Transferrin Monoklonaler Antikörper
Transferrin Monoklonal Antikörper für IF
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
IF
Konjugation
CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
2B4C6
Kat-Nr. : CL488-66171
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
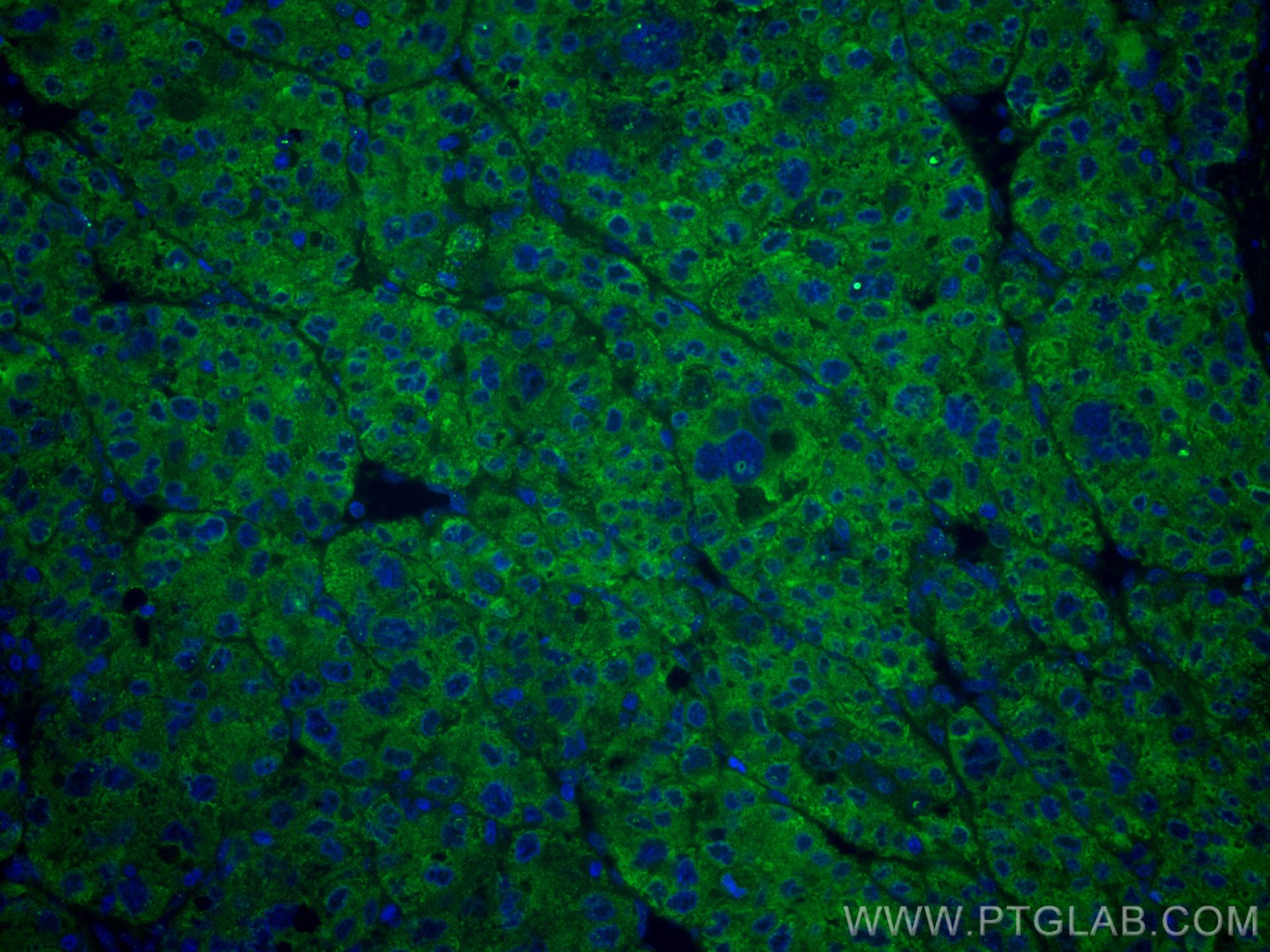
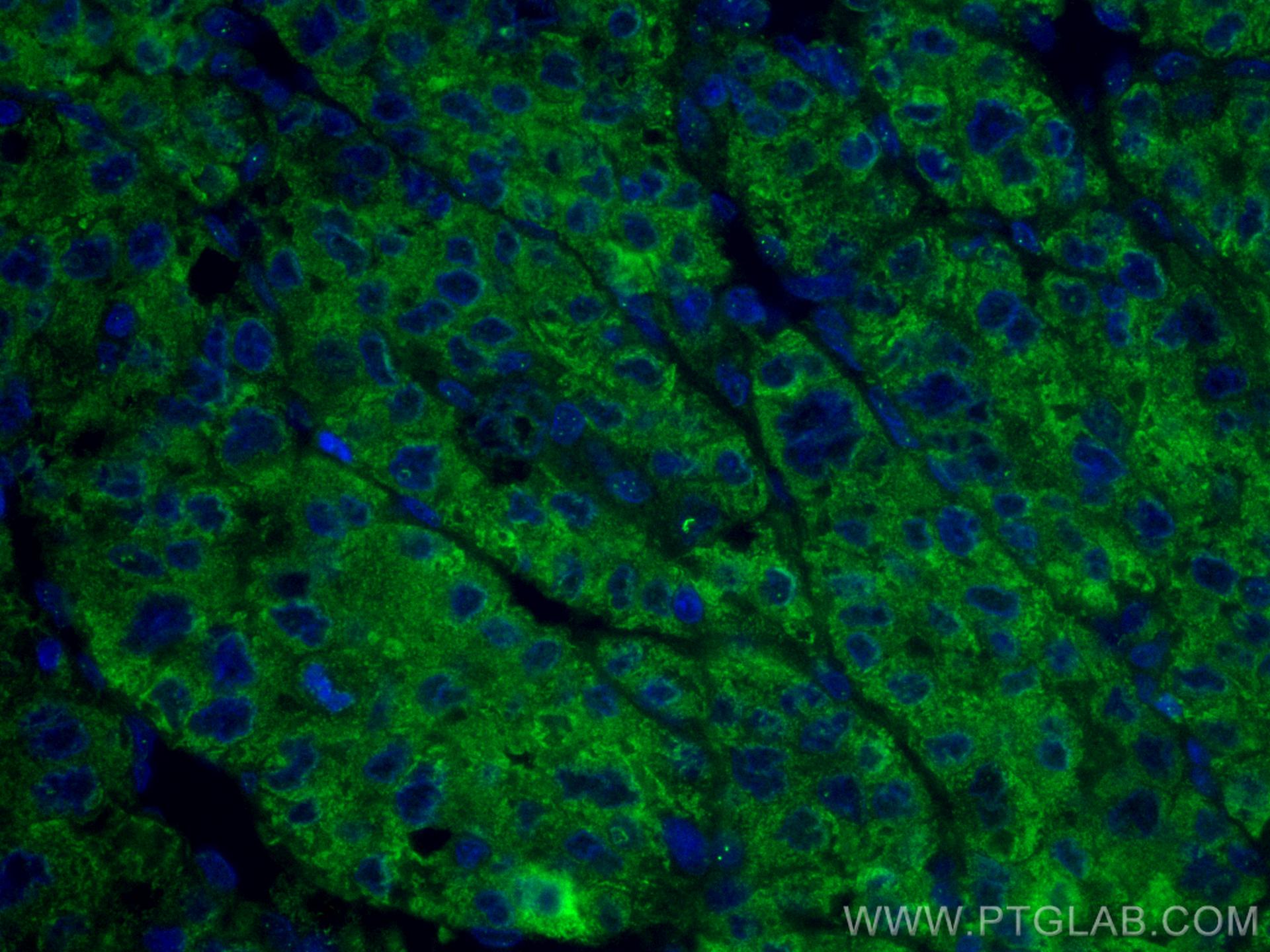
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | humanes Leberkarzinomgewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
CL488-66171 bindet in IF Transferrin und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Transferrin fusion protein Ag11668 |
| Vollständiger Name | transferrin |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 698 aa, 77 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 77 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC059367 |
| Gene symbol | TF |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7018 |
| Konjugation | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | BS mit 50% Glyzerin, 0,05% Proclin300, 0,5% BSA, pH 7,3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Vor Licht schützen. Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
What is the tissue specificity of TF?
Transferrin is synthesized mainly in the liver.
What is the calculated molecular weight of TF?
77 kDa
How many iron atoms can bind to TF?
Each of the two lobes of TF has one high-affinity Fe(III) binding site. Since binding of iron and bicarbonate
releases free H+ ions, affinity decreases in acidic conditions, in which TF also remains bound to its receptor.
What is the primary role of TF?
TF serves as a serum metal-binding protein, playing a key role in iron metabolism and delivery for erythropoiesis.
What is the role of TF in human diseases?
TF deficiency results in an exhibition of congenital atransferrinemia (hypotransferrinemia) in which there is a
decrease in hepcidin expression, causing increased iron levels.
Is TF essential for iron delivery?
Congenital atransferrinemia results in an iron overload in some tissues, such as the liver, suggesting that while TF is not essential for iron delivery to all organs, it is needed for iron level regulation.
In what circumstances do TF levels decrease?
Inflammation and iron overload both can cause a decline in TF levels.
How does TF affect hormonal balance?
TF positively regulates expression of hepcidin, a peptide hormone synthesized by the liver.
How does TF deficiency cause increased iron levels?
TF regulates hepcidin, which in turn is a negative regulator of intestinal iron absorption, resulting in TF
deficiency causing both anemia, and, paradoxically, increased iron levels in some tissues.
PMIDs: 23046645, 9635730, 22294463, 24589273
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 Transferrin antibody CL488-66171 | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |