MEF2C Polyklonaler Antikörper
MEF2C Polyklonal Antikörper für IF, IHC, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ChIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 18290-1-AP
Synonyme
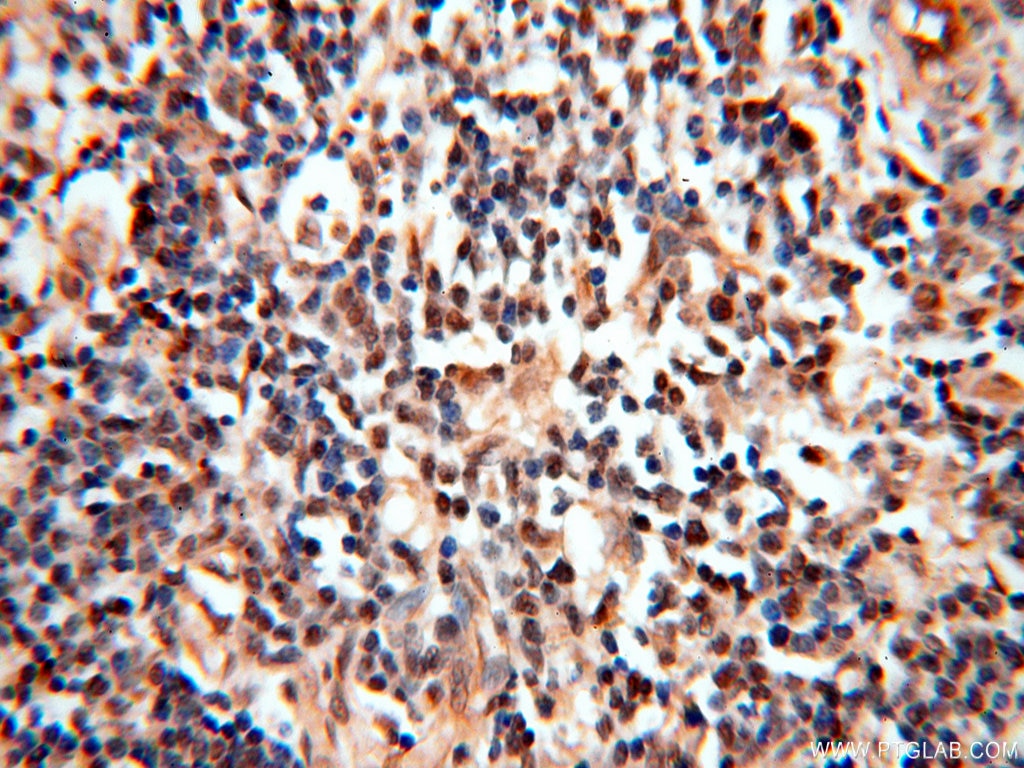
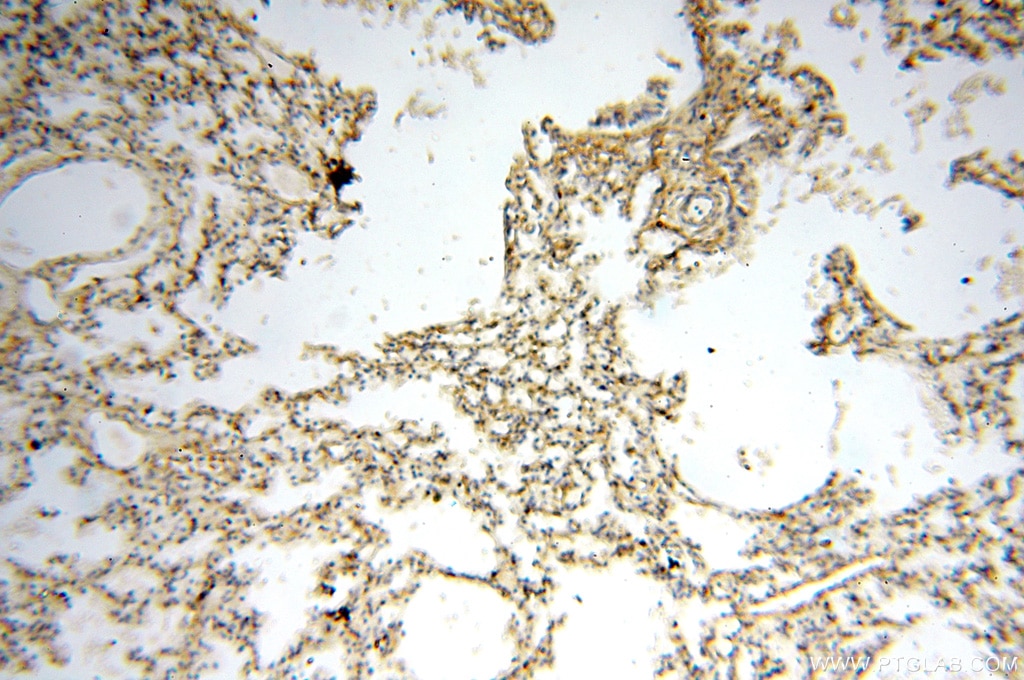
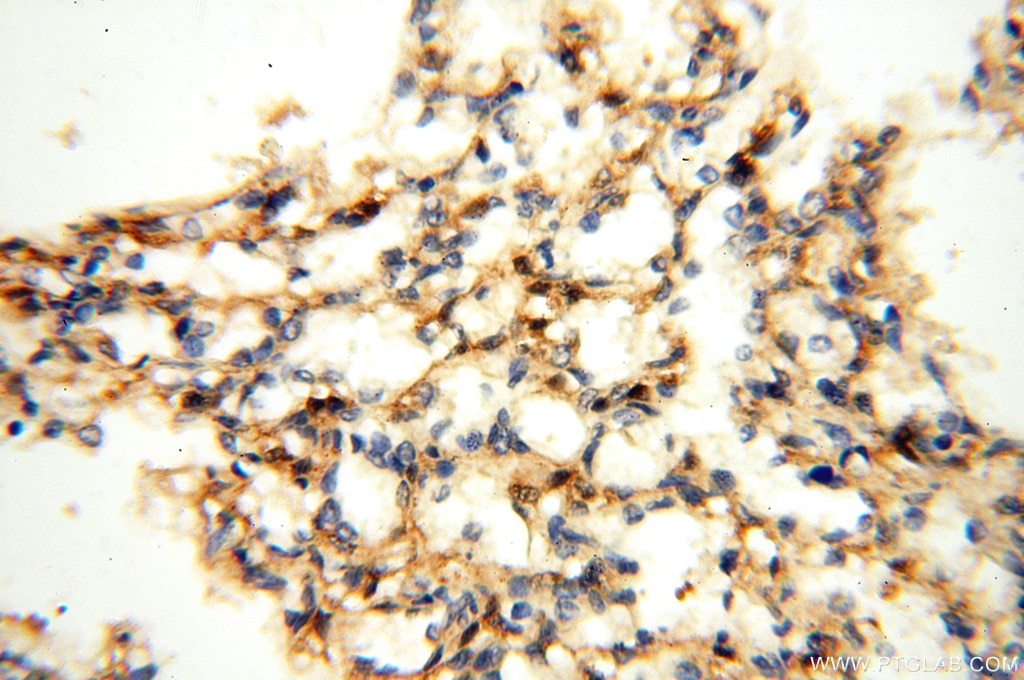
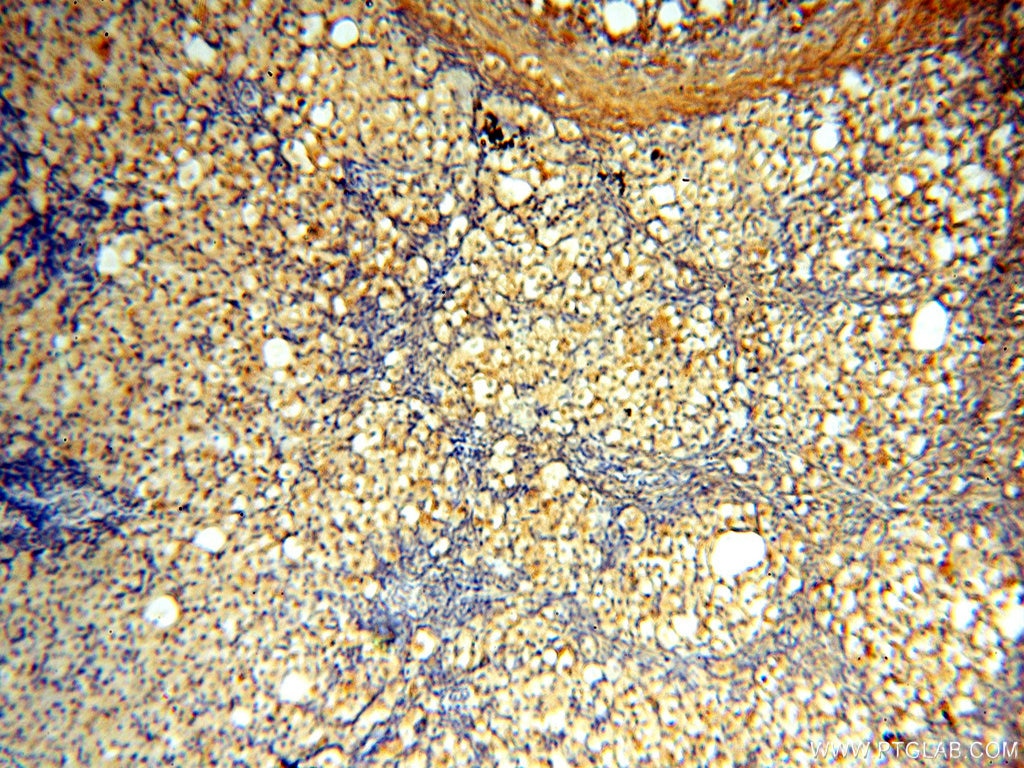
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
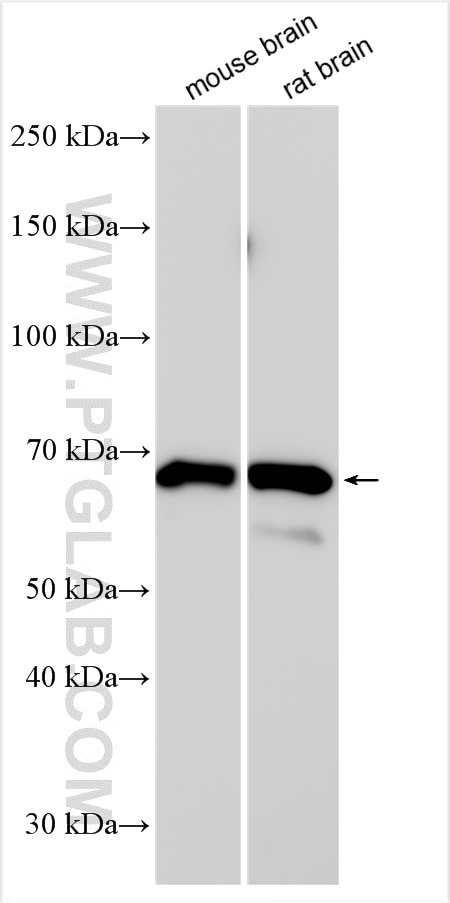
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Maushirngewebe, Rattenhirngewebe |
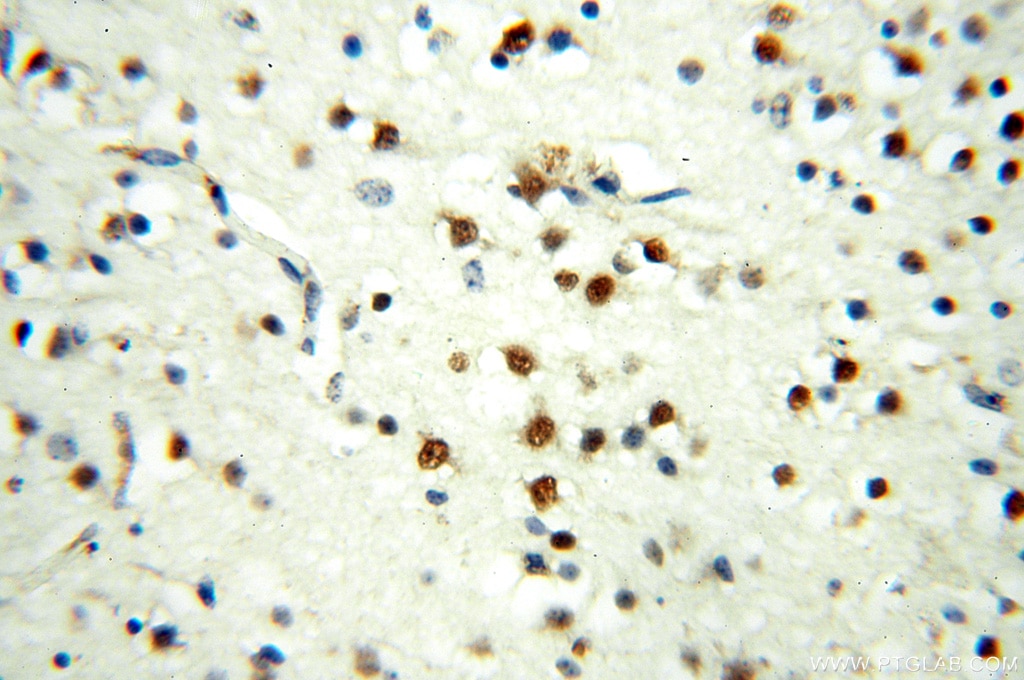
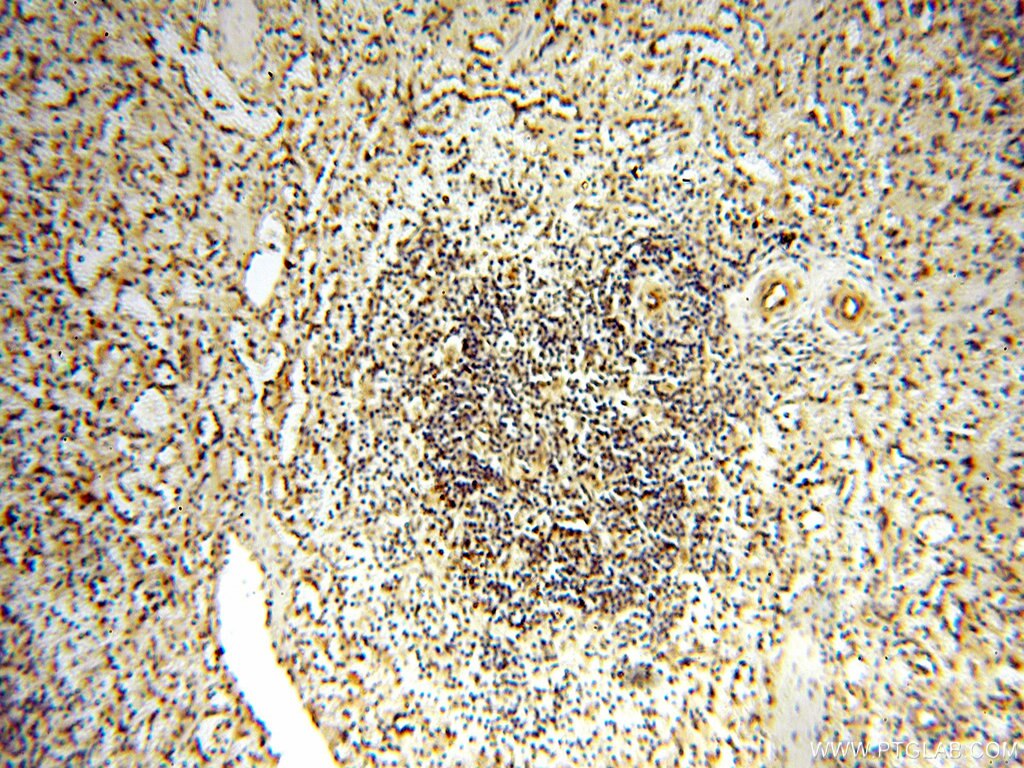
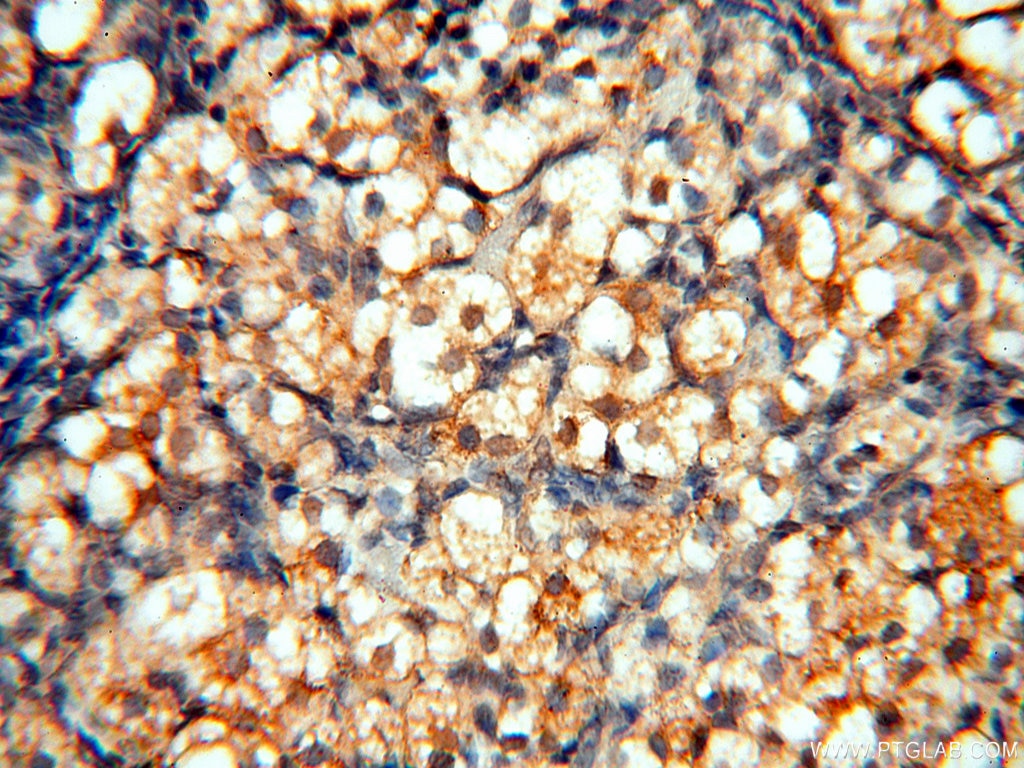
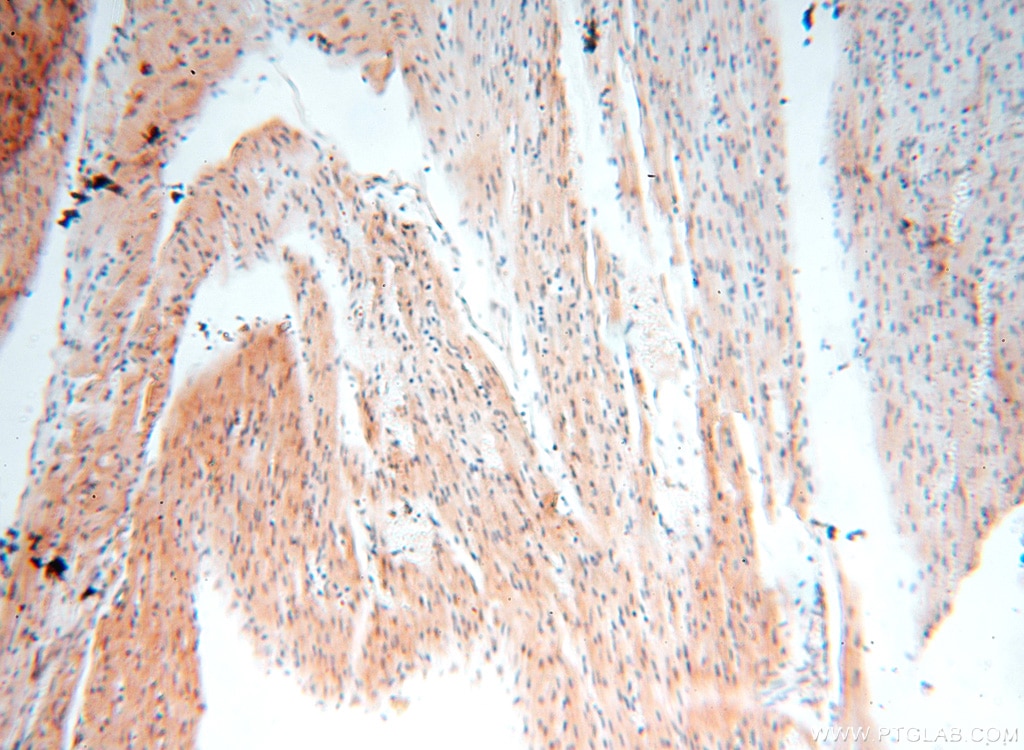
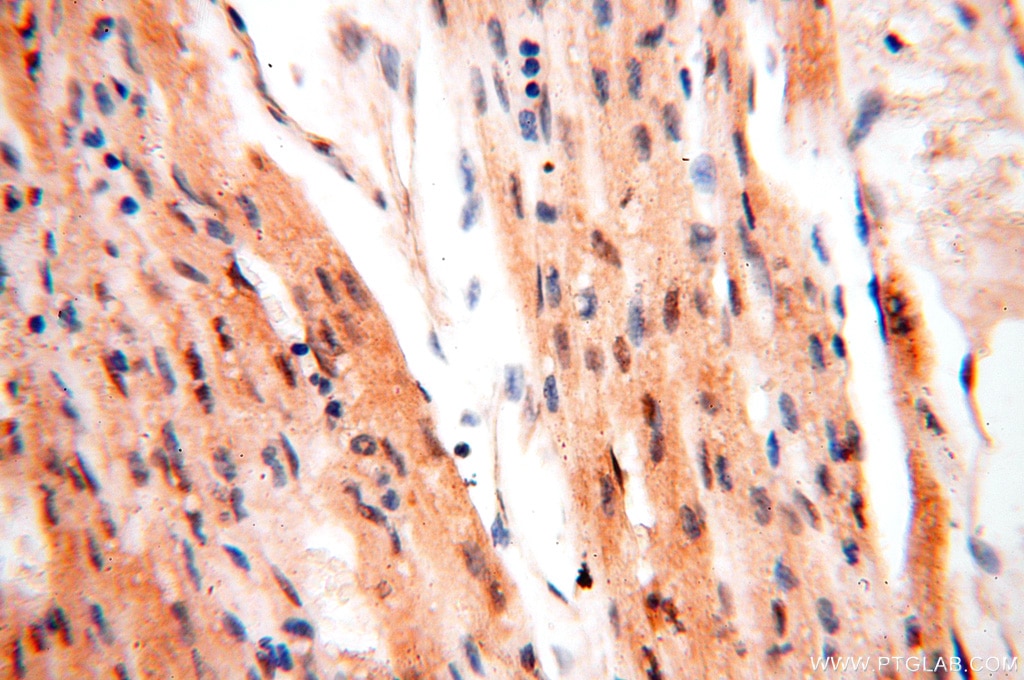
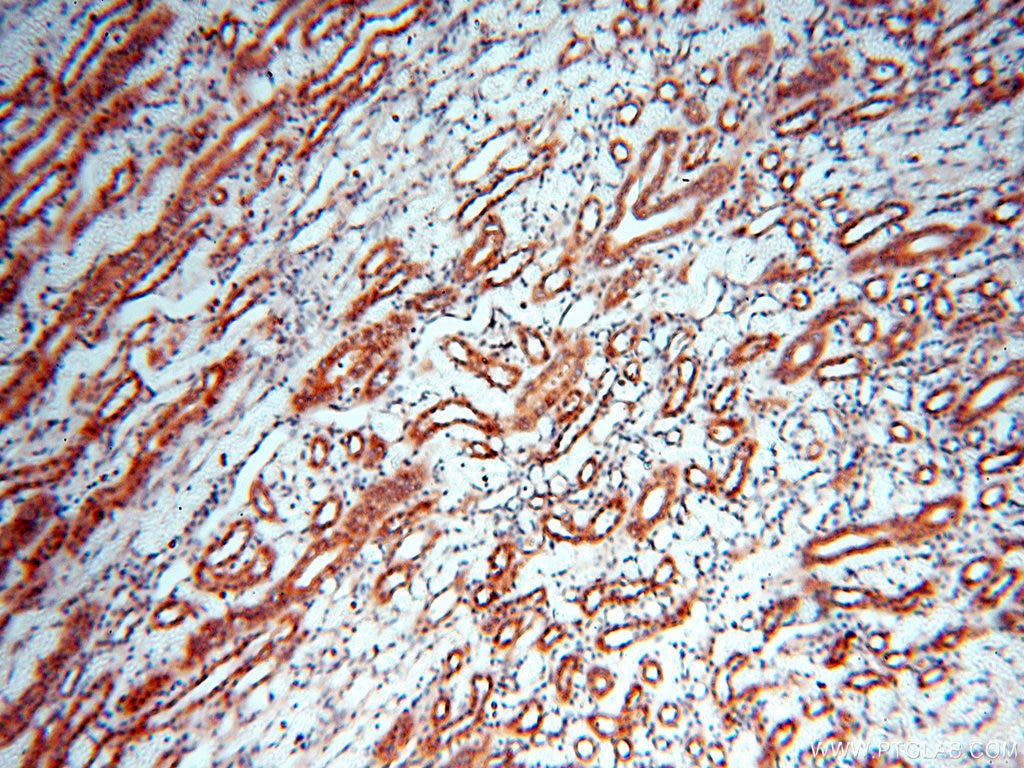
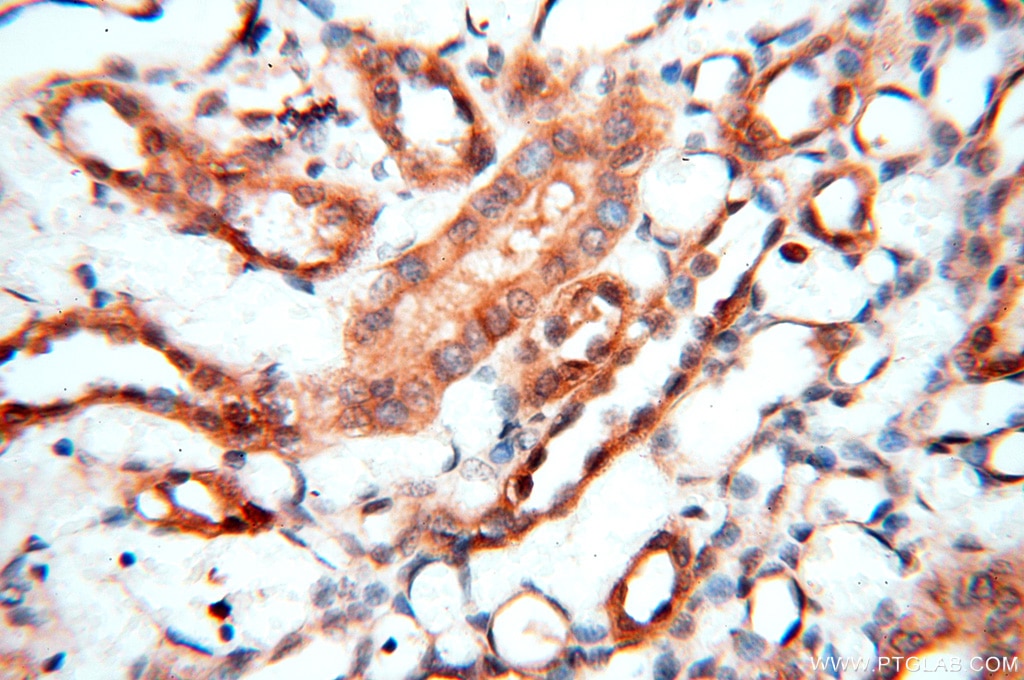
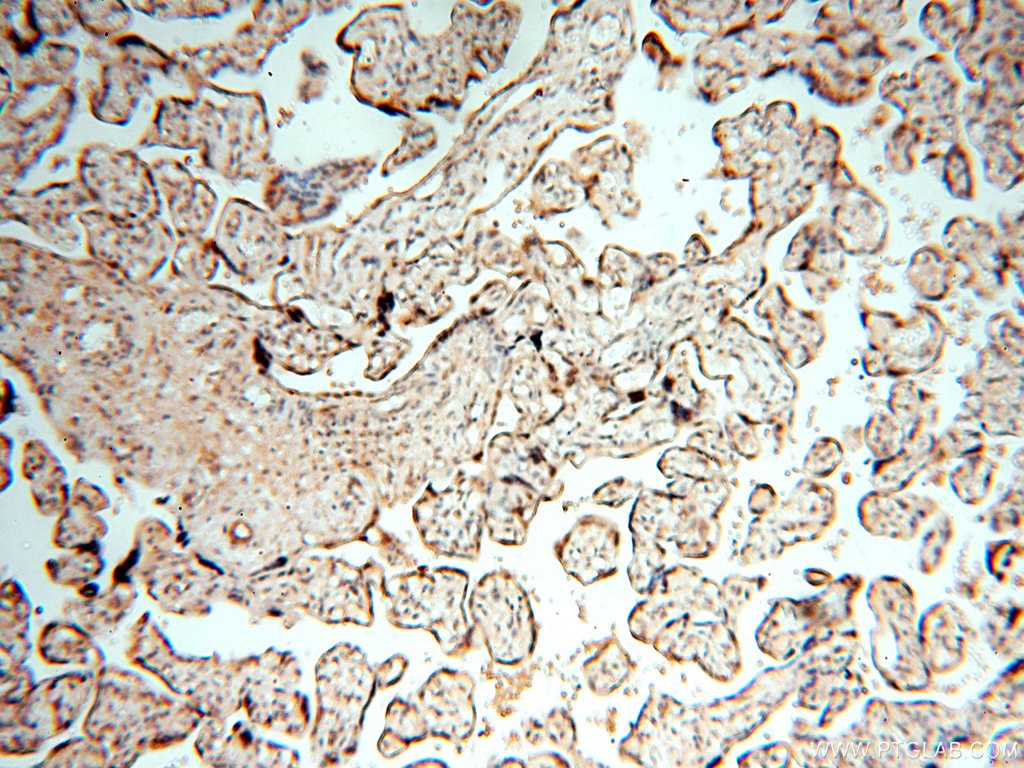
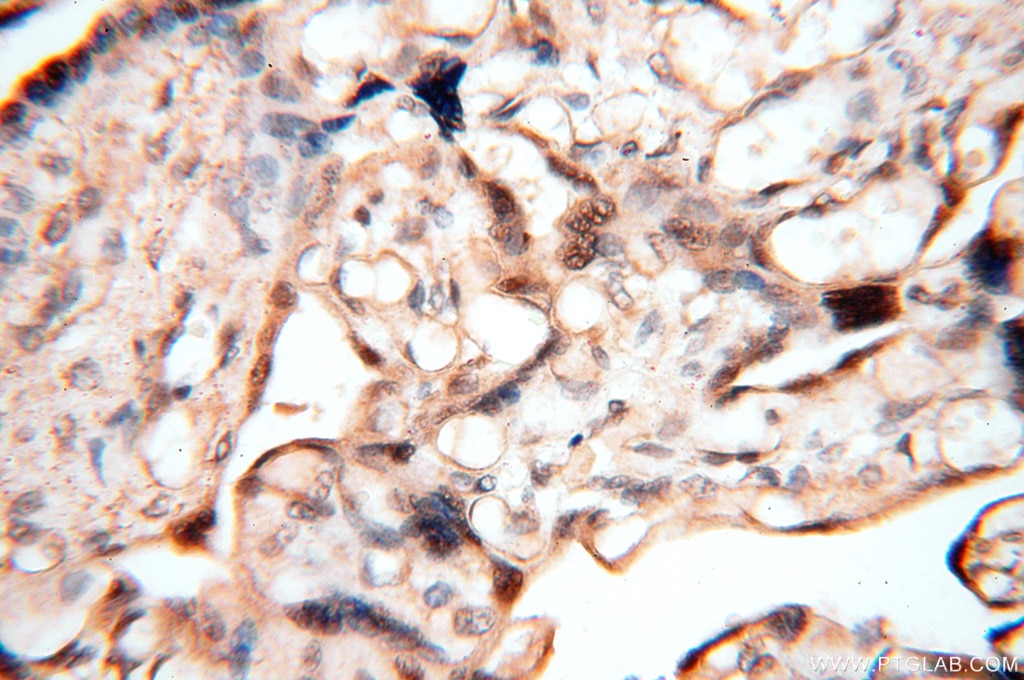
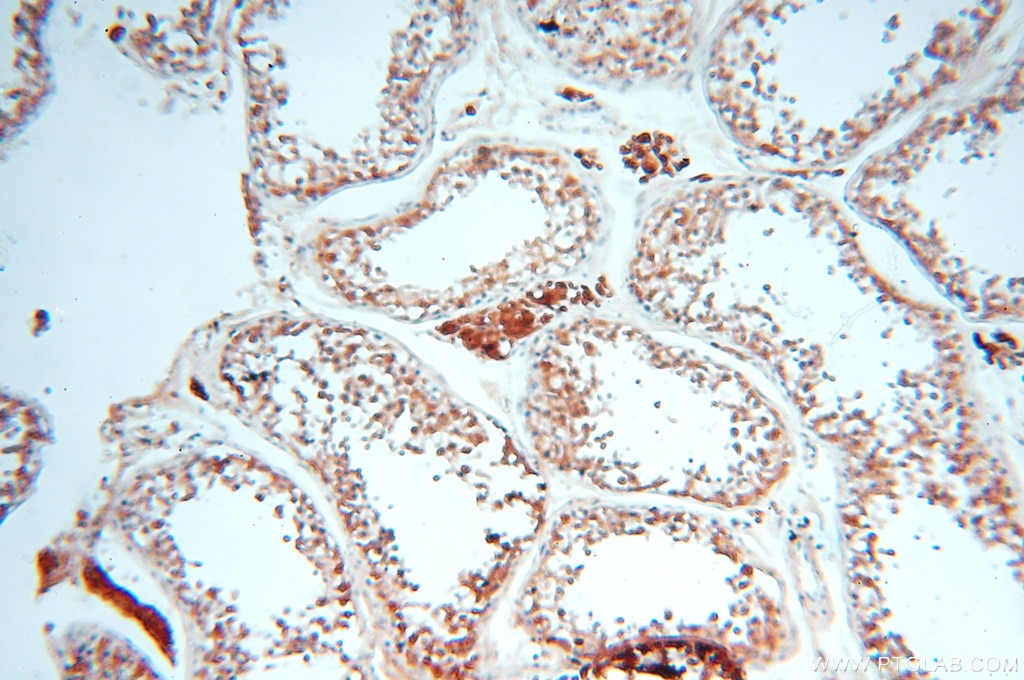
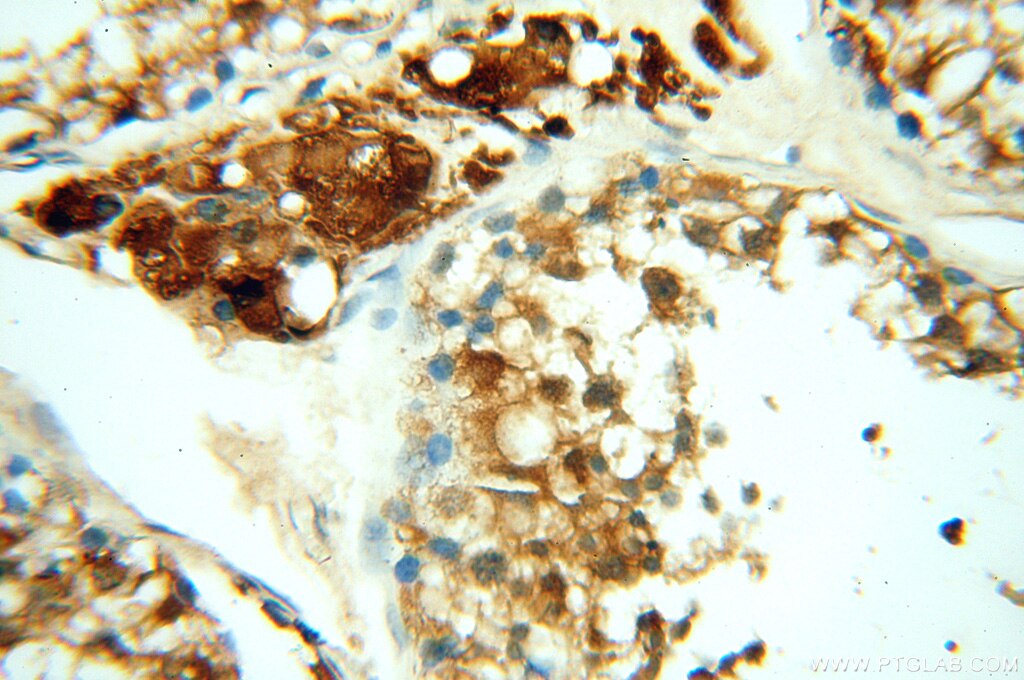
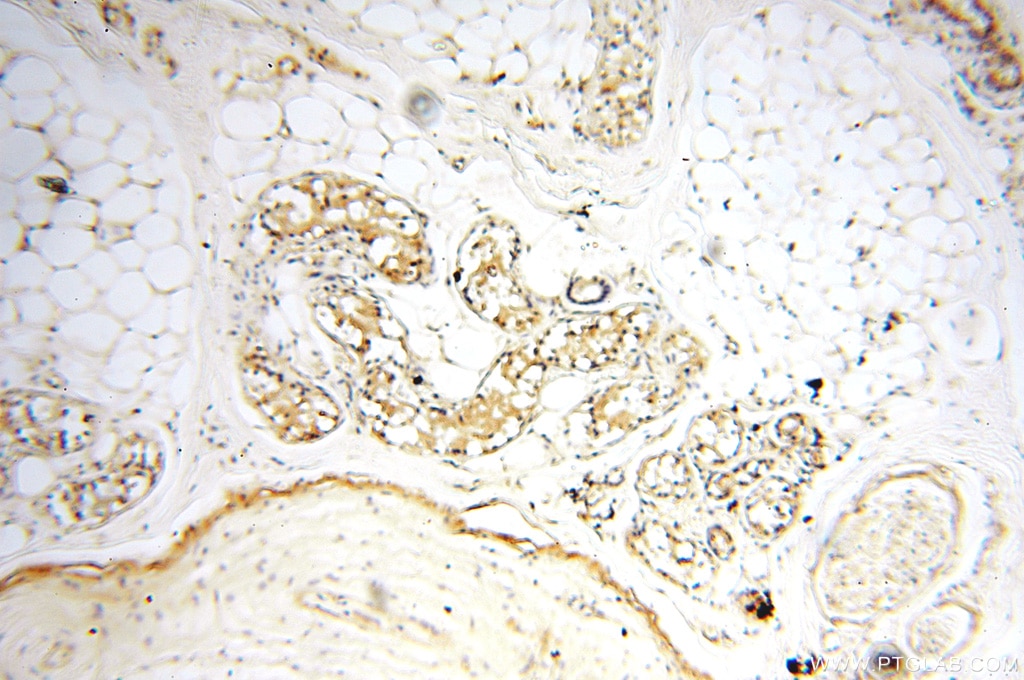
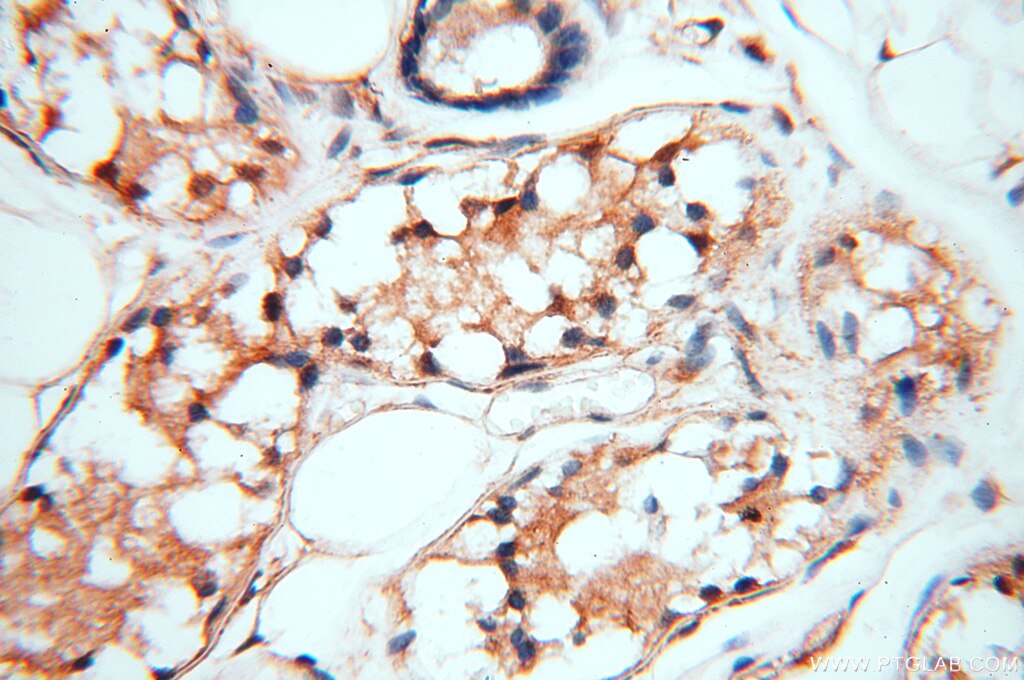
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Hirngewebe, humanes Eierstockgewebe, humanes Hautgewebe, humanes Herzgewebe, humanes Hodengewebe, humanes Lungengewebe, humanes Milzgewebe, humanes Nierengewebe, humanes Plazenta-Gewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
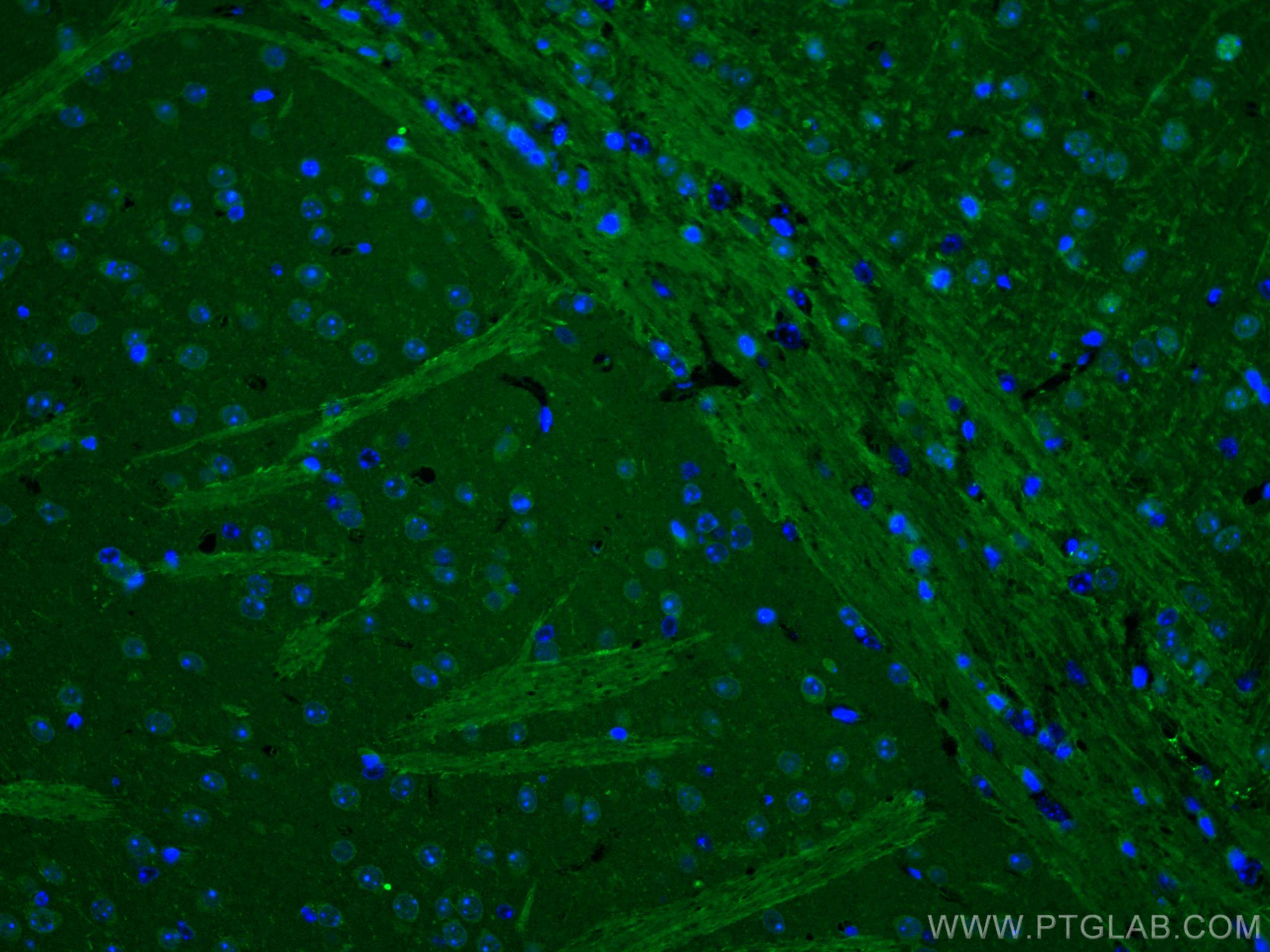
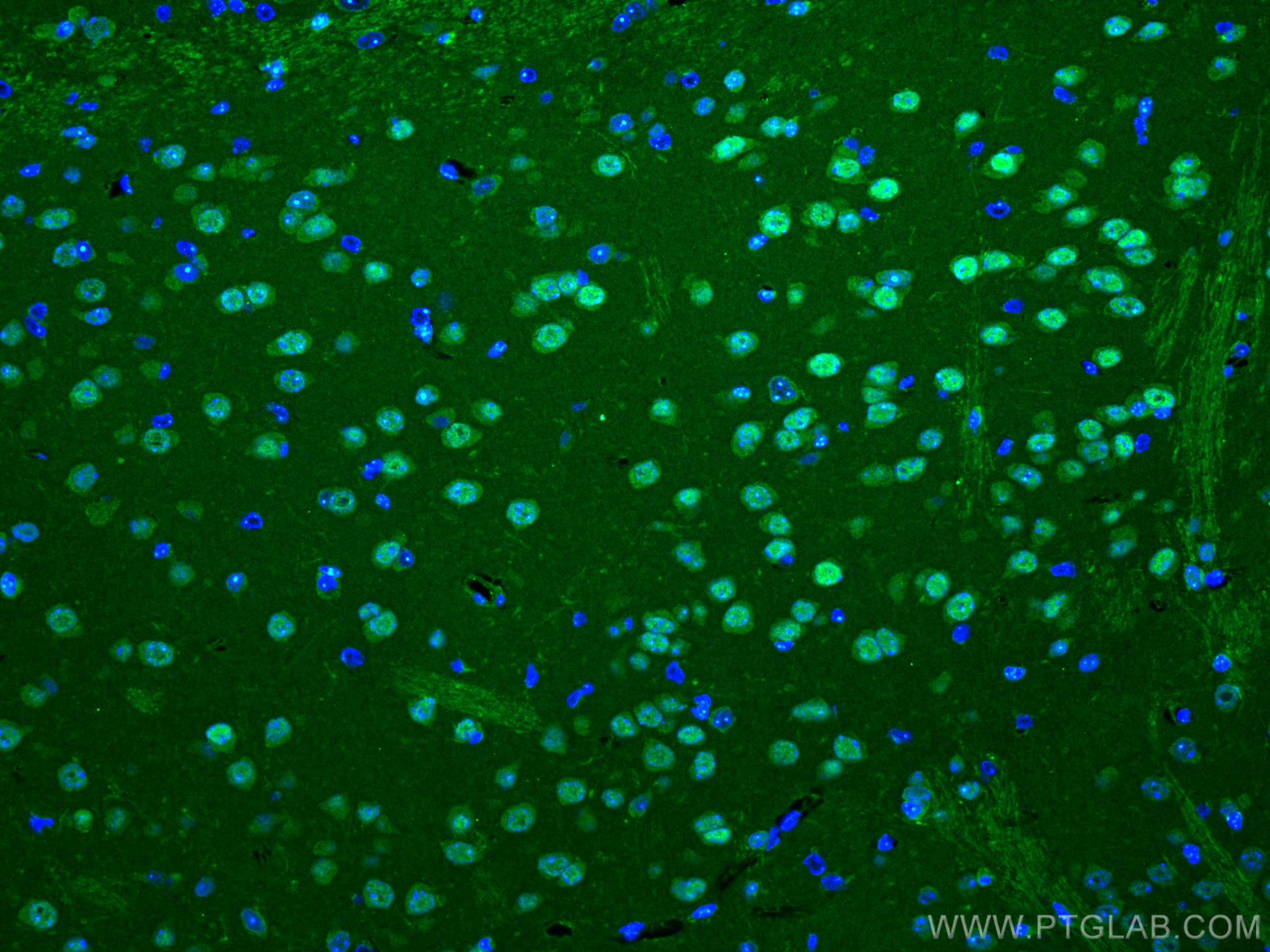
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | Maushirngewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
18290-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ChIP, ELISA MEF2C und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | myocyte enhancer factor 2C |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 51 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 45-70 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | NM_002397 |
| Gene symbol | MEF2C |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4208 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
MEF2C belongs to the MEF2 family. It is a transcription activator which binds specifically to the MEF2 element present in the regulatory regions of many muscle-specific genes. MEF2C controls cardiac morphogenesis and myogenesis, and is also involved in vascular development[PMID: 20221419]. It plays an essential role in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory by suppressing the number of excitatory synapses and thus regulating basal and evoked synaptic transmission[PMID:18599438]. It is crucial for normal neuronal development, distribution, and electrical activity in the neocortex and is necessary for proper development of megakaryocytes and platelets and for bone marrow B lymphopoiesis[PMID: 21666133]. This protein is required for B-cell survival and proliferation in response to BCR stimulation, efficient IgG1 antibody responses to T-cell-dependent antigens and for normal induction of germinal center B cells. It may also be involved in neurogenesis and in the development of cortical architecture. MEF2C exists some isoforms with MV 50-52 kDa, 47 kDa, and 45 kDa, but modified MEF2C is about 55-66 kDa.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for MEF2C antibody 18290-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for MEF2C antibody 18290-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for MEF2C antibody 18290-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nature Genetic and epigenetic coordination of cortical interneuron development.
| ||
Biol Reprod Integrated microRNA and mRNA network analysis of the human myometrial transcriptome in the transition from quiescence to labor. | ||
Cell Rep Chromatin Environment and Cellular Context Specify Compensatory Activity of Paralogous MEF2 Transcription Factors. | ||
Cell Genom Single nucleus multiomics identifies ZEB1 and MAFB as candidate regulators of Alzheimer's disease-specific cis-regulatory elements |