MRPS15 Polyklonaler Antikörper
MRPS15 Polyklonal Antikörper für IF, IHC, IP, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 17006-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
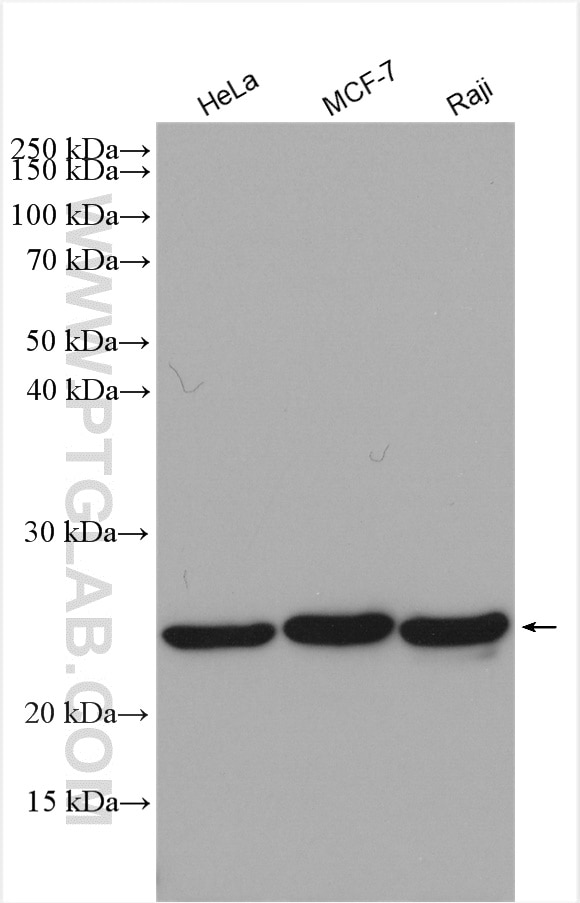
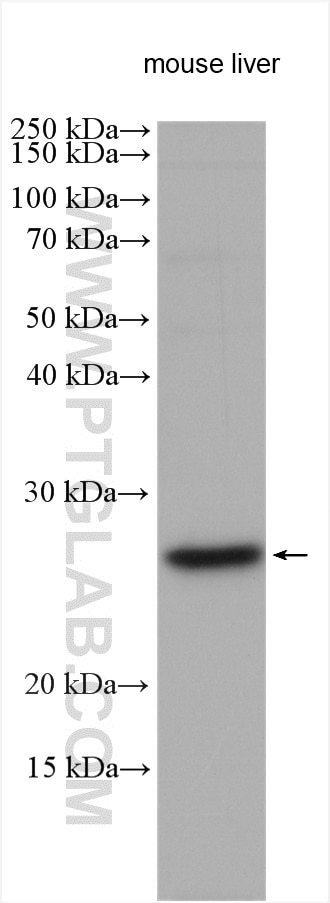
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HeLa-Zellen, Mauslebergewebe, MCF-7-Zellen, Raji-Zellen |
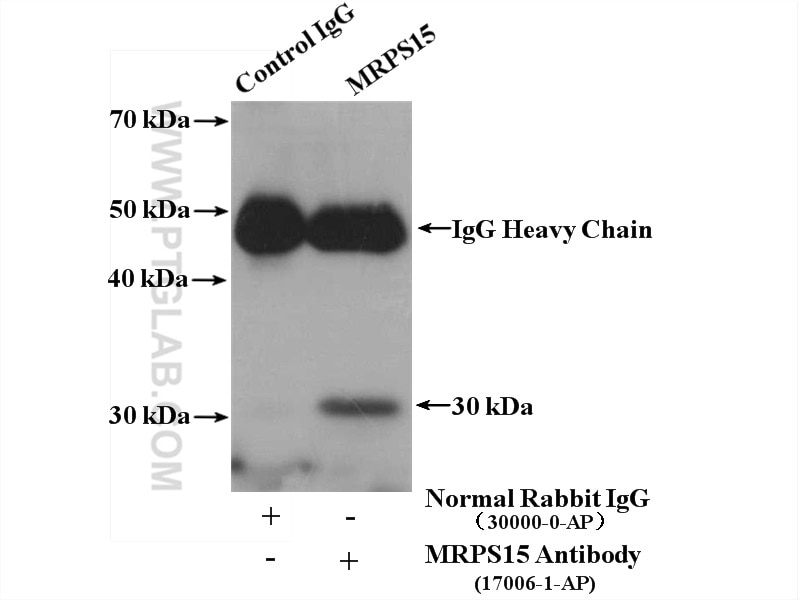
| Erfolgreiche IP | Maushirngewebe |
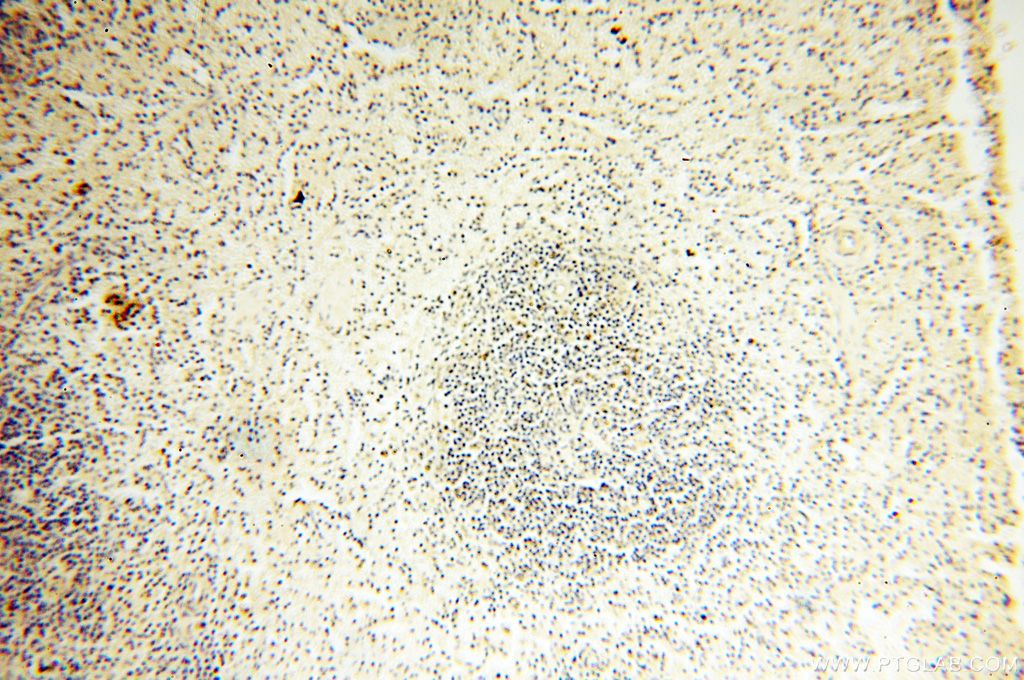
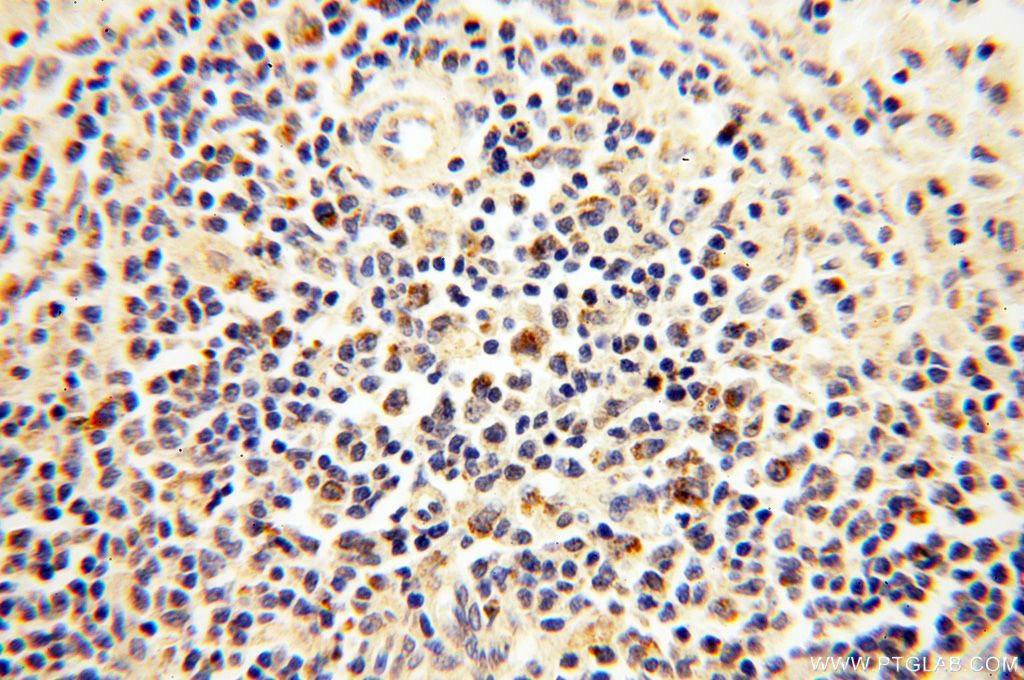
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Milzgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
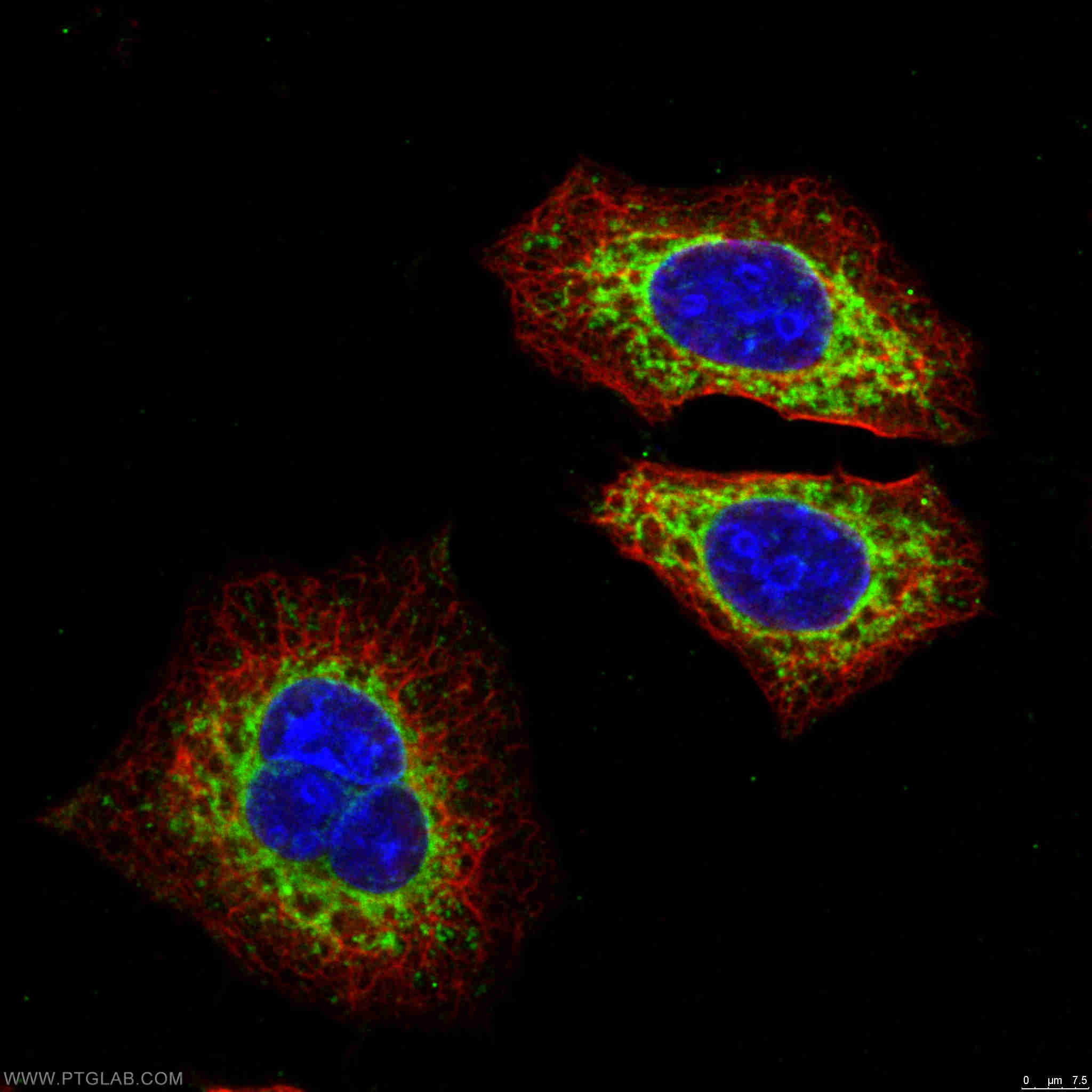
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | HepG2-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 11 publications below |
Produktinformation
17006-1-AP bindet in WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA MRPS15 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | MRPS15 fusion protein Ag10702 |
| Vollständiger Name | mitochondrial ribosomal protein S15 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 257 aa, 30 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 25-30 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC031336 |
| Gene symbol | MRPS15 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 64960 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
MRPS15, also named as RPMS15 or DC37, is a 257 amino acid protein, which belongs to the ribosomal protein S15P family. MRPS15 localizes in the Mitochondrion and is a component of the mitochondrial ribosome small subunit (28S) which comprises a 12S rRNA and about 30 distinct proteins. MRPS15 is involved into the mitochondrial proteins biosynthesis and ribosomal biogenesis.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for MRPS15 antibody 17006-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for MRPS15 antibody 17006-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for MRPS15 antibody 17006-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for MRPS15 antibody 17006-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab Initial steps in RNA processing and ribosome assembly occur at mitochondrial DNA nucleoids. | ||
Hum Mol Genet Mutations in the MRPS28 gene encoding the small mitoribosomal subunit protein bS1m in a patient with intrauterine growth retardation, craniofacial dysmorphism and multisystemic involvement. | ||
J Biol Chem Mitochondrial rRNA Methyltransferase Family Members are Positioned to Modify Nascent rRNA in Foci Near the mtDNA Nucleoid. |