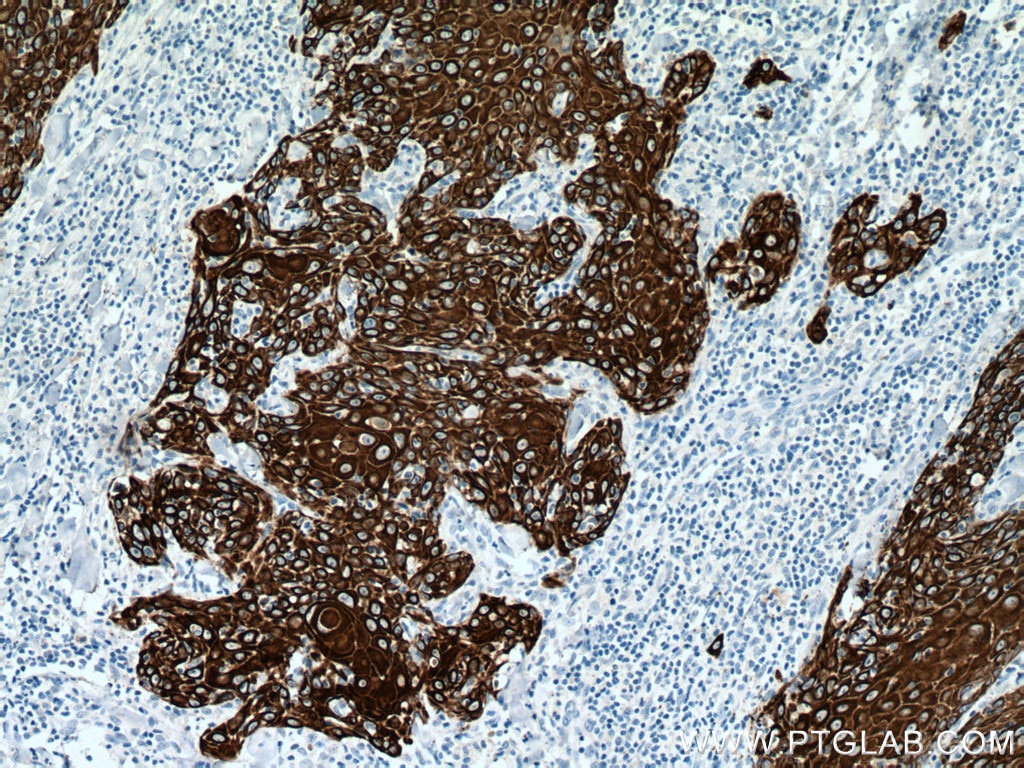
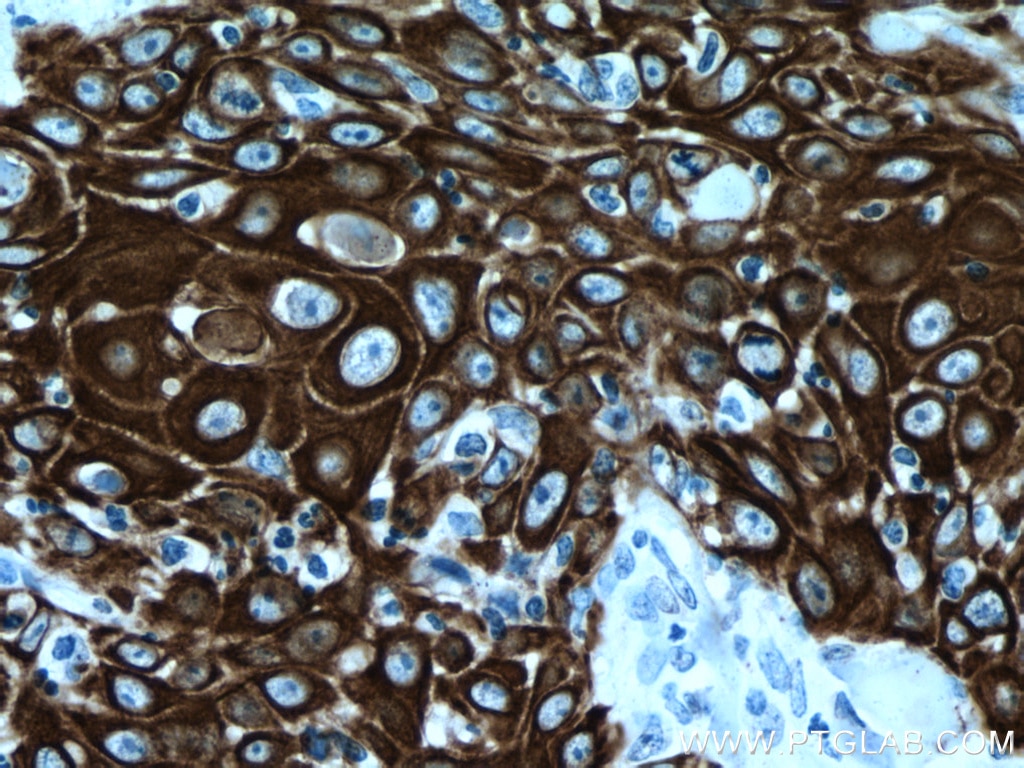
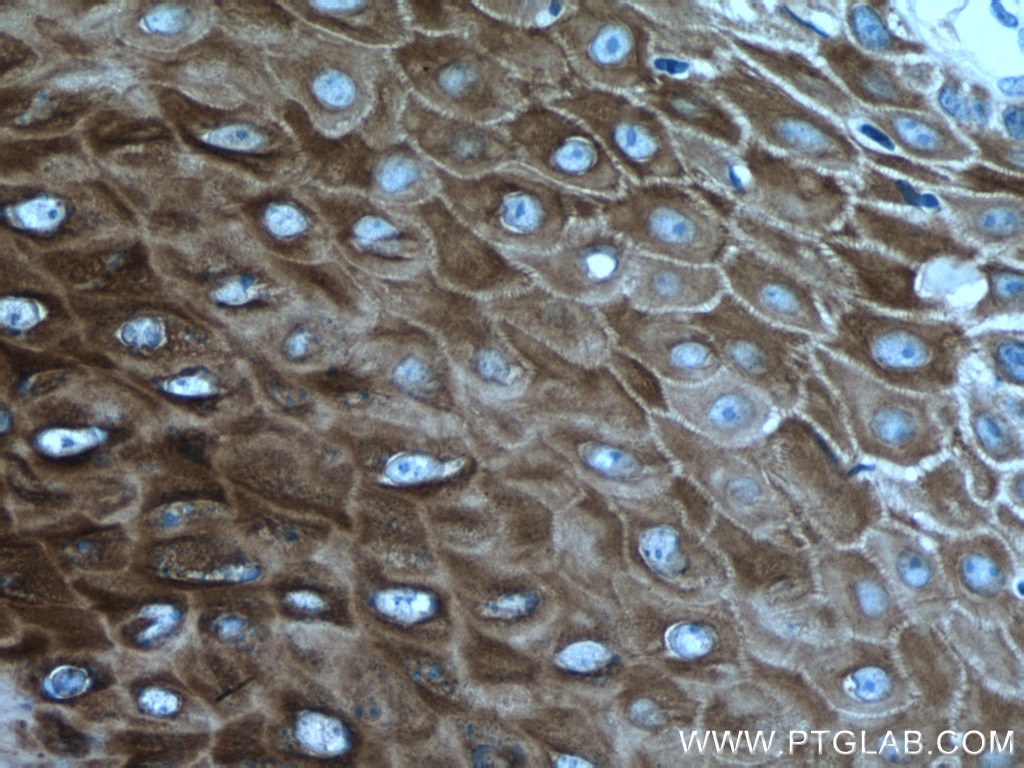
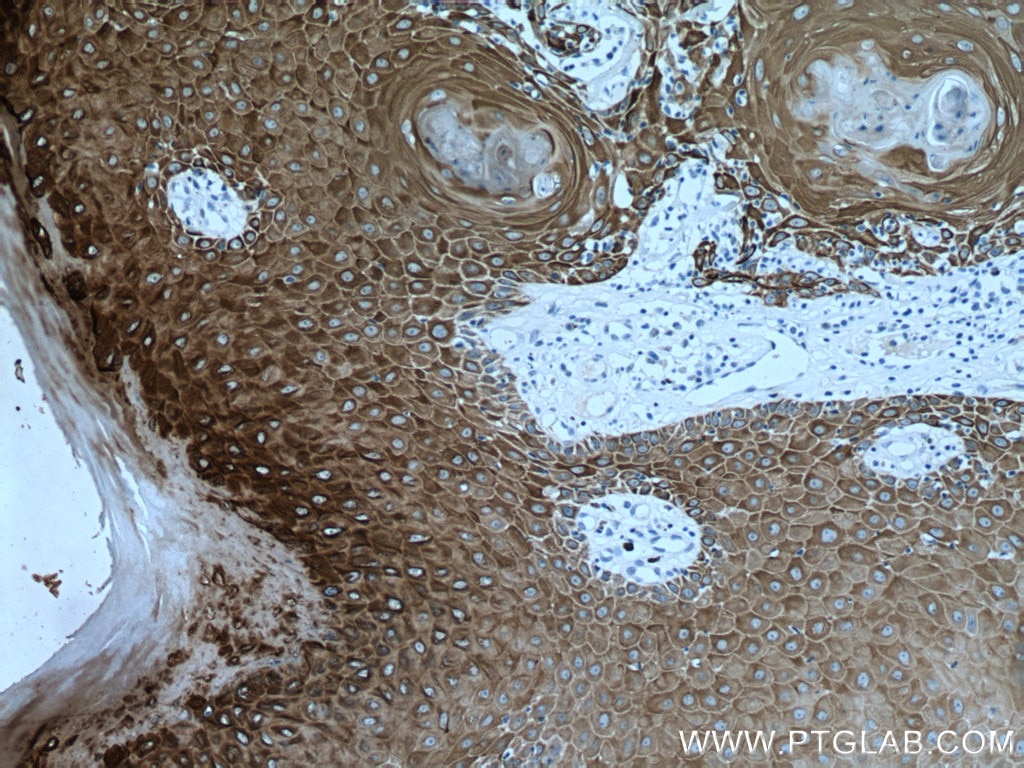
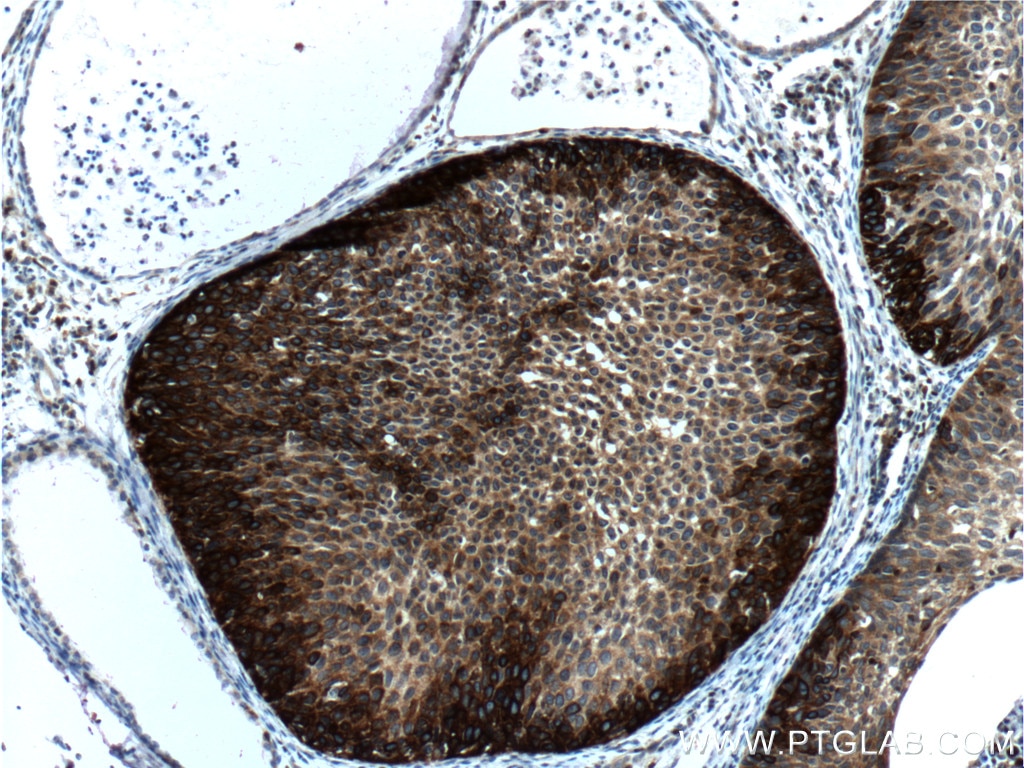
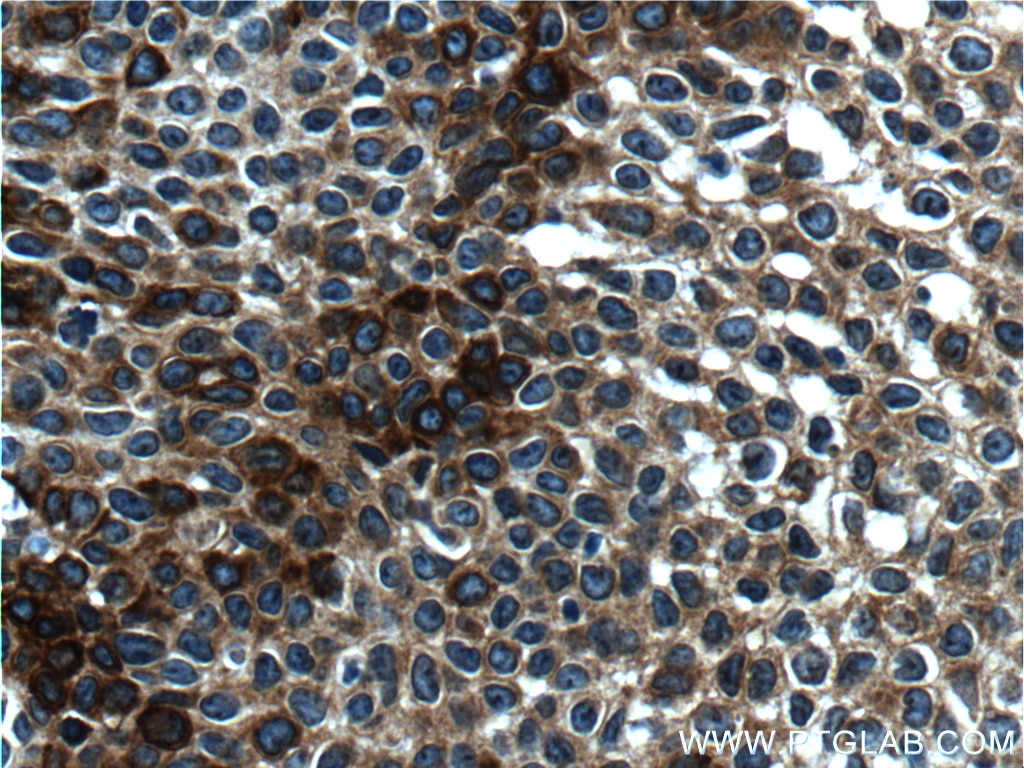
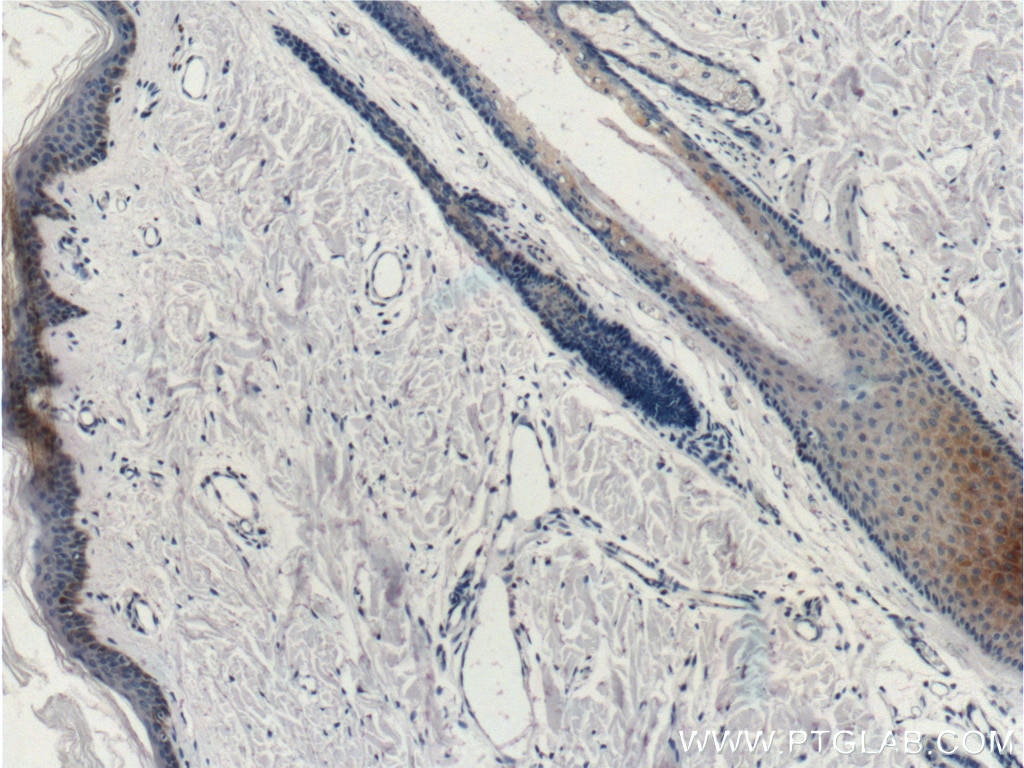
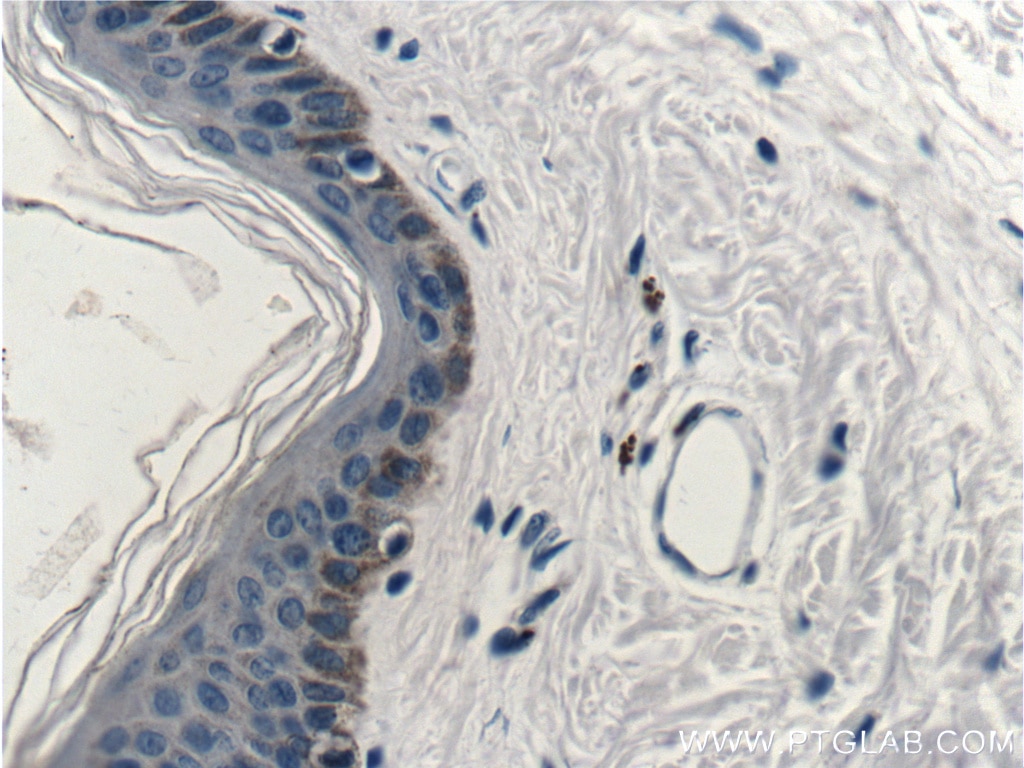
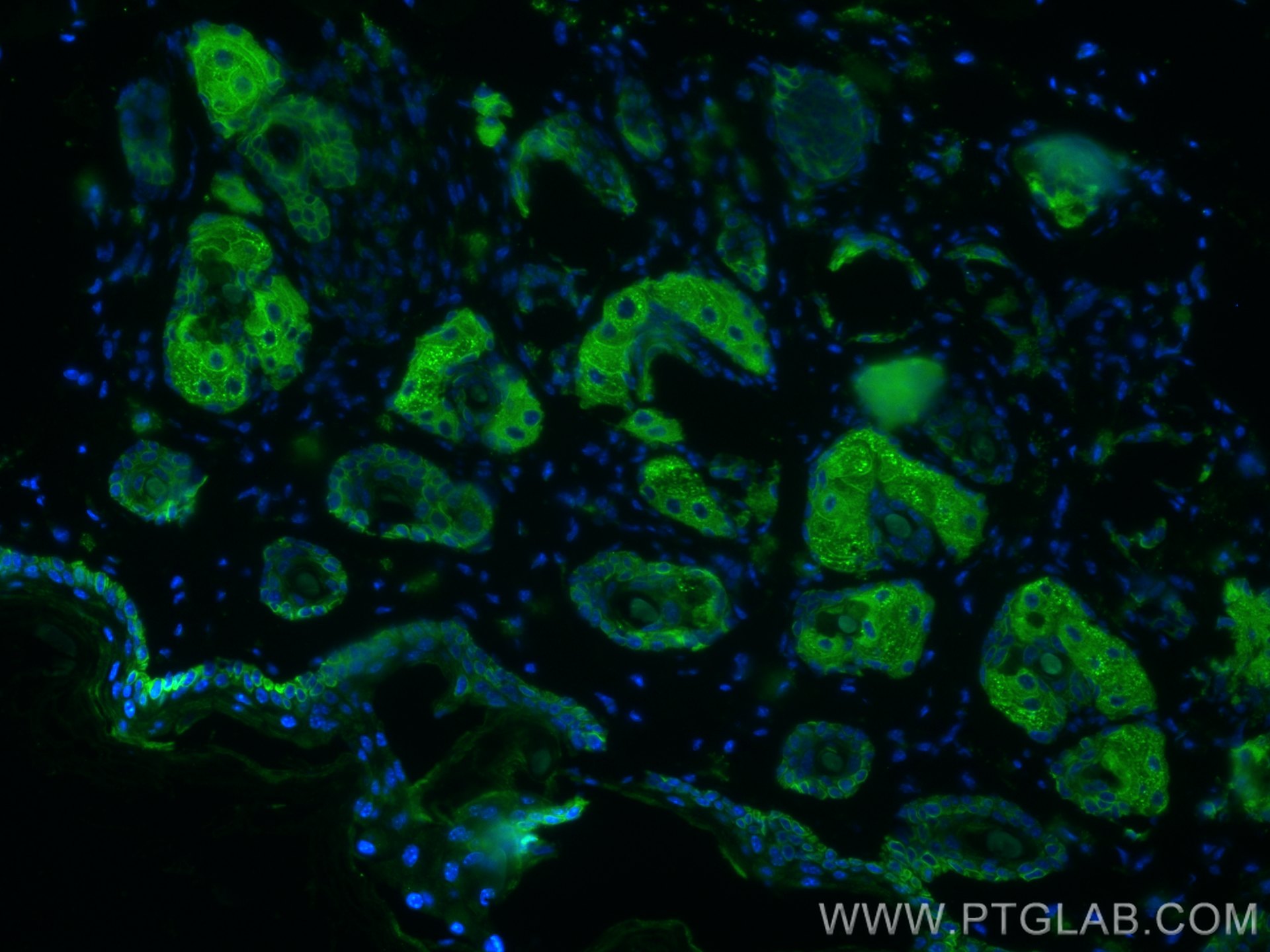
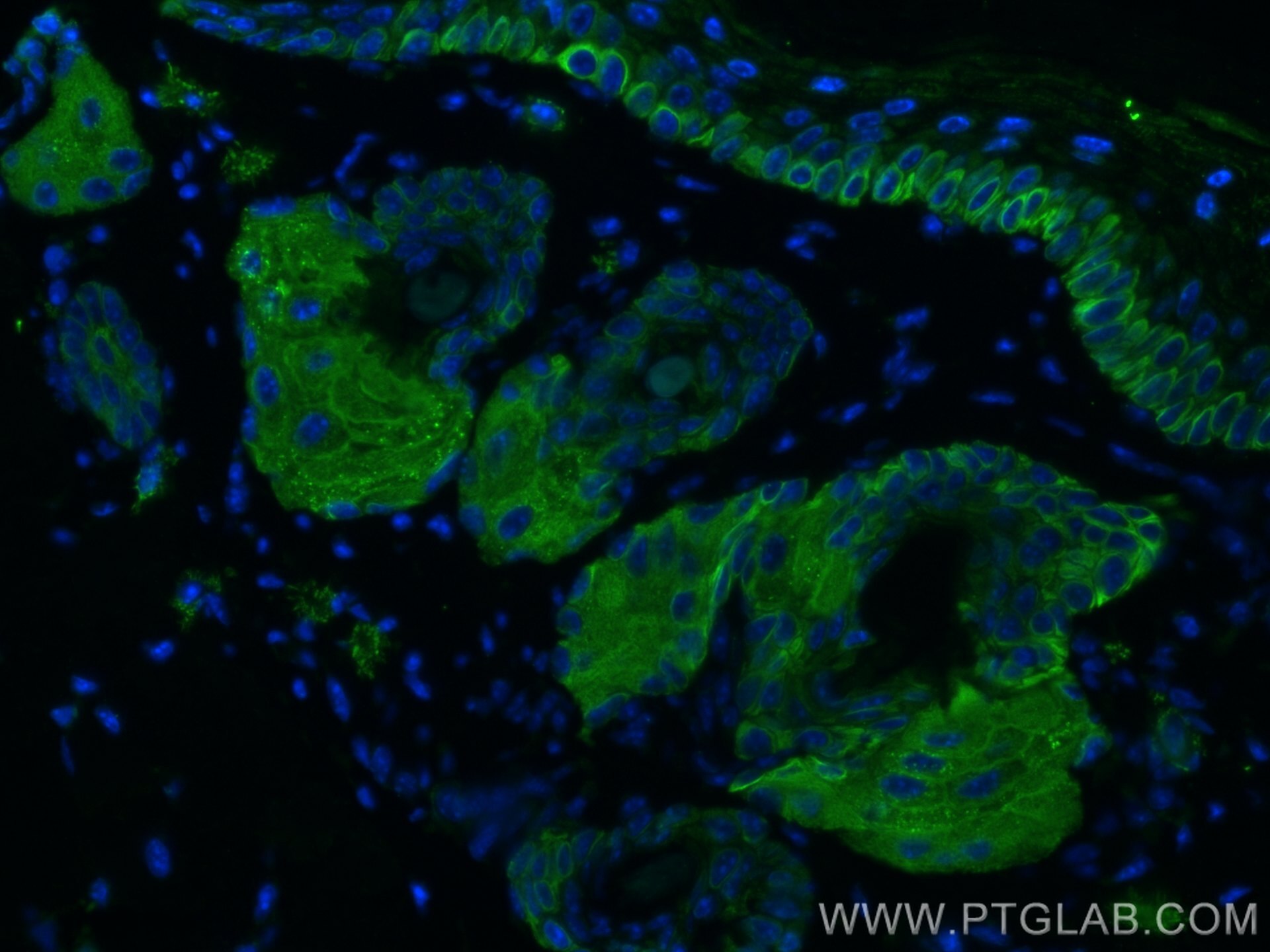
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du poumon humain, tissu cutané de rat, tissu cutané humain, tissu de cancer de la peau humain, tissu de cancer du col de l'utérus humain, tissu d'hyperplasie mammaire humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
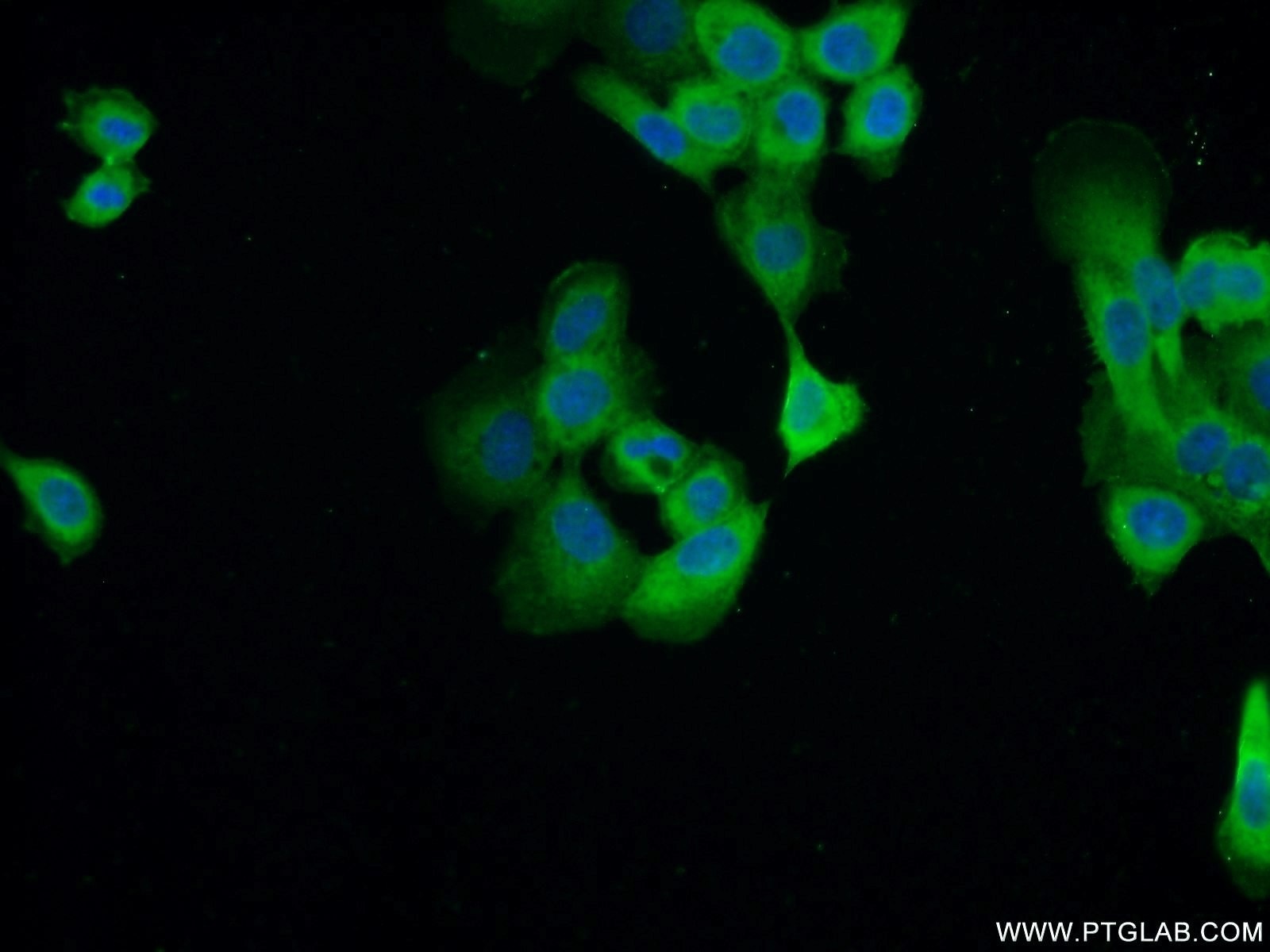
| Résultats positifs en IF | cellules A431, tissu cutané de souris |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:400-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 4 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 12 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
60320-1-Ig cible Cytokeratin 14 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, porc, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, porc, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Cytokeratin 14 Protéine recombinante Ag17559 |
| Nom complet | keratin 14 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 472 aa, 52 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 52 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC002690 |
| Symbole du gène | KRT14 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 3861 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine G |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Keratins are a large family of proteins that form the intermediate filament cytoskeleton of epithelial cells, which are classified into two major sequence types. Type I keratins are a group of acidic intermediate filament proteins, including K9-K23, and the hair keratins Ha1-Ha8. Type II keratins are the basic or neutral courterparts to the acidic type I keratins, including K1-K8, and the hair keratins, Hb1-Hb6. Keratin 14 is a type I cytokeratin. It is usually found as a heterotetramer with keratin 5. Keratins K14 and K5 have long been considered to be biochemical markers of the stratified squamous epithelia, including epidermis.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Cytokeratin 14 antibody 60320-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Cytokeratin 14 antibody 60320-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Cytokeratin 14 antibody 60320-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Small Eco-Friendly and Scalable Synthesis of Fullerenols with High Free Radical Scavenging Ability for Skin Radioprotection. | ||
Breast Cancer Res Anillin regulates breast cancer cell migration, growth, and metastasis by non-canonical mechanisms involving control of cell stemness and differentiation. | ||
Environ Sci Technol Graphene Quantum Dots Disrupt Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation by Interfering with the Methylation Level of Sox2. | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Exosomes from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived keratinocytes accelerate burn wound healing through miR-762 mediated promotion of keratinocytes and endothelial cells migration. | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells facilitate diabetic wound healing through the restoration of epidermal cell autophagy via the HIF-1α/TGF-β1/SMAD pathway |