Anticorps Monoclonal anti-CD80/B7-1
CD80/B7-1 Monoclonal Antibody for IHC, WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG1
Réactivité testée
Humain, porc, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1E2F10
N° de cat : 66406-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
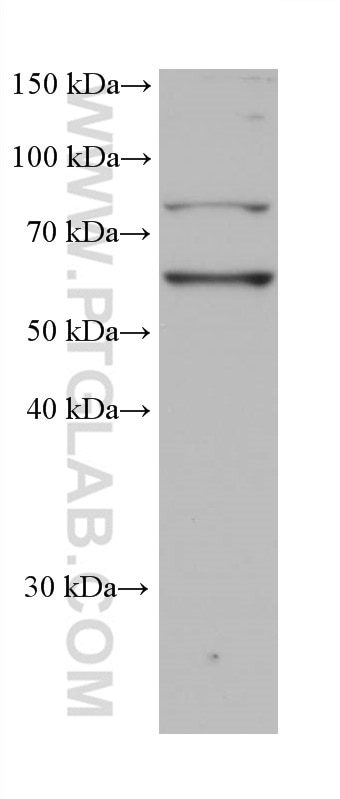
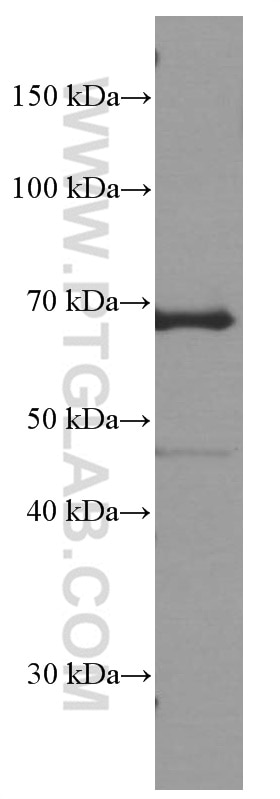
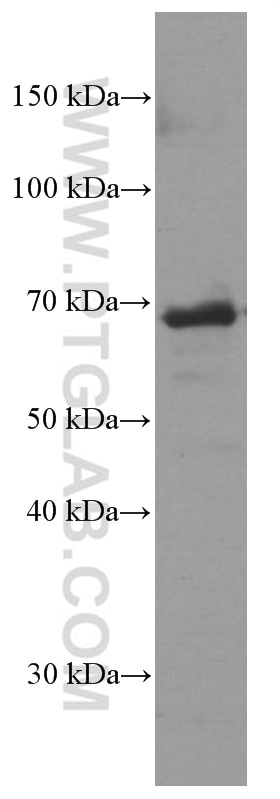
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules Raji, cellules Daudi, cellules DC2.4 |
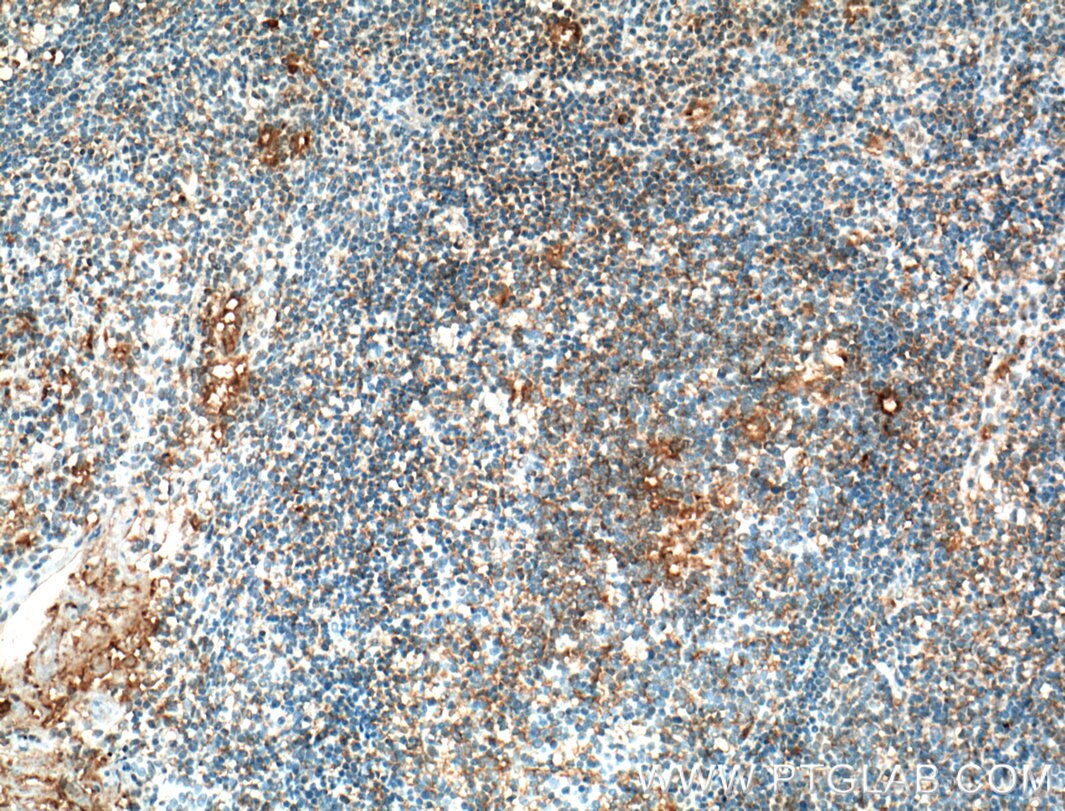
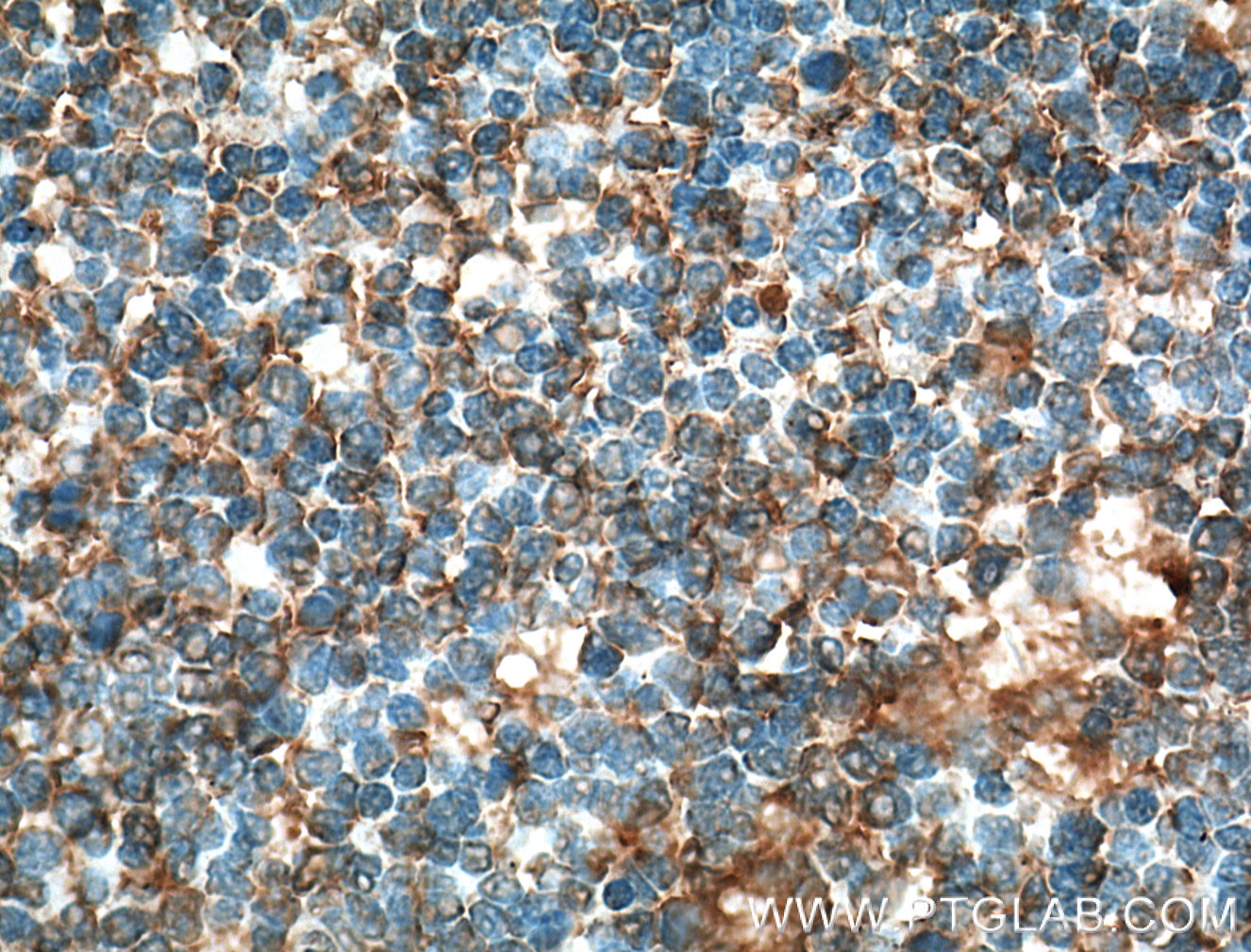
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu d'amygdalite humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 11 publications below |
| IHC | See 9 publications below |
| IF | See 7 publications below |
| FC | See 3 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66406-1-Ig cible CD80/B7-1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, porc, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, porc, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, porc, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CD80/B7-1 Protéine recombinante Ag5615 |
| Nom complet | CD80 molecule |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 33 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 68 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC042665 |
| Symbole du gène | CD80 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 941 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
CD80 (also known as B7-1) is a type I membrane protein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, with an extracellular immunoglobulin constant-like domain and a variable-like domain required for receptor binding. It is expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including B cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, and macrophages. CD80 is the receptor for the proteins CD28 and CTLA-4 found on the surface of T-cells. It is involved in the costimulatory signal essential for T-lymphocyte activation. T-cell proliferation and cytokine production is induced by the binding of CD28, binding to CTLA-4 has opposite effects and inhibits T-cell activation. CD80 also acts as a cellular attachment receptor for adenovirus subgroup B. (PMID: 7545666; 12015893; 16920215)
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CD80/B7-1 antibody 66406-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CD80/B7-1 antibody 66406-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Acta Pharm Sin B Converting bacteria into autologous tumor vaccine via surface biomineralization of calcium carbonate for enhanced immunotherapy | ||
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces Surface Coating of Pulmonary siRNA Delivery Vectors Enabling Mucus Penetration, Cell Targeting, and Intracellular Radical Scavenging for Enhanced Acute Lung Injury Therapy. | ||
Theranostics ILT4 inhibition prevents TAM- and dysfunctional T cell-mediated immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in NSCLC with EGFR activation. | ||
Free Radic Biol Med Mutual antagonism between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 regulates the maturation status of DCs in liver fibrosis. | ||
Life Sci Activation of GABA receptor attenuates intestinal inflammation by modulating enteric glial cells function through inhibiting NF-κB pathway | ||
Int J Biochem Cell Biol Knockdown of LncRNA MALAT1 contributes to cell apoptosis via regulating NF-κB/CD80 axis in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. |