NK1.1 (CD161) Monoklonaler Antikörper
NK1.1 (CD161) Monoklonal Antikörper für FC
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2a, kappa
Getestete Reaktivität
Maus
Anwendung
FC
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
PK136
Kat-Nr. : 65138-1-Ig
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
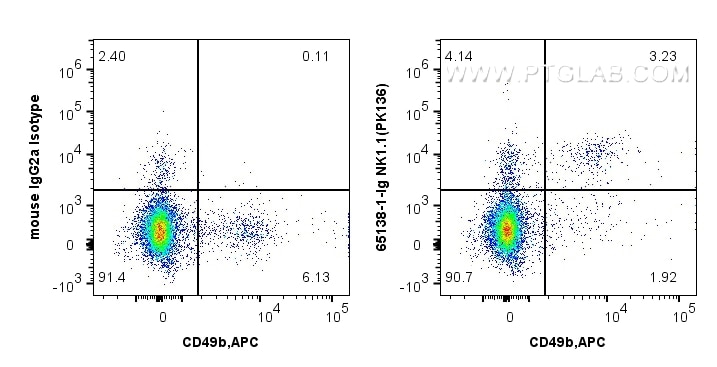
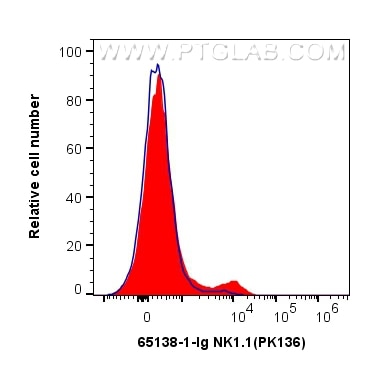
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC | C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
65138-1-Ig bindet in FC NK1.1 (CD161) und zeigt Reaktivität mit Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2a, kappa |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | NK-1+-Zellen aus Mausmilz und -knochenmark |
| Vollständiger Name | killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1A |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC120707 |
| Gene symbol | Klrb1a |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 17057 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Store at 2-8°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Hintergrundinformationen
NK1.1 (CD161), also known as KLRB1 or NKR-P1A, is a type II transmembrane C-type lectin-like receptor and is expressed on the cell membrane as disulfide-linked homodimer (PMID: 8077657). It is expressed by the majority of NK cells and subsets of peripheral T cells, including both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and is expressed preferentially on adult T cells with a "memory" antigenic phenotype (PMID: 8077657; 22566826). Expression of CD161 correlates with the cytotoxic function of CD16+ NK cells, and ligation of CD161 with its ligand LLT1 inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion (PMID: 29686665).
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for NK1.1 (CD161) antibody 65138-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |