Phospho-Beta Catenin (Ser33) Rekombinanter Antikörper
Phospho-Beta Catenin (Ser33) Rekombinant Antikörper für FC, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, FC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
3K1
Kat-Nr. : 80067-1-RR
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
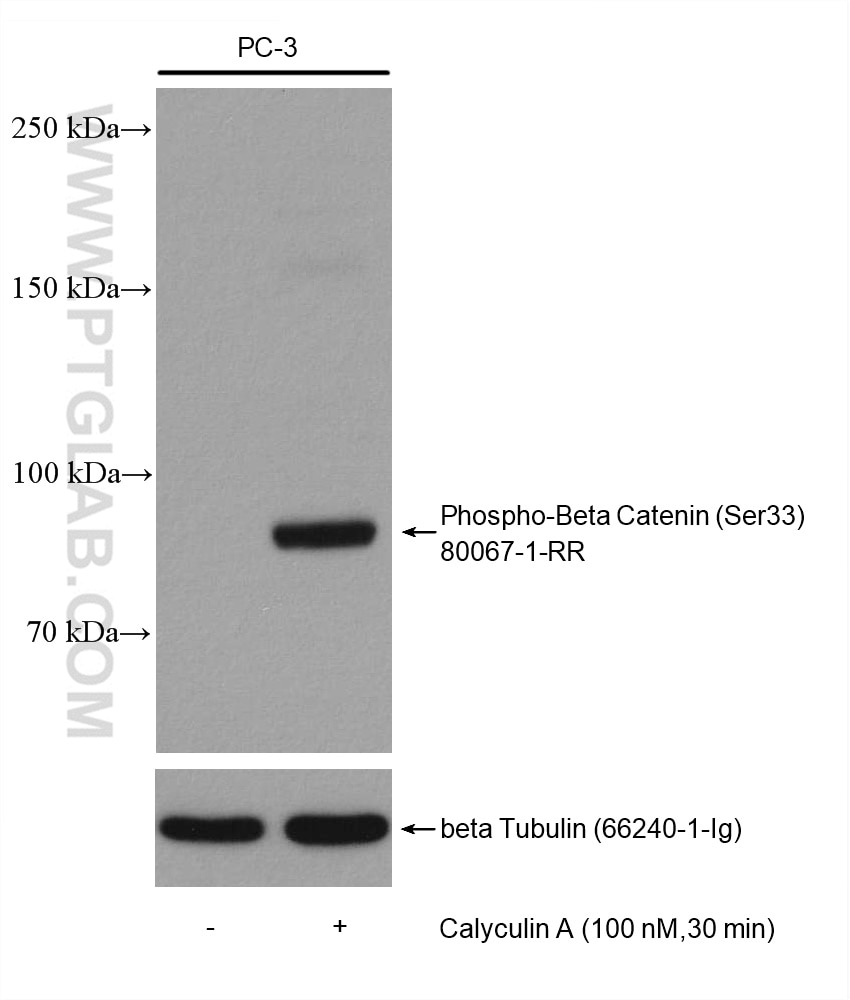
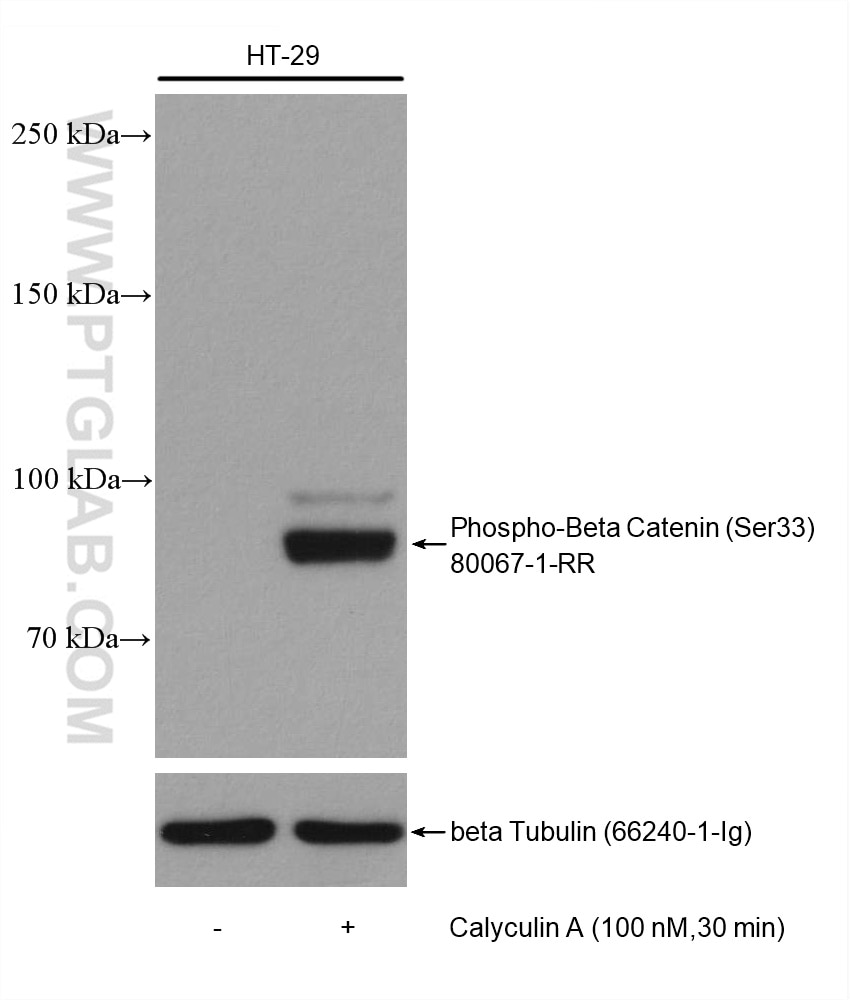
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | PC-3-Zellen, HT-29-Zellen, mit Calyculin A behandelte HT-29-Zellen, Mit Calyculin A behandelte PC-3-Zellen |
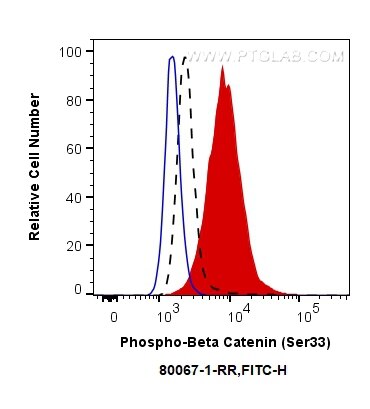
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC | Mit Calyculin A behandelte PC-3-Zellen, PC-3-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) | FC : 0.25 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 5 publications below |
Produktinformation
80067-1-RR bindet in WB, FC, ELISA Phospho-Beta Catenin (Ser33) und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Rekombinant |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 781 aa, 86 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 90 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC058926 |
| Gene symbol | CTNNB1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1499 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
β-Catenin, also known as CTNNB1, is an evolutionarily conserved, multifunctional intracellular protein. β-Catenin was originally identified in cell adherens junctions (AJs) where it functions to bridge the cytoplasmic domain of cadherins to a-catenin and the actin cytoskeleton. Besides its essential role in the AJs, β-catenin is also a key downstream component of the canonical Wnt pathway that plays diverse and critical roles in embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is also involved in the activation of other intracellular messengers such as calcium fluxes, JNK, and SRC kinases. Deregulation of β-catenin activity is associated with multiple diseases including cancers. (PMID: 22617422; 18334222). CK1 phosphorylates β-Catenin at Ser45. This phosphorylation event primes β-Catenin for subsequent phosphorylation by GSK-3β. GSK-3β destabilizes β-catenin by phosphorylating it at Ser33, Ser37, and Thr41. Mutations at these sites result in the stabilization of β-Catenin protein levels and have been found in many tumor cell lines .
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Phospho-Beta Catenin (Ser33) antibody 80067-1-RR | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mediators Inflamm Liraglutide Attenuates Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway | ||
Front Pharmacol Autophagy Blockade by Ai Du Qing Formula Promotes Chemosensitivity of Breast Cancer Stem Cells Via GRP78/β-Catenin/ABCG2 Axis. | ||
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) Targeting GRP78 enhances the sensitivity of HOS osteosarcoma cells to pyropheophorbide-α methyl ester-mediated photodynamic therapy via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. | ||
Exp Ther Med Insulin and liraglutide attenuate brain pathology in diabetic mice by enhancing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. | ||
Environ Toxicol Microplastics cause hepatotoxicity in diabetic mice by disrupting glucolipid metabolism via PP2A/AMPK/HNF4A and promoting fibrosis via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway |