MAP9 Polyklonaler Antikörper
MAP9 Polyklonal Antikörper für IF, WB,ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 26078-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
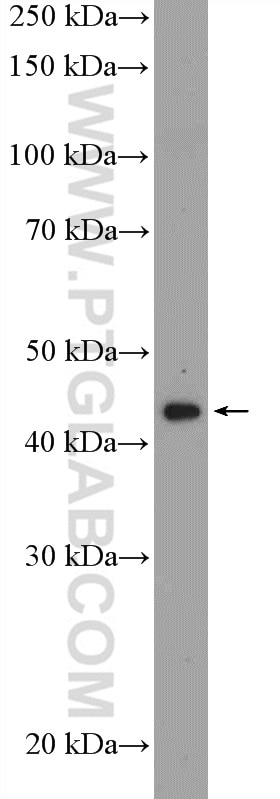
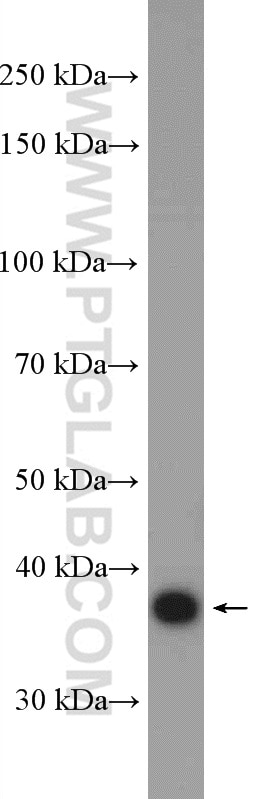
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | SH-SY5Y-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, K-562-Zellen |
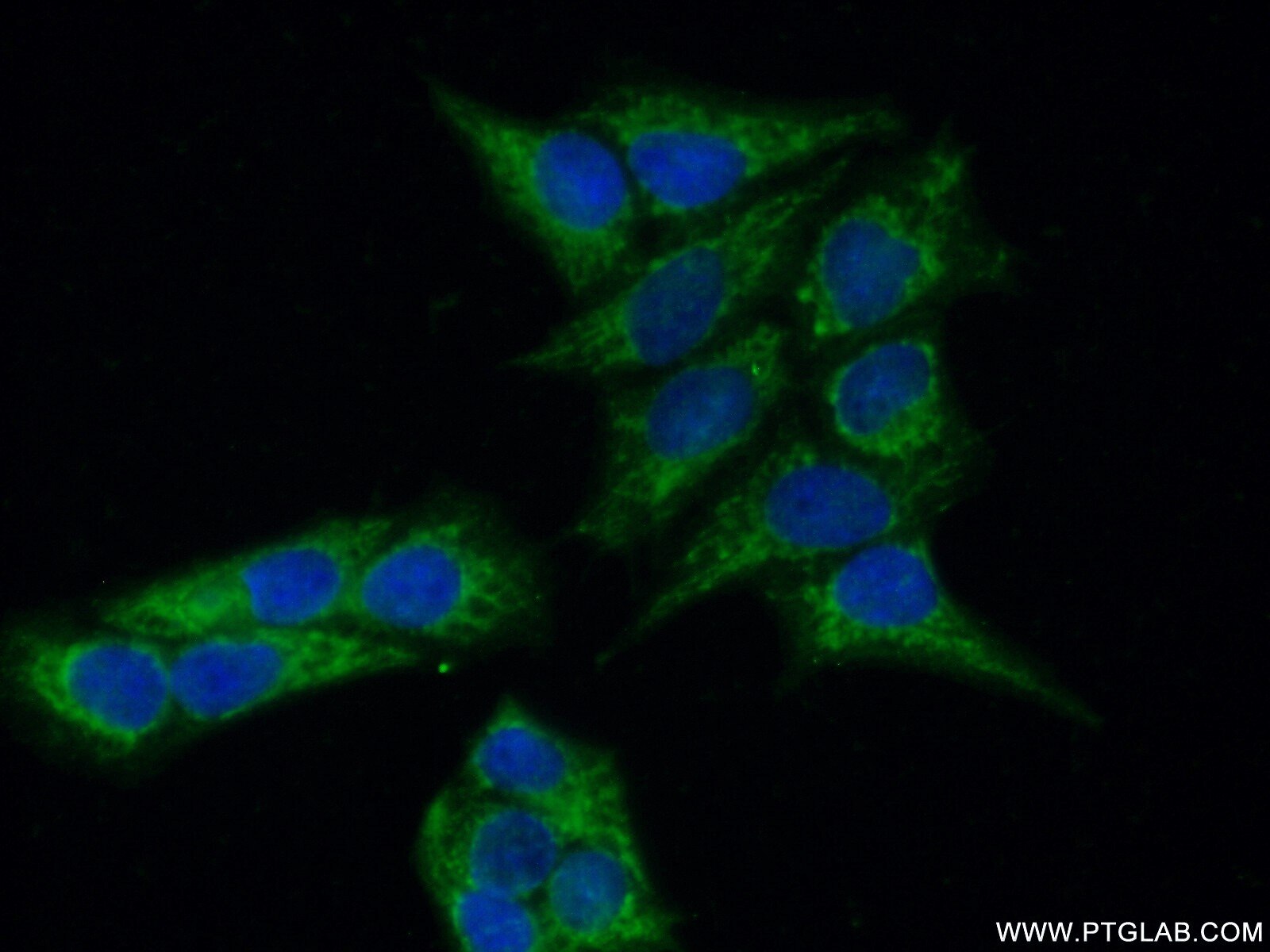
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | HeLa-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
26078-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA MAP9 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Hund |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | MAP9 fusion protein Ag23446 |
| Vollständiger Name | microtubule-associated protein 9 |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 38-42 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC146864 |
| Gene symbol | MAP9 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 79884 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for MAP9 antibody 26078-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for MAP9 antibody 26078-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Front Cell Neurosci Molecular characterization of MAP9 in the photoreceptor sensory cilia as a modifier in canine RPGRIP1-associated cone-rod dystrophy | ||