- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Cathepsin D
Cathepsin D Monoclonal Antibody for FC, IF, IHC, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
Humain et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
2F6F7
N° de cat : 66534-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
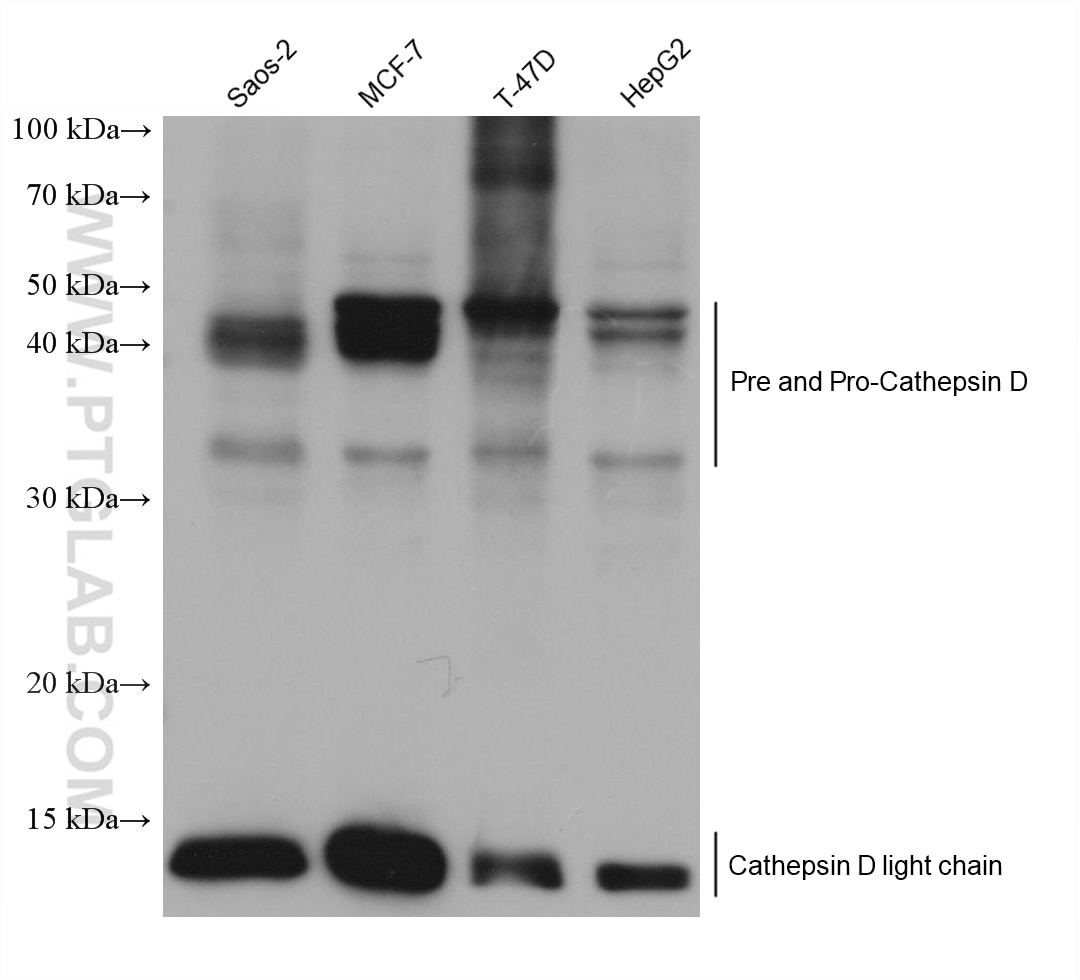
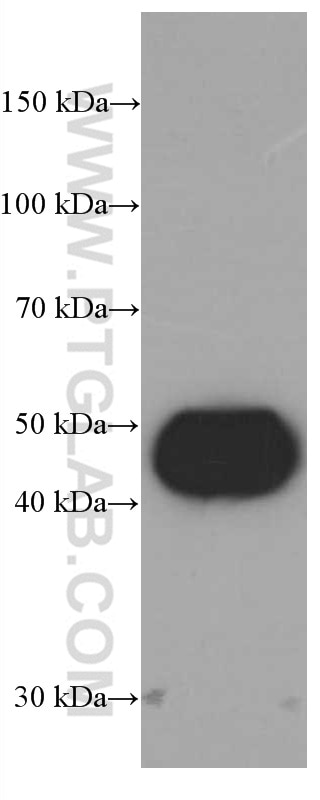
| Résultats positifs en WB | Saos-2 cells, cellules HepG2, cellules MCF-7, cellules T-47D |
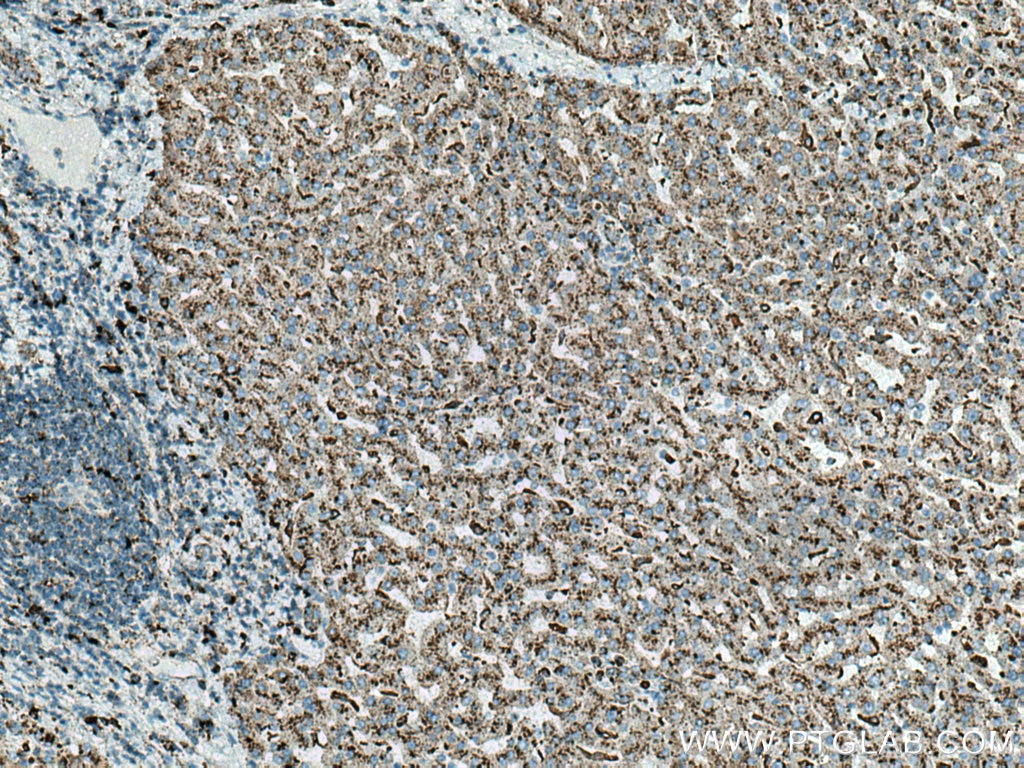
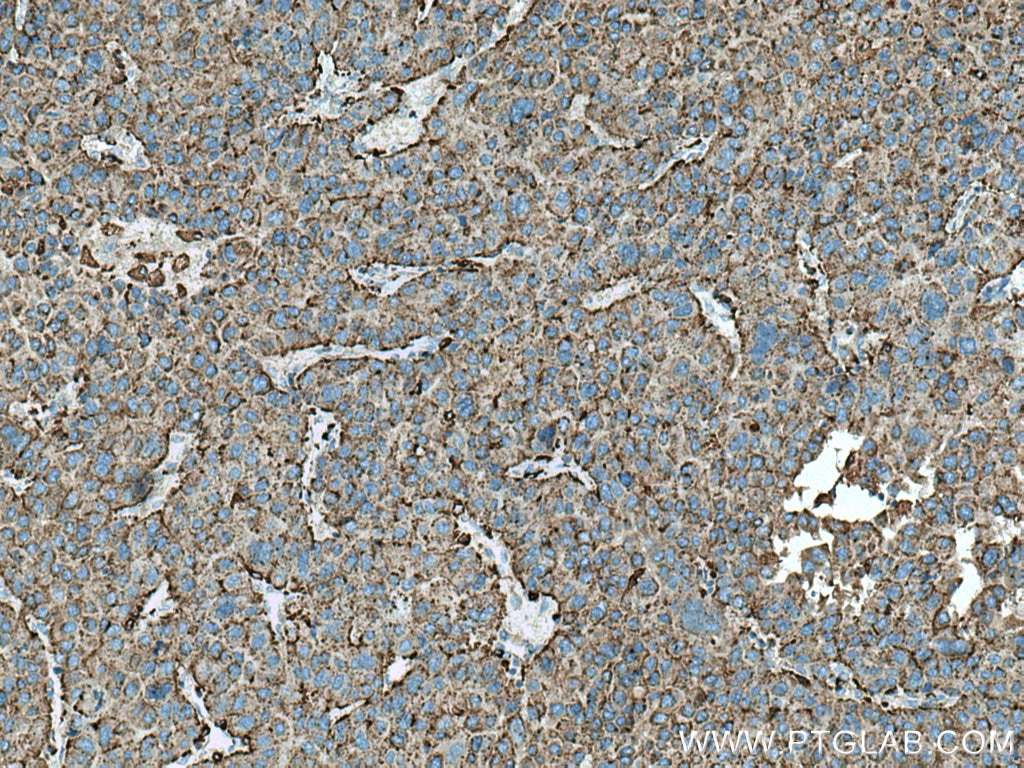
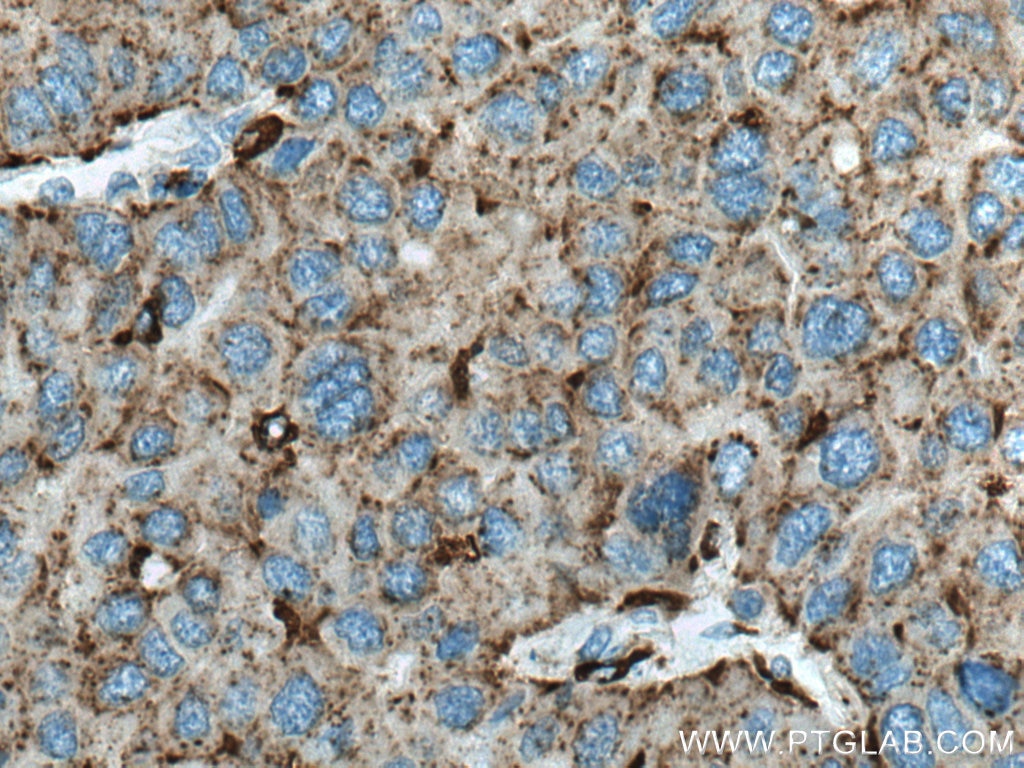
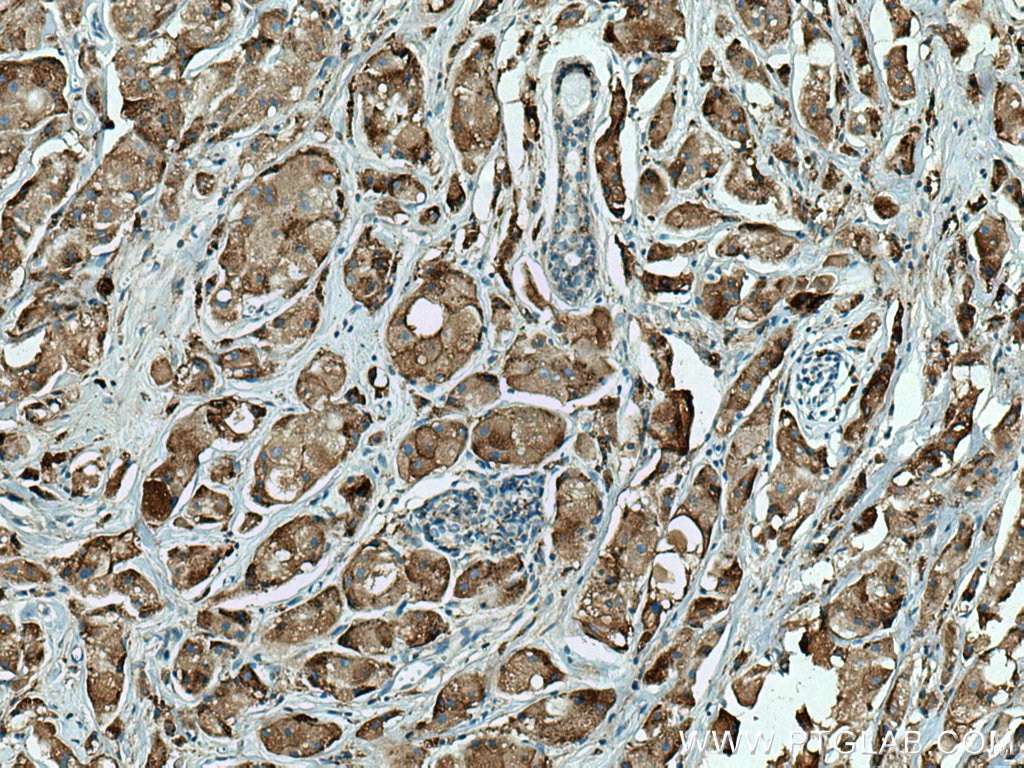
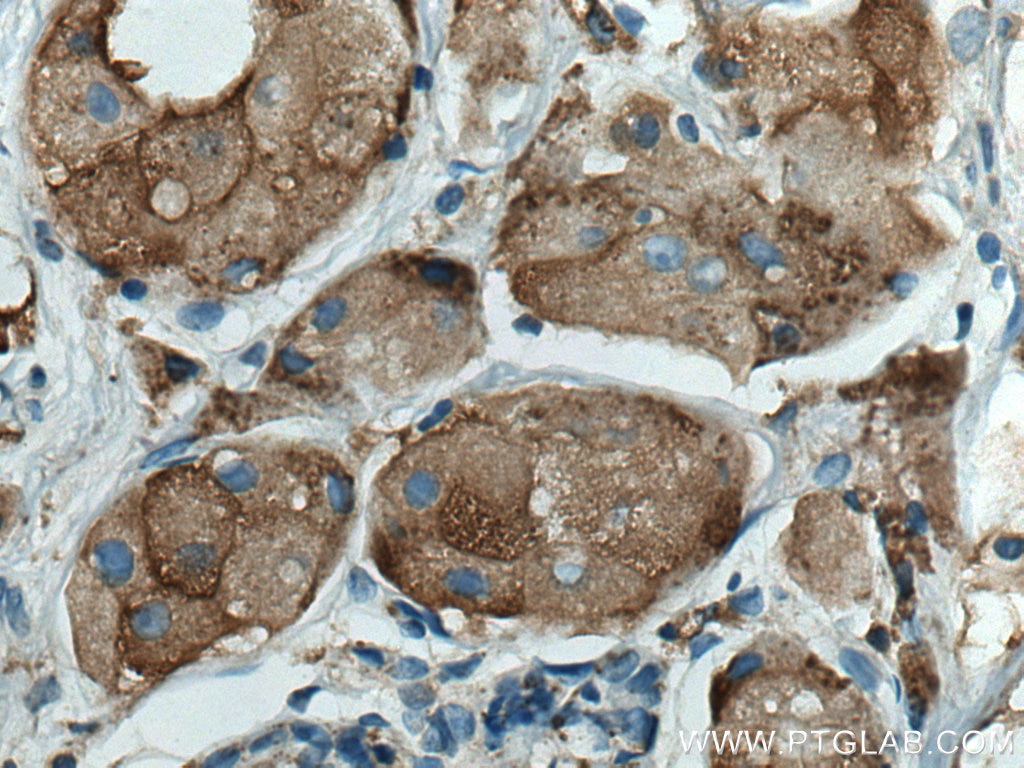
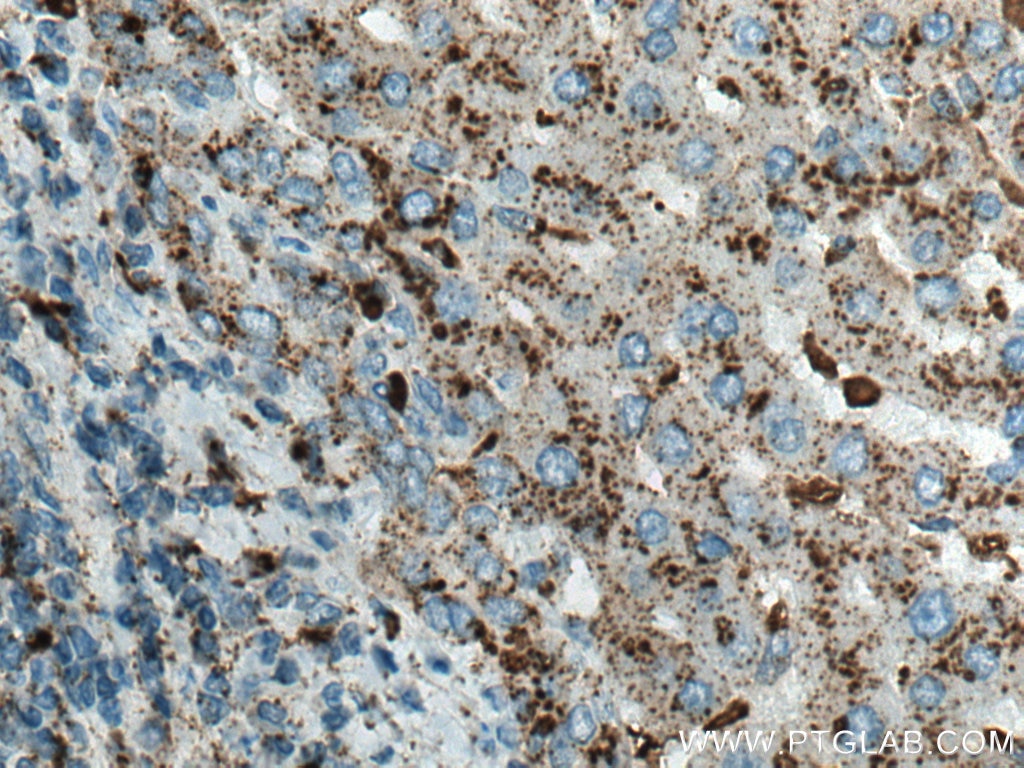
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du foie humain, tissu de cancer du sein humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
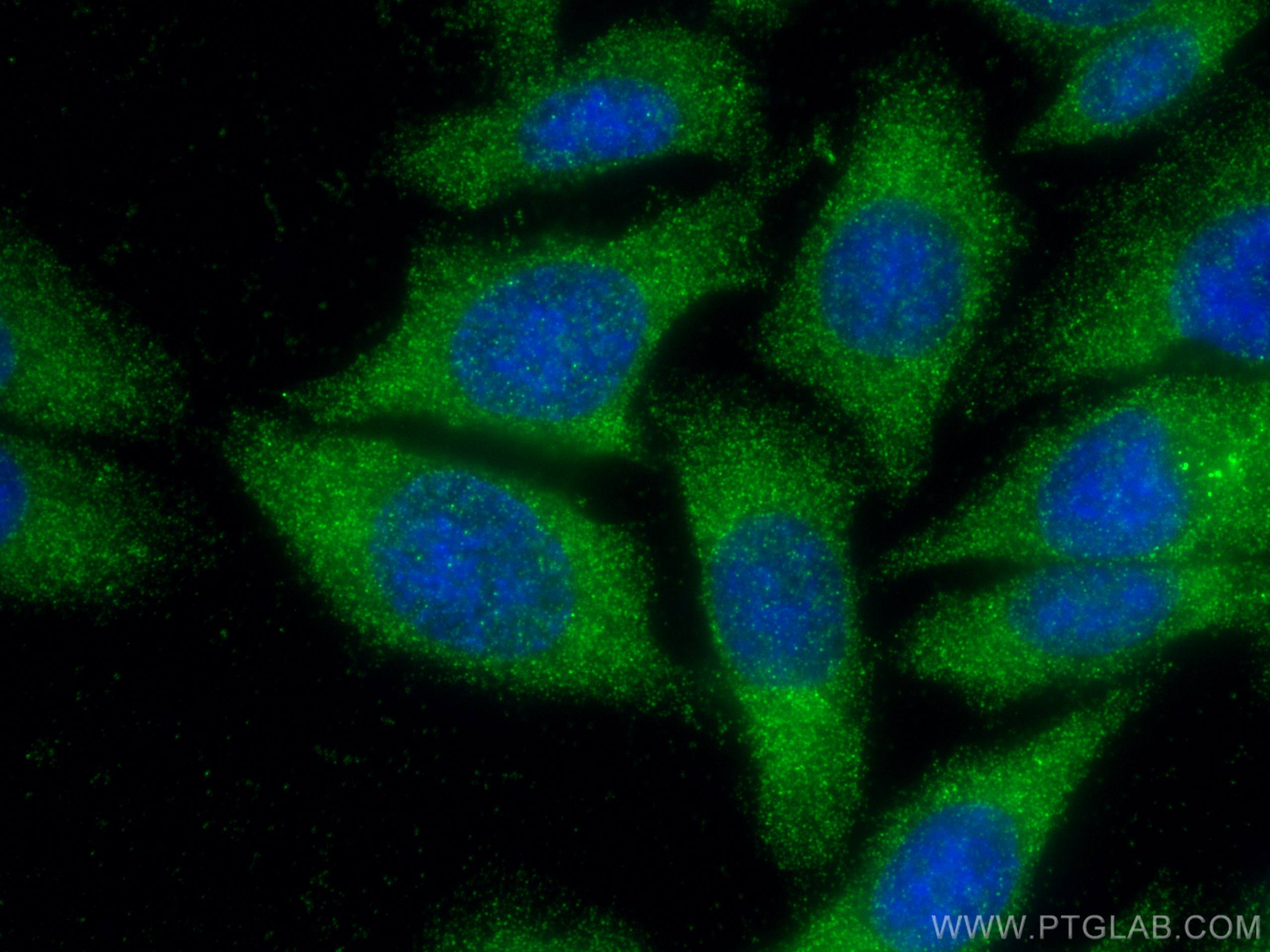
| Résultats positifs en IF | cellules HepG2, |
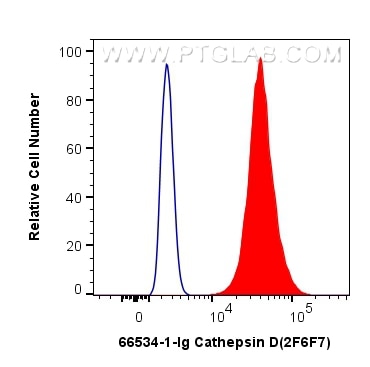
| Résultats positifs en cytométrie | cellules HepG2, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | IF : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 5 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66534-1-Ig cible Cathepsin D dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Cathepsin D Protéine recombinante Ag15254 |
| Nom complet | cathepsin D |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 412 aa, 45 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 32 kDa, 48 kDa, 52 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC016320 |
| Symbole du gène | CTSD |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 1509 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
CTSD (Cathepsin D) is also named as CPSD, belongs to the peptidase A1 family. It is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in proteolytic degradation, cell invasion, and apoptosis. Human CTSD is synthesized as a 52-kDa precursor that is converted into an active 48-kDa single-chain intermediate in the endosomes, and then into a fully active mature form, composed of a 34-kDa heavy chain and a 14-kDa light chain, in the lysosomes. It is a lysosomal acid protease found in neutrophils and monocytes and involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases such as breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. (PMID: 27114232, PMID: 30717773, PMID: 30051532)
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Cathepsin D antibody 66534-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Cathepsin D antibody 66534-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Cathepsin D antibody 66534-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| FC protocol for Cathepsin D antibody 66534-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Gastroenterology Proteomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of gastrointestinal stromal tumors | ||
Life (Basel) Melibiose Confers a Neuroprotection against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Ameliorating Autophagy Flux via Facilitation of TFEB Nuclear Translocation in Neurons. | ||
Cell Rep Intracellular complement C5a/C5aR1 stabilizes β-catenin to promote colorectal tumorigenesis.
| ||
FEBS Lett Senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease arise from Aβ- and Cathepsin D-enriched mixtures leaking out during intravascular haemolysis and microaneurysm rupture | ||
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf The inhibition of TRPML1/TFEB leads to lysosomal biogenesis disorder, contributes to developmental fluoride neurotoxicity | ||
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf TFE3-mediated impairment of lysosomal biogenesis and defective autophagy contribute to fluoride-induced hepatotoxicity |