Anticorps Monoclonal anti-CD56
CD56 Monoclonal Antibody for FC
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
FC
Conjugaison
FITC Plus Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
B-A19
N° de cat : FITC-65264
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
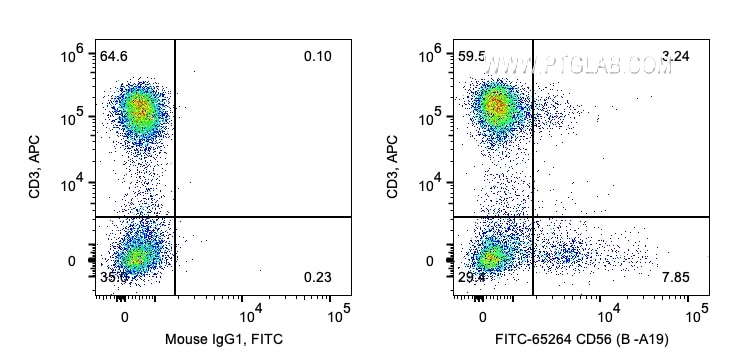
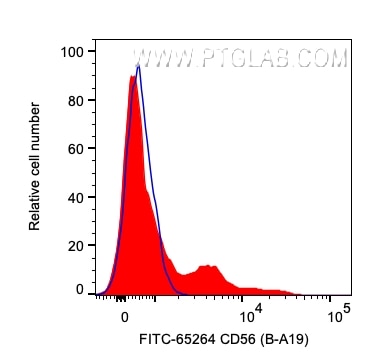
| Résultats positifs en cytométrie | CMSP humaines, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
FITC-65264 cible CD56 dans les applications de FC et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | s/o |
| Nom complet | neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC014205 |
| Symbole du gène | NCAM1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4684 |
| Conjugaison | FITC Plus Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 495 nm / 524 nm |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA. |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Informations générales
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurons, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety of human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for FITC Plus CD56 antibody FITC-65264 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |