Cytokeratin 14 Monoklonaler Antikörper
Cytokeratin 14 Monoklonal Antikörper für IF, IHC, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG1
Getestete Reaktivität
Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
2G1E2
Kat-Nr. : 60320-1-Ig
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
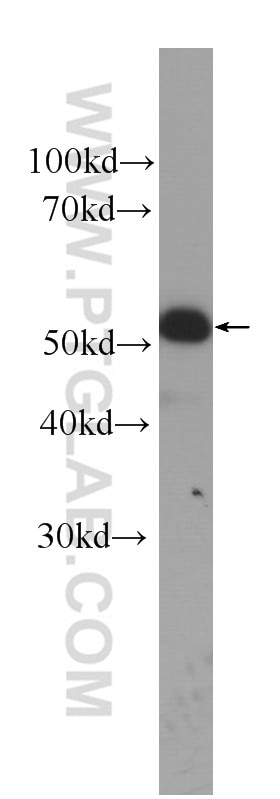
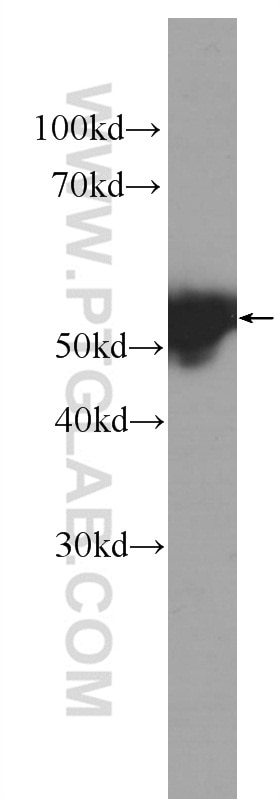
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | A431-Zellen, Maushautgewebe |
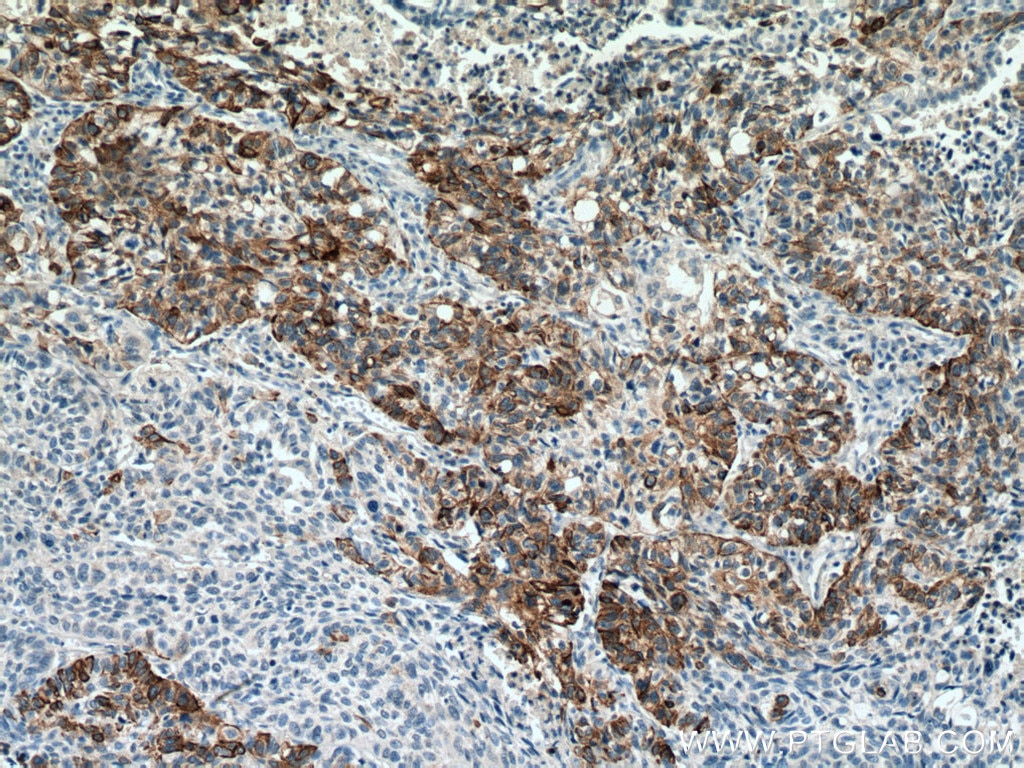
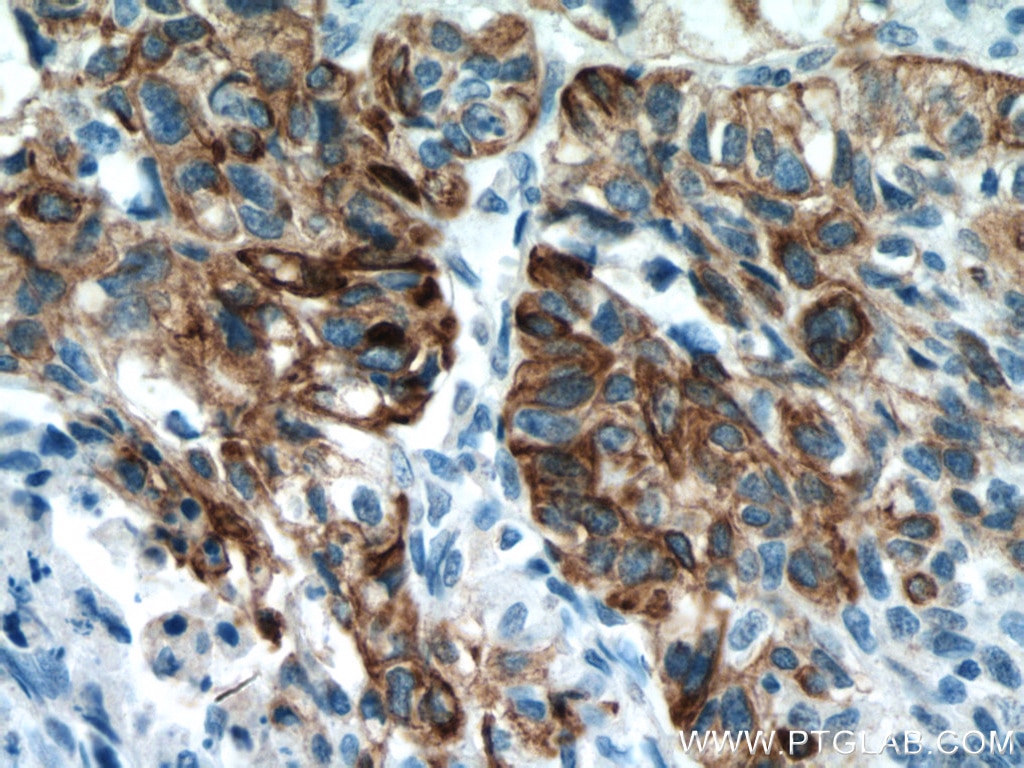
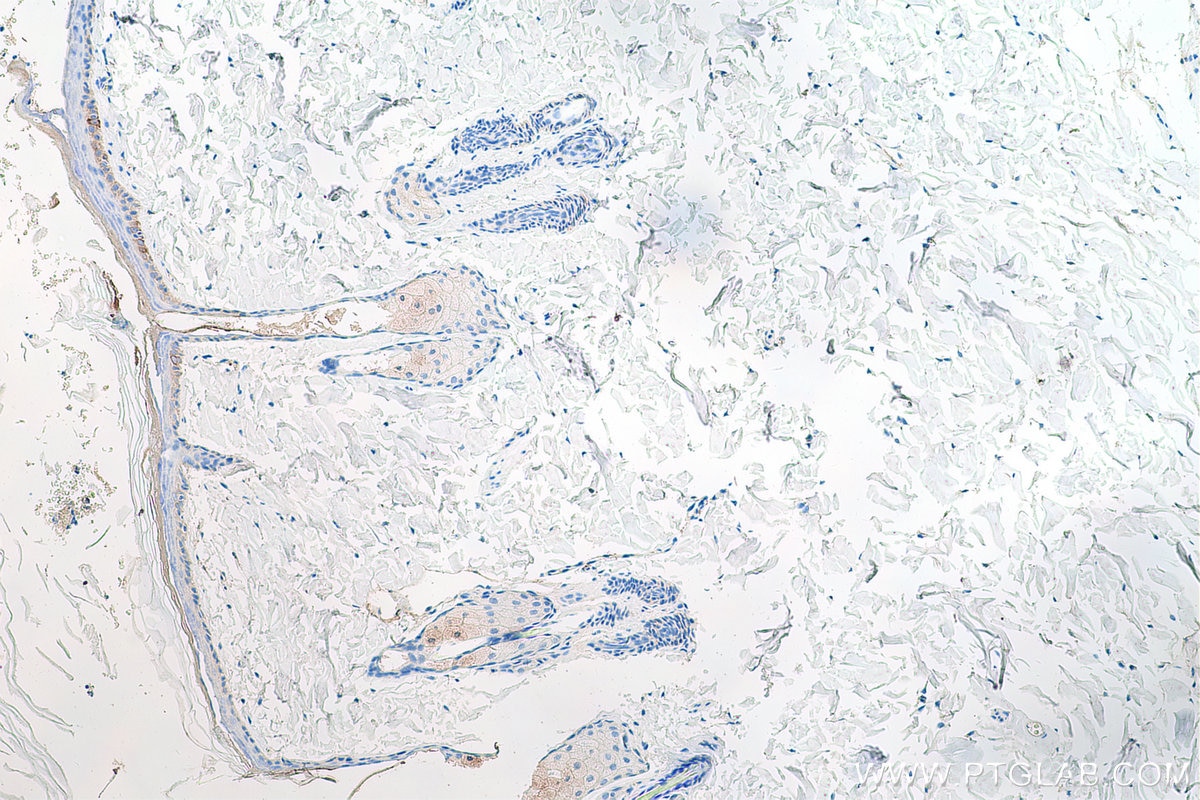
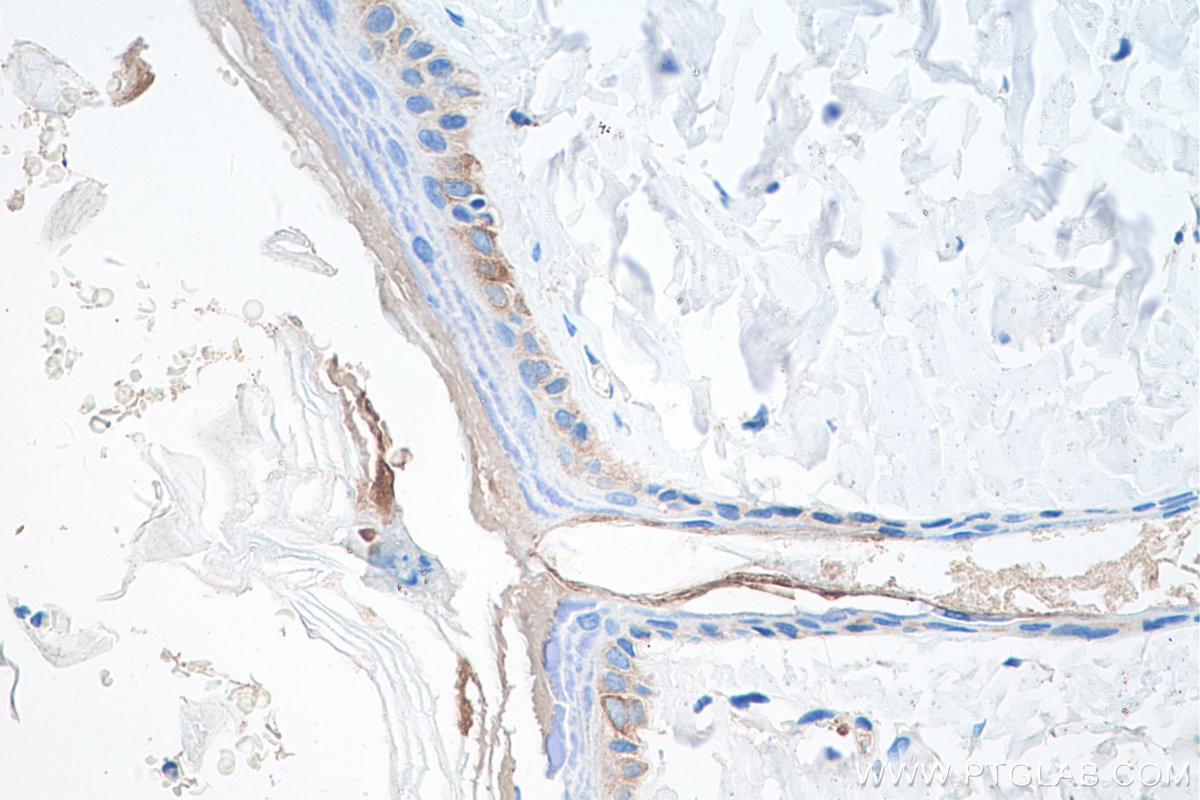
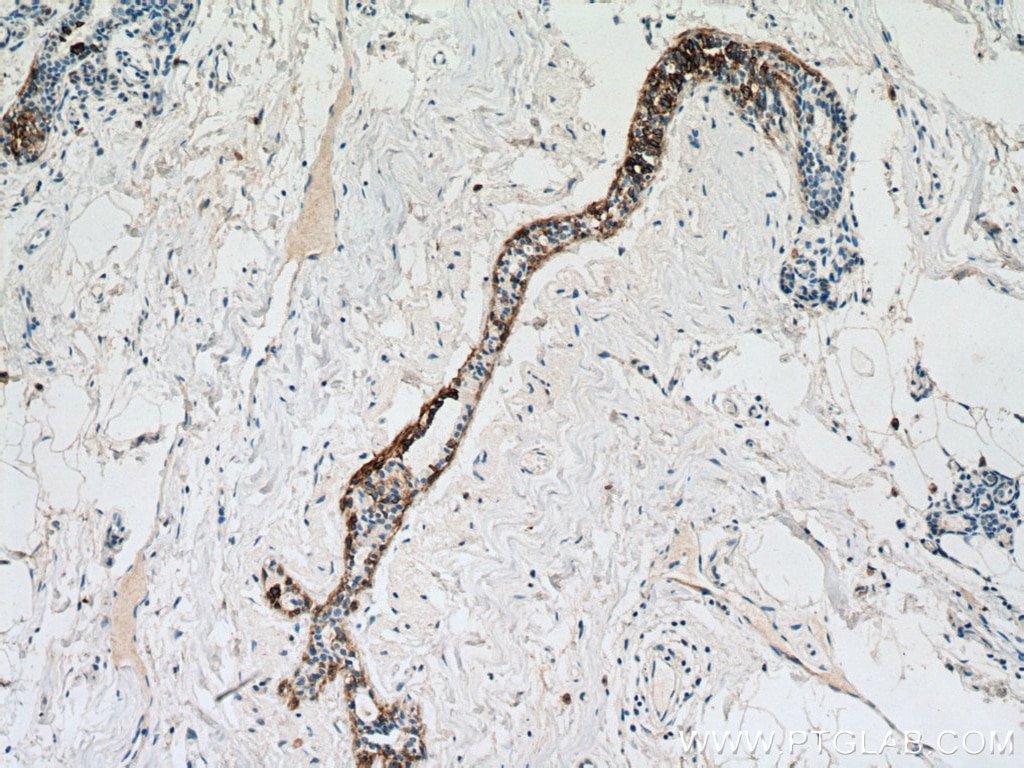
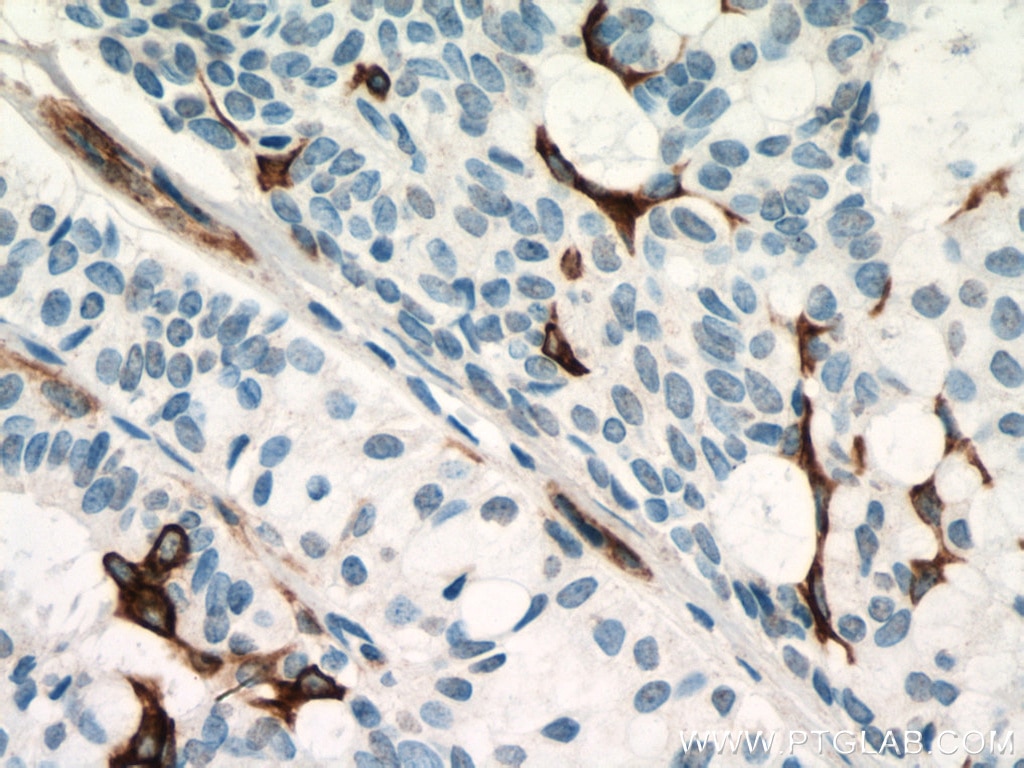
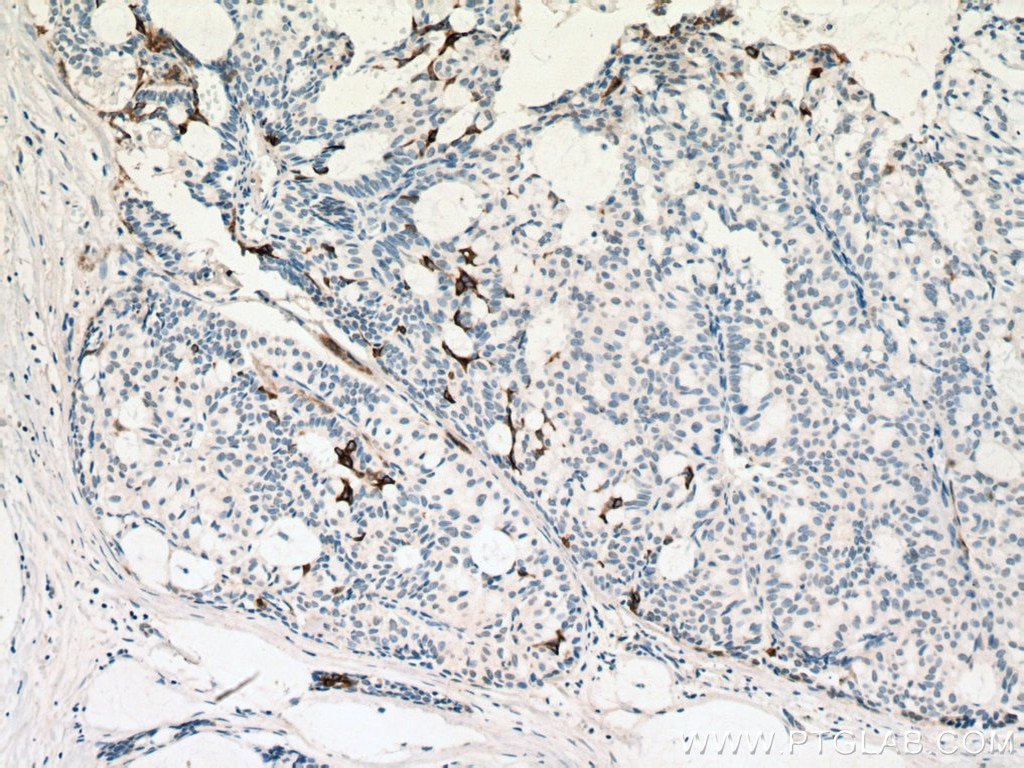
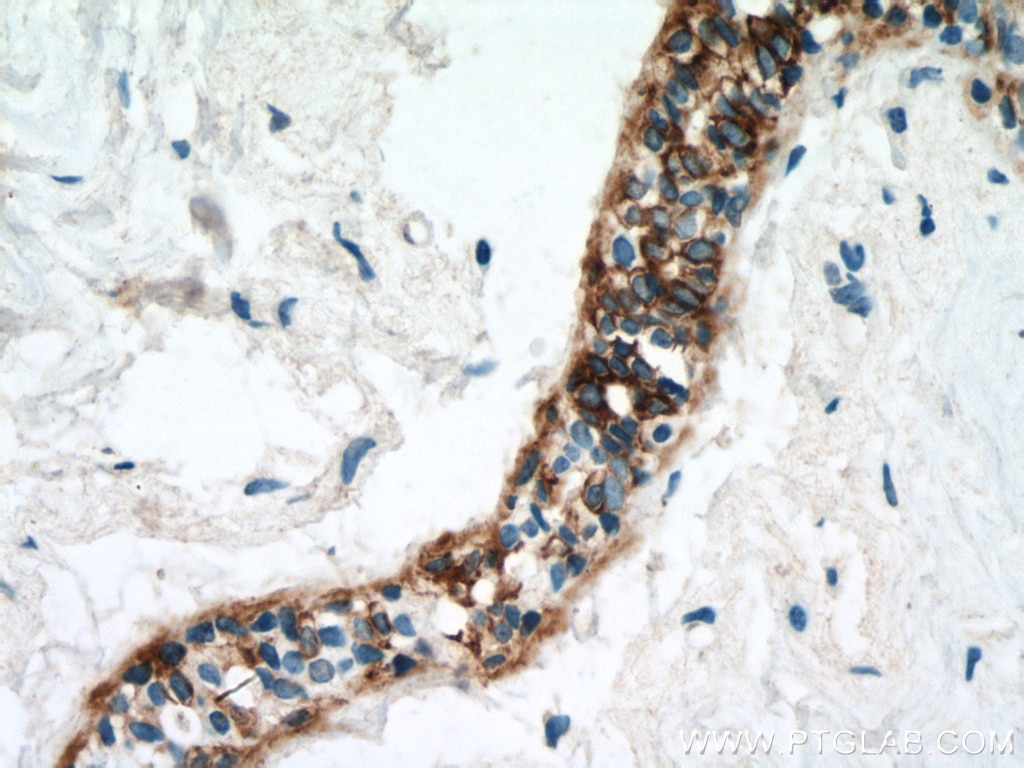
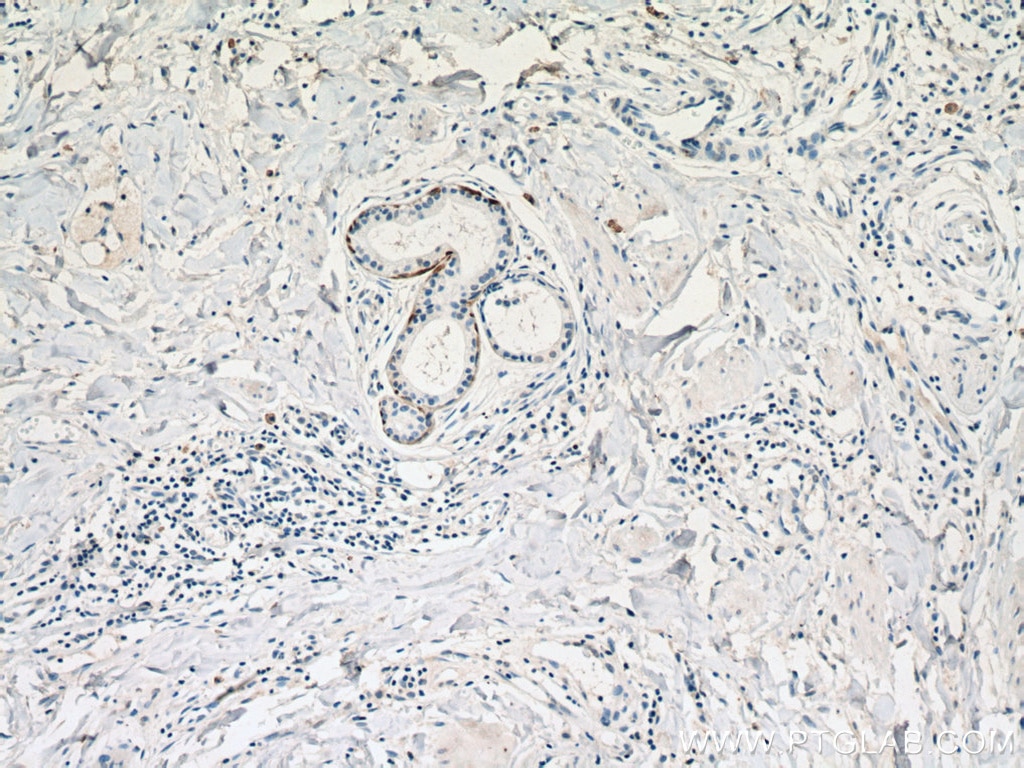
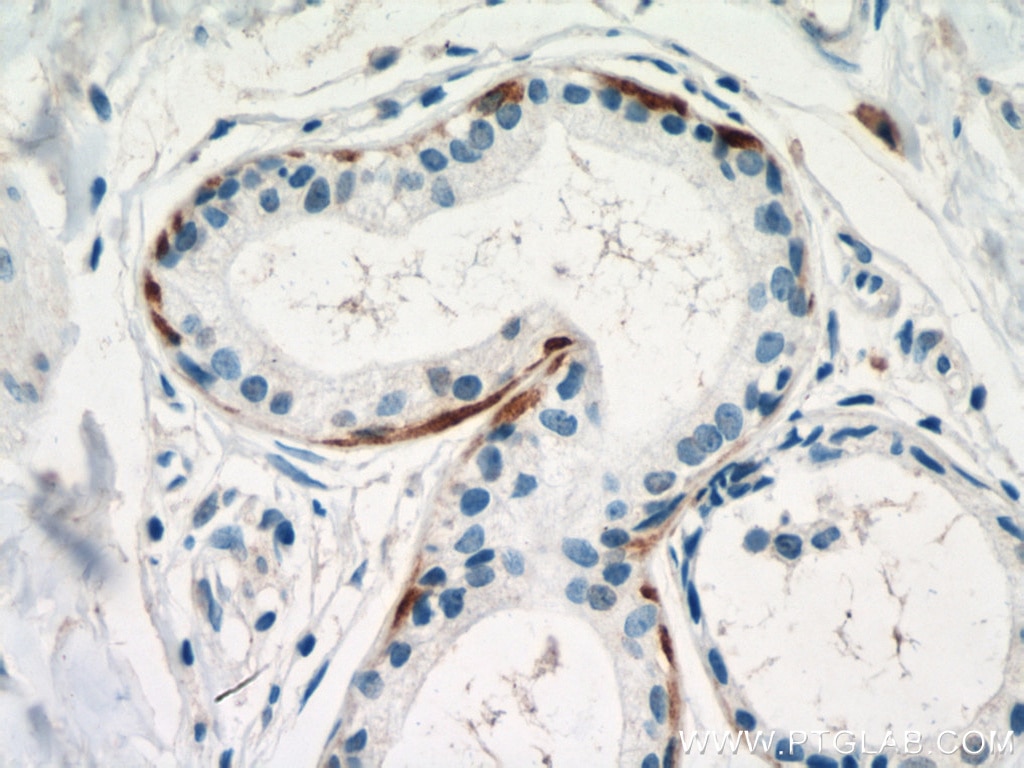
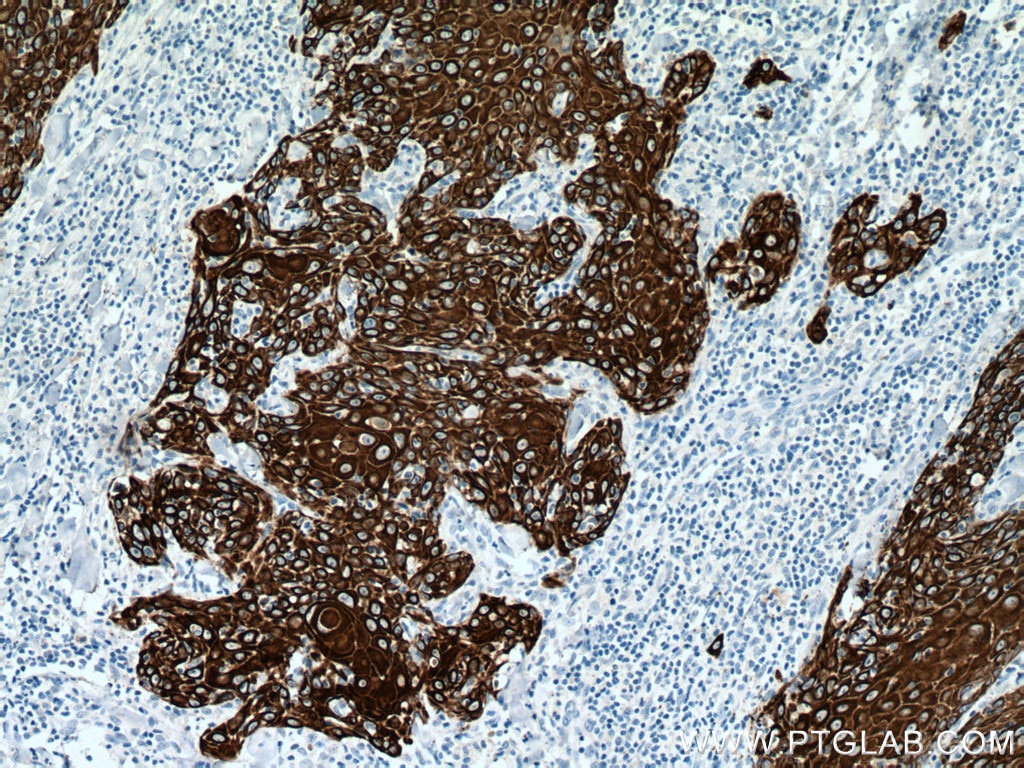
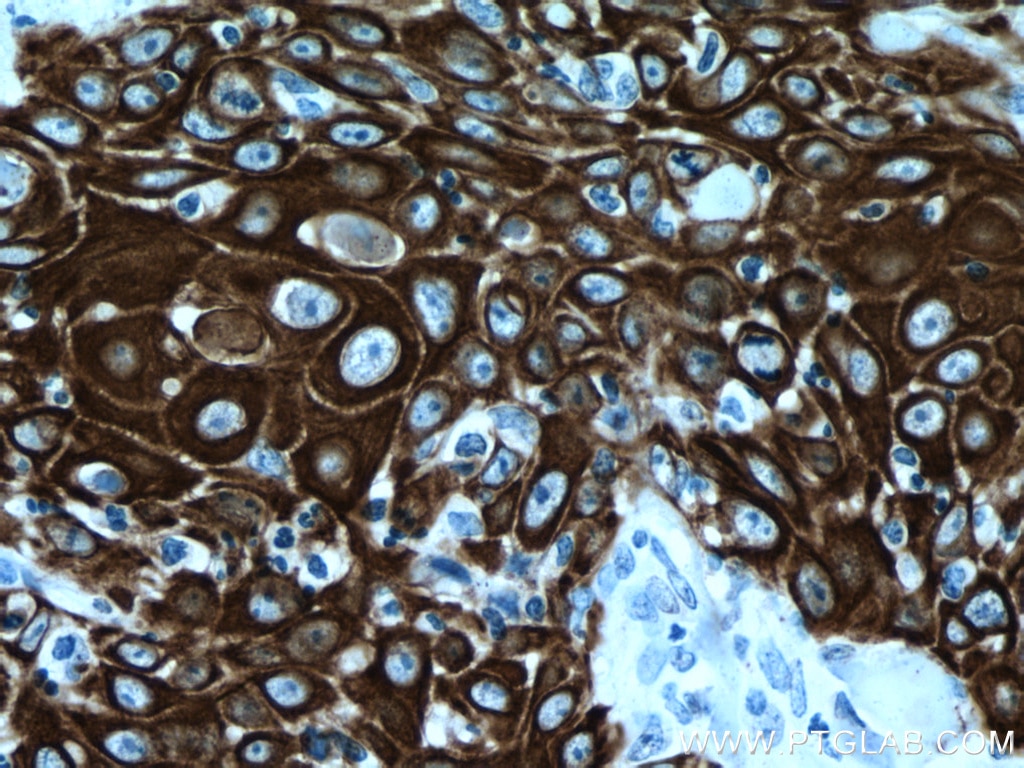
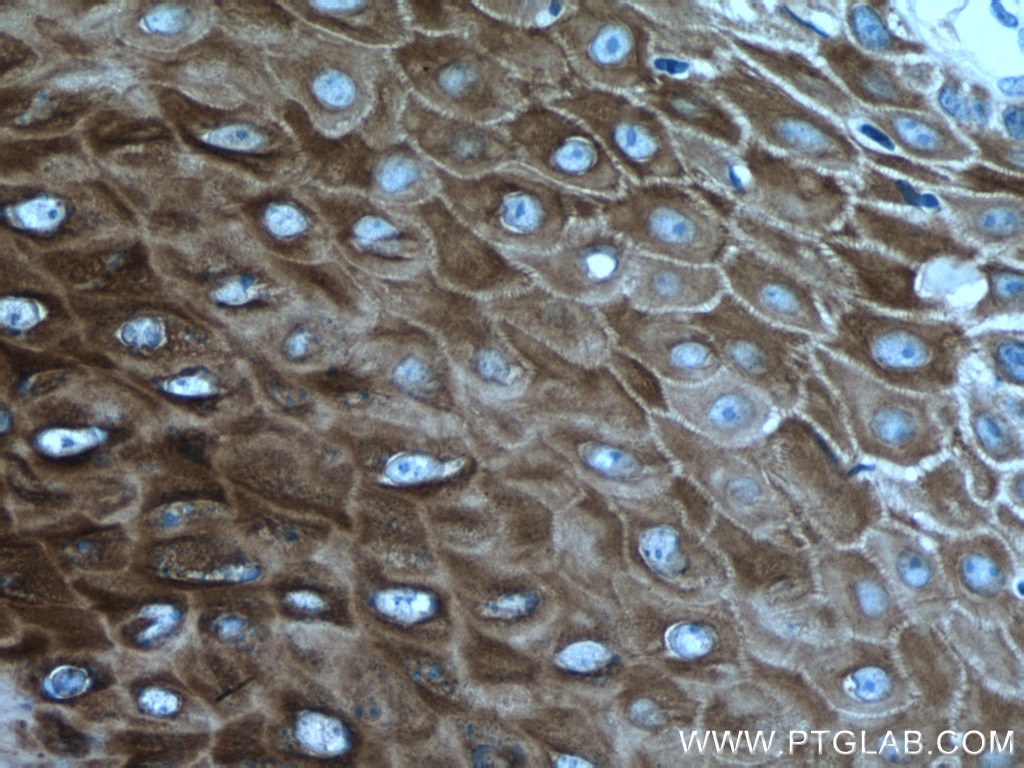
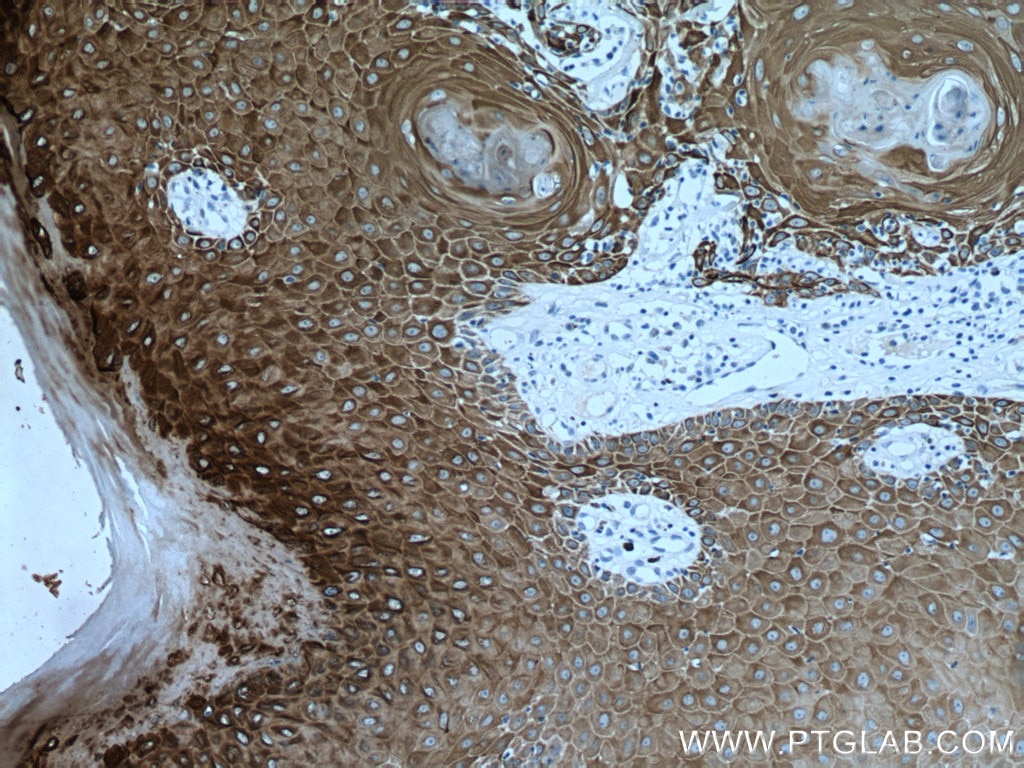
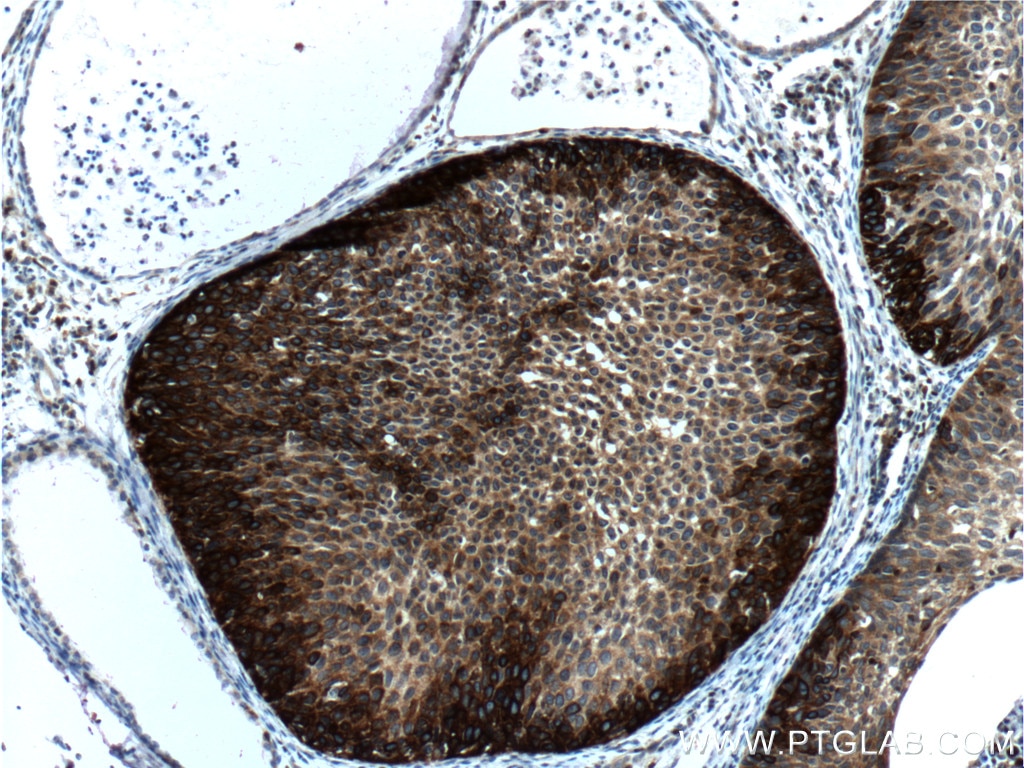
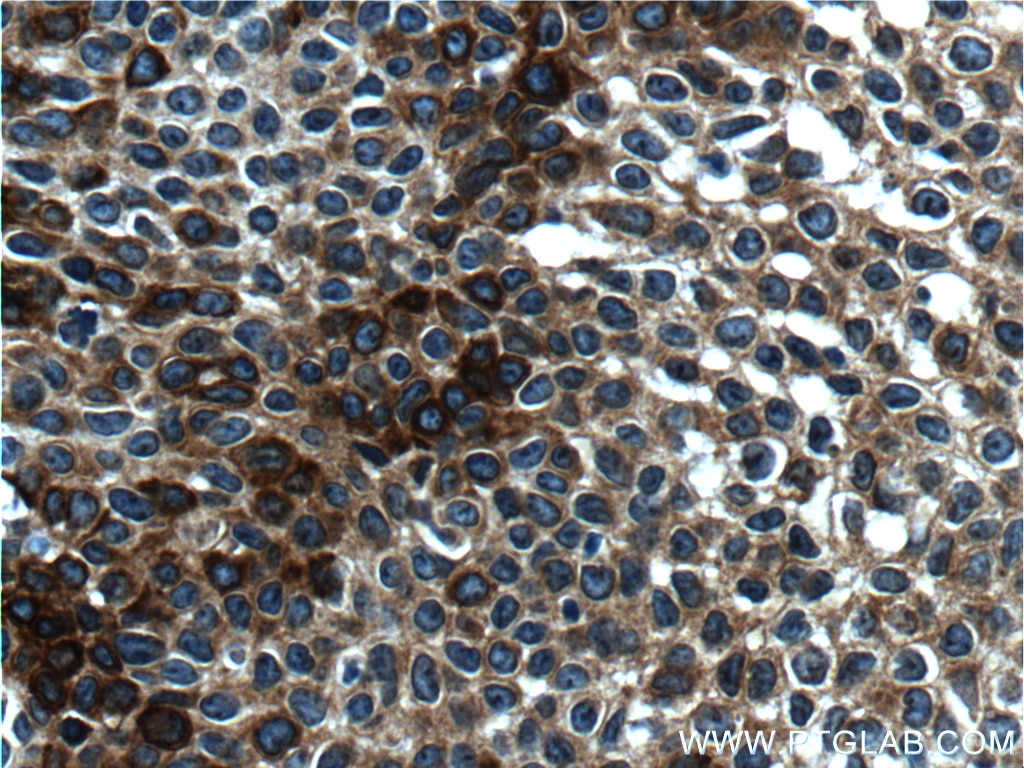
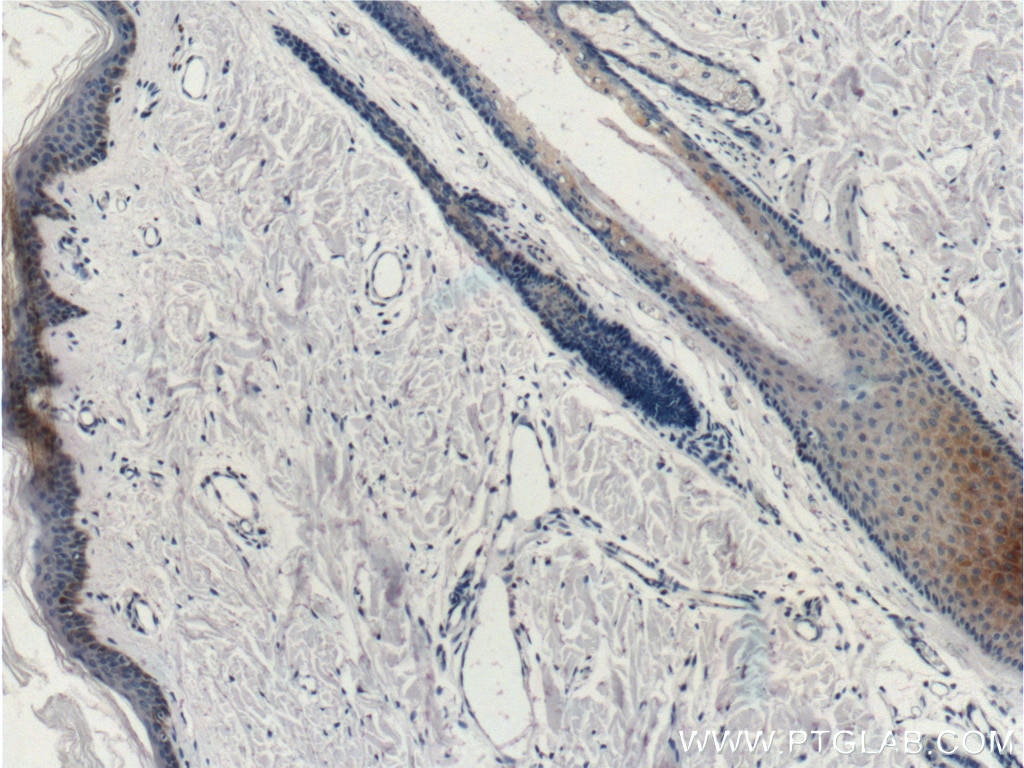
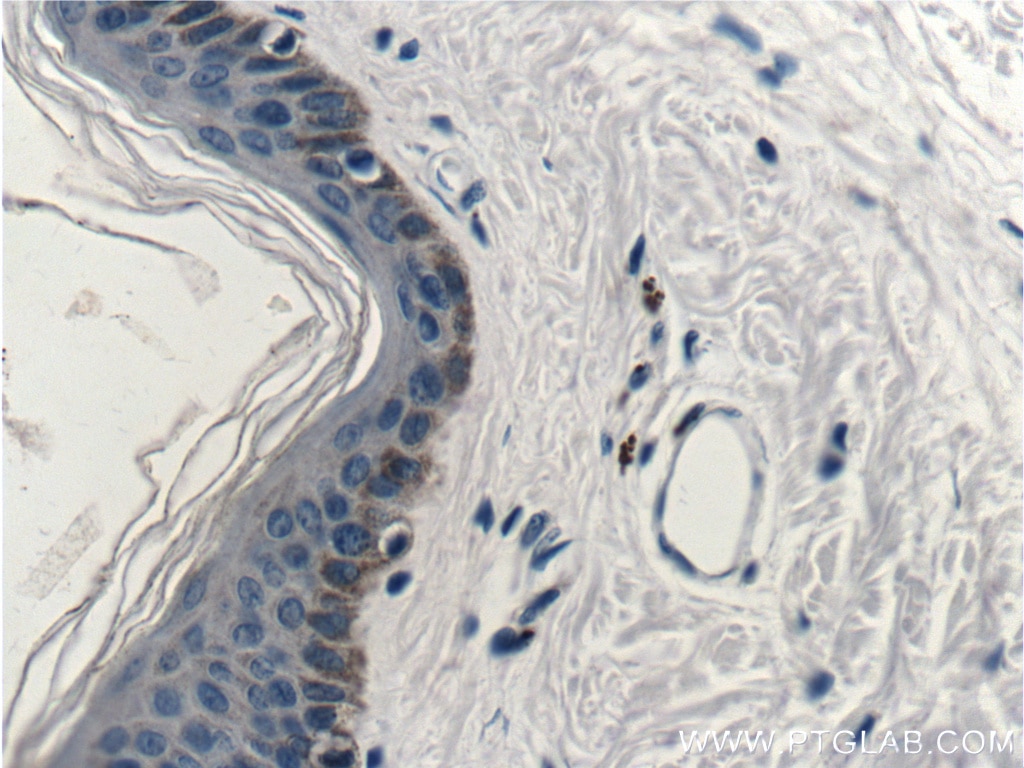
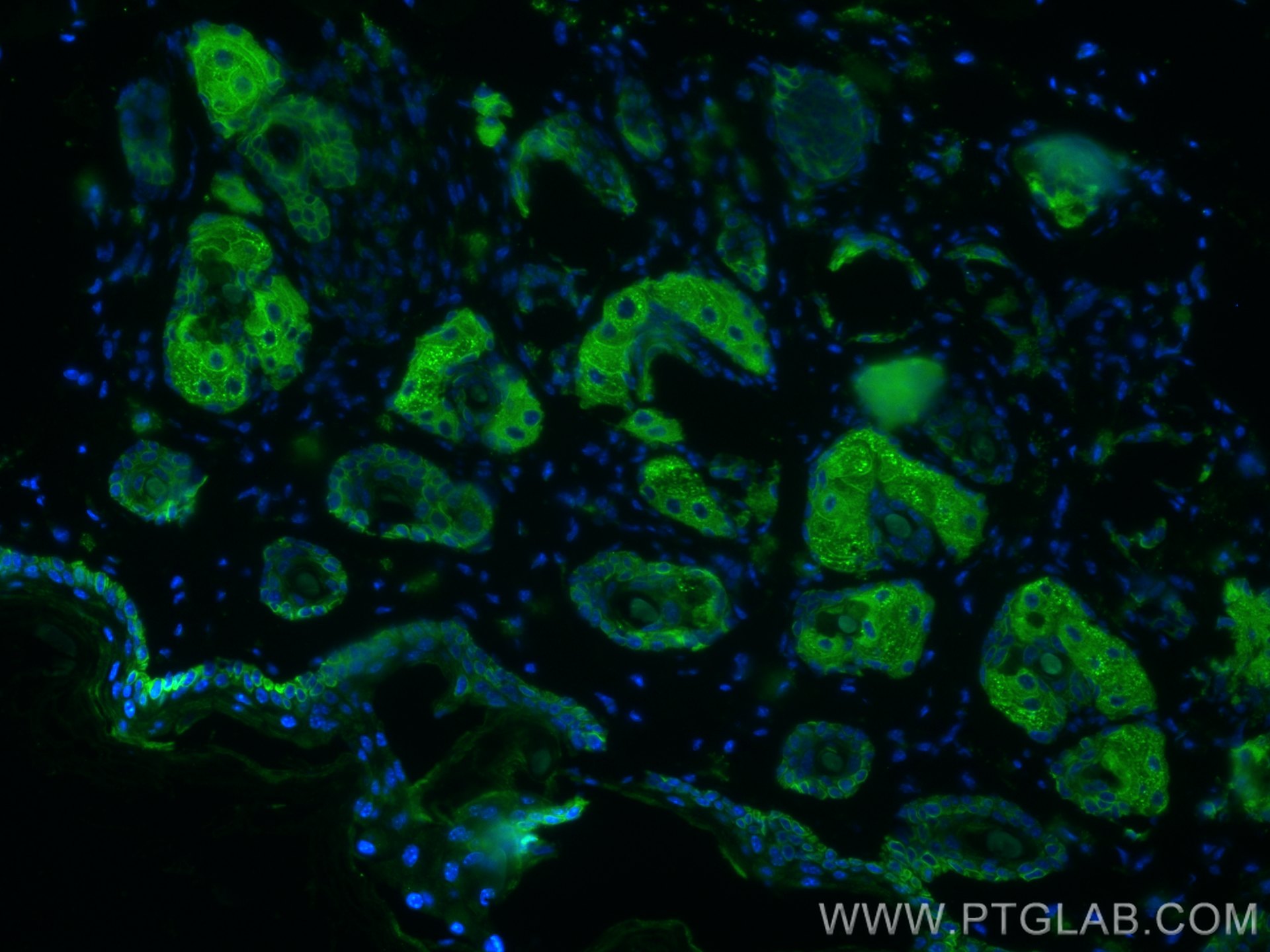
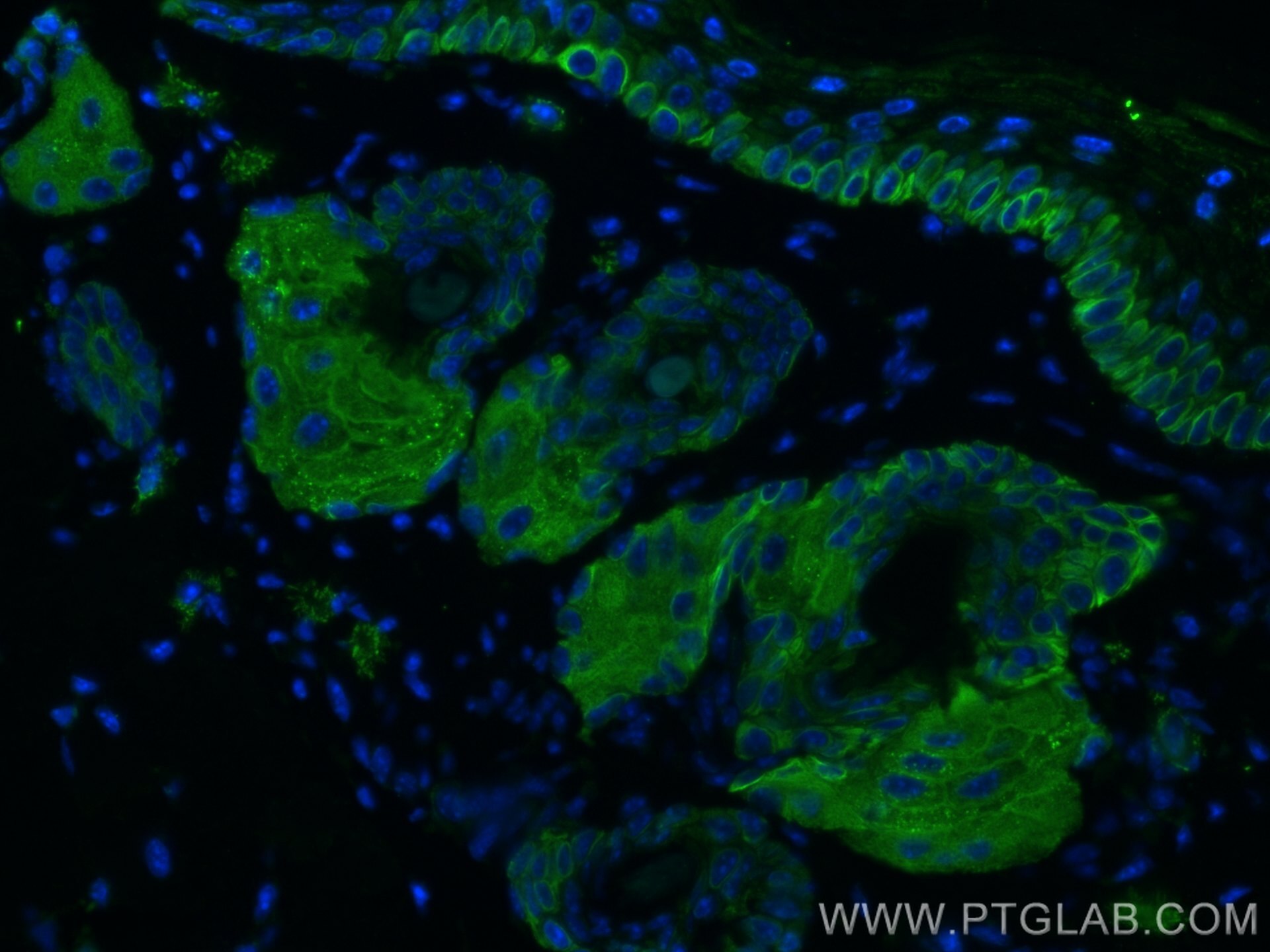
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Lungenkarzinomgewebe, humanes Hautgewebe, humanes Hautkrebsgewebe, humanes Mammahyperplasie-Gewebe, humanes Zervixkarzinomgewebe, Rattenhautgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
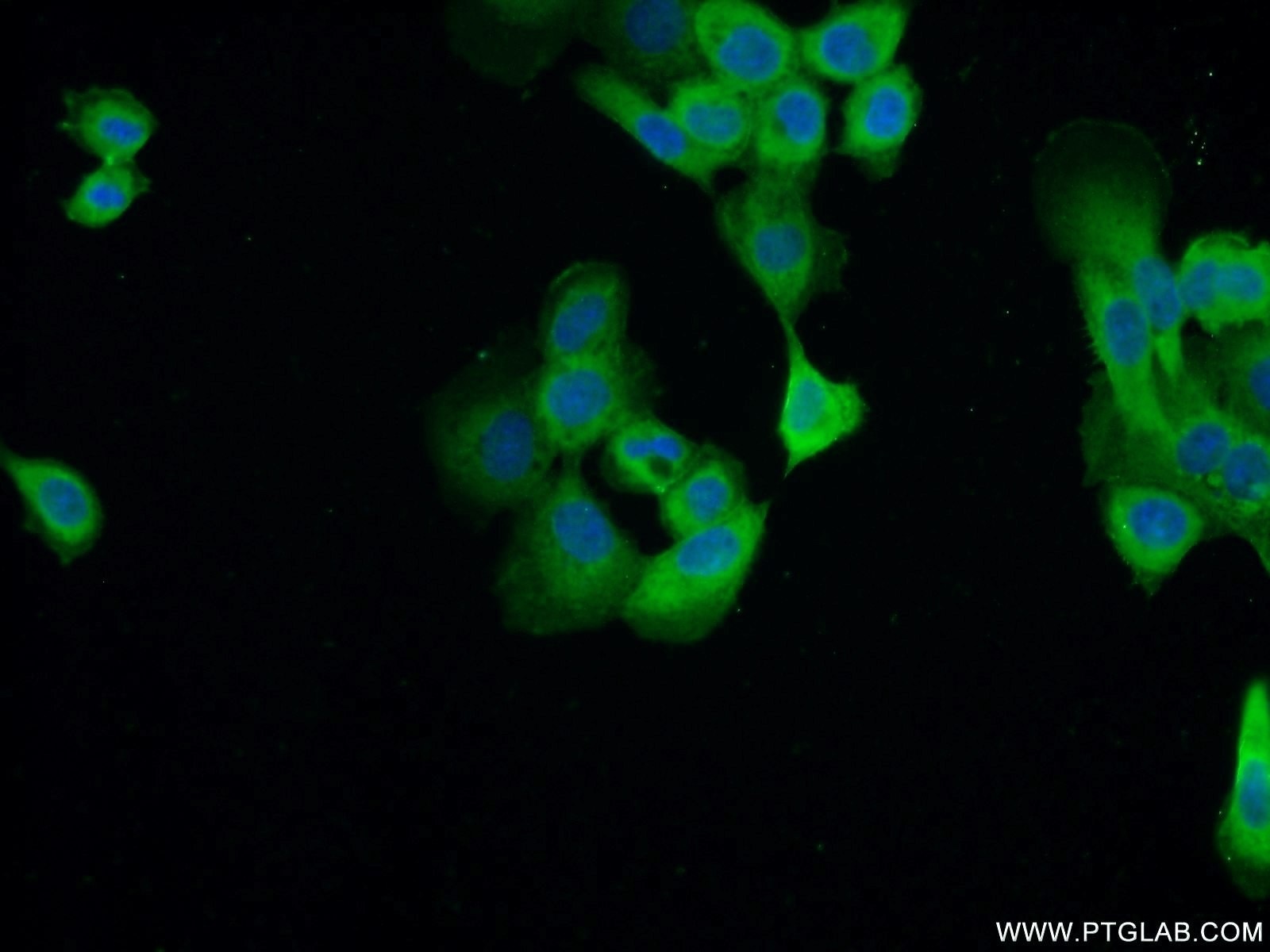
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | A431-Zellen, Maushautgewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:400-1:800 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 4 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 12 publications below |
Produktinformation
60320-1-Ig bindet in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA Cytokeratin 14 und zeigt Reaktivität mit Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | Hausschwein, human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG1 |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Cytokeratin 14 fusion protein Ag17559 |
| Vollständiger Name | keratin 14 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 472 aa, 52 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 52 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC002690 |
| Gene symbol | KRT14 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3861 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-G-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Keratins are a large family of proteins that form the intermediate filament cytoskeleton of epithelial cells, which are classified into two major sequence types. Type I keratins are a group of acidic intermediate filament proteins, including K9-K23, and the hair keratins Ha1-Ha8. Type II keratins are the basic or neutral courterparts to the acidic type I keratins, including K1-K8, and the hair keratins, Hb1-Hb6. Keratin 14 is a type I cytokeratin. It is usually found as a heterotetramer with keratin 5. Keratins K14 and K5 have long been considered to be biochemical markers of the stratified squamous epithelia, including epidermis.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Cytokeratin 14 antibody 60320-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Cytokeratin 14 antibody 60320-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for Cytokeratin 14 antibody 60320-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Small Eco-Friendly and Scalable Synthesis of Fullerenols with High Free Radical Scavenging Ability for Skin Radioprotection. | ||
Breast Cancer Res Anillin regulates breast cancer cell migration, growth, and metastasis by non-canonical mechanisms involving control of cell stemness and differentiation. | ||
Environ Sci Technol Graphene Quantum Dots Disrupt Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation by Interfering with the Methylation Level of Sox2. | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Exosomes from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived keratinocytes accelerate burn wound healing through miR-762 mediated promotion of keratinocytes and endothelial cells migration. | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells facilitate diabetic wound healing through the restoration of epidermal cell autophagy via the HIF-1α/TGF-β1/SMAD pathway |