Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Alpha Tubulin
Alpha Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody for WB
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB
Conjugaison
CoraLite® Plus 750 Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
1E4C11
N° de cat : CL750-66031
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
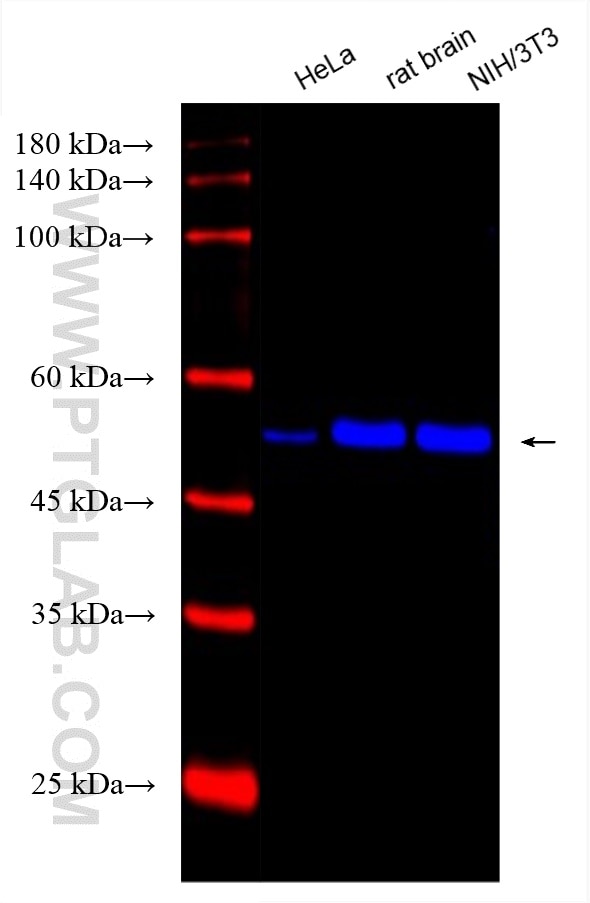
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HeLa, cellules NIH/3T3, tissu cérébral de rat |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
CL750-66031 cible Alpha Tubulin dans les applications de WB et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Alpha Tubulin Protéine recombinante Ag18034 |
| Nom complet | tubulin, alpha 1b |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 50 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 50-55 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC009314 |
| Symbole du gène | TUBA1B |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 10376 |
| Conjugaison | CoraLite® Plus 750 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 755 nm / 780 nm |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec glycérol à 50 %, Proclin300 à 0,05 % et BSA à 0,5 %, pH 7,3. |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20 °C. Éviter toute exposition à la lumière. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
What is the function of alpha tubulin?
Alpha-tubulin belongs to a large superfamily of tubulin proteins. There are a number of different subtypes that have a molecular weight of ~50kDa and are able to bind to beta-tubulin, forming a heterodimer that polymerises to microtubules as part of the cytoskeleton. These maintain cell structure, provide platforms for intracellular transport and are also involved in cell division.
Where is alpha-tubulin expressed?
Alpha tubulin is highly conserved and is present in nearly all eukaryotic cells as one of the building blocks of microtubules. The ubiquitous nature of this protein has led to its common use as a control protein for many tissue types as well as highlighting the structure of the cytoskeleton.
What are the post-translational modifications of alpha tubulin?
The function and properties of microtubules are drastically affected by the post-translational modifications undergone by tubulin, which may occur to the tubulin dimer directly or to the polymerised mictotubule. For example, the first modification to be identified was detyrosination1, as most alpha-tubulins have a tyrosine at their terminus. This process affects microtubules more than dimers and leads to patches of detyronisation along the structure, regulating protein interactions and allowing subcellular compartments to be defined.2,3 Polyglutamylation also occurs on several sites within the carboxy-terminal tails. However, to date, the most-studied alpha tubulin modification is related to acetylation of lysine 40 (K40).
1. Gundersen, G. G., Khawaja, S. & Bulinski, J. C. Postpolymerization detyrosination of alpha-tubulin: a mechanism for subcellular differentiation of microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 105, 251-64 (1987).
2. Galjart, N. Plus-End-Tracking Proteins and Their Interactions at Microtubule Ends. Curr. Biol. 20, R528-R537 (2010).
3. Jiang, K. & Akhmanova, A. Microtubule tip-interacting proteins: a view from both ends. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 94-101 (2011).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CL Plus 750 Alpha Tubulin antibody CL750-66031 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |