Anticorps Monoclonal anti-ELF1
ELF1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
WB, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2D4A11
N° de cat : 67138-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
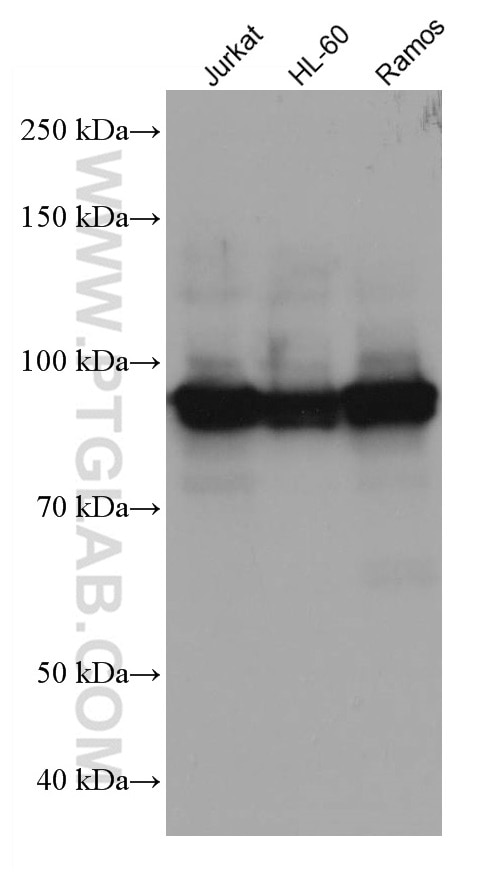
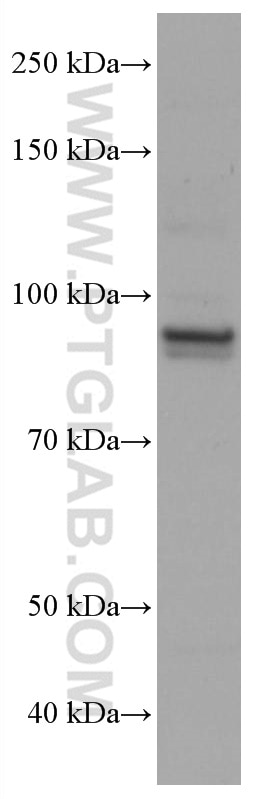
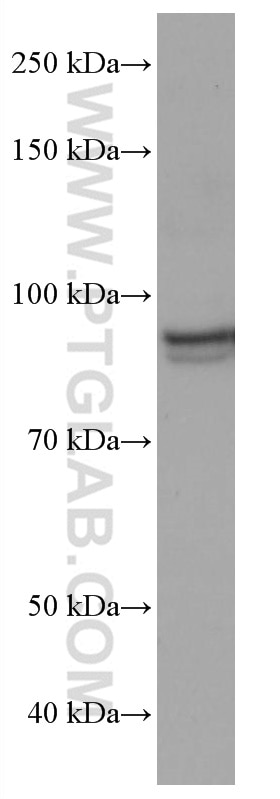
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules Jurkat, cellules A431, cellules HL-60, cellules PC-3, cellules Ramos |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
67138-1-Ig cible ELF1 dans les applications de WB, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | ELF1 Protéine recombinante Ag14689 |
| Nom complet | E74-like factor 1 (ets domain transcription factor) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 619 aa, 67 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 93-97 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC030507 |
| Symbole du gène | ELF1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 1997 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
ELF1, also named as ETS-related transcription factor Elf-1, is originally cloned from a human T-cell cDNA library by hybridization with a probe encoding the DNA binding domain (ETS domain) of the human Ets-1 cDNA. Based on its preferential expression in embryonic lymphoid organs (thymus and spleen), a wide variety of epithelial cells and fetal liver as well as in adult haematopoietic tissues, including thymus, spleen and bone marrow, Elf-1 emerged as a potential key regulator of haematopoietic gene expression. Consistent with this notion, Elf-1 has been shown to be a direct upstream regulator of genes important for haematopoiesis such as Scl, Fli-1, Lyl-1, Runx1 and Lmo2 . Elf-1 has also been shown to be important for blood vessel development, a process that is closely linked to early haematopoiesis during embryonic development. Elf-1 has been reported to take part in the transcriptional control of major regulators of blood vessel development such as Tie1, Tie2, angiopoietin-2, the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1), the endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) and endoglin . Functional activity of Ets proteins is modulated at multiple levels. It is known that ELF-1 appears in the cytoplasm as a 80 KDa protein that is O -glycosylated and phosphorylated in order to be translocated into the nucleus where it can be detected as a 98 KDa protein. After dephosphorylation, the protein is degraded through the proteasome pathway. The inactive form of Elf-1 is an 80-kDa protein that lacks DNA-binding activity and is confined to the cytoplasm of the cell. Phosphorylation and O-linked glycosylation increase the molecular weight of Elf-1 to 98 kDa, the active form; 98 kDa Elf-1 binds to the promoter of the gene that codes for CD3ζ inducing its transcription.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for ELF1 antibody 67138-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |