- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
ICAM-1 Monoklonaler Antikörper
ICAM-1 Monoklonal Antikörper für FC, IF
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2b
Getestete Reaktivität
human
Anwendung
IF, FC
Konjugation
CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye
CloneNo.
2F9A8
Kat-Nr. : CL488-60299
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
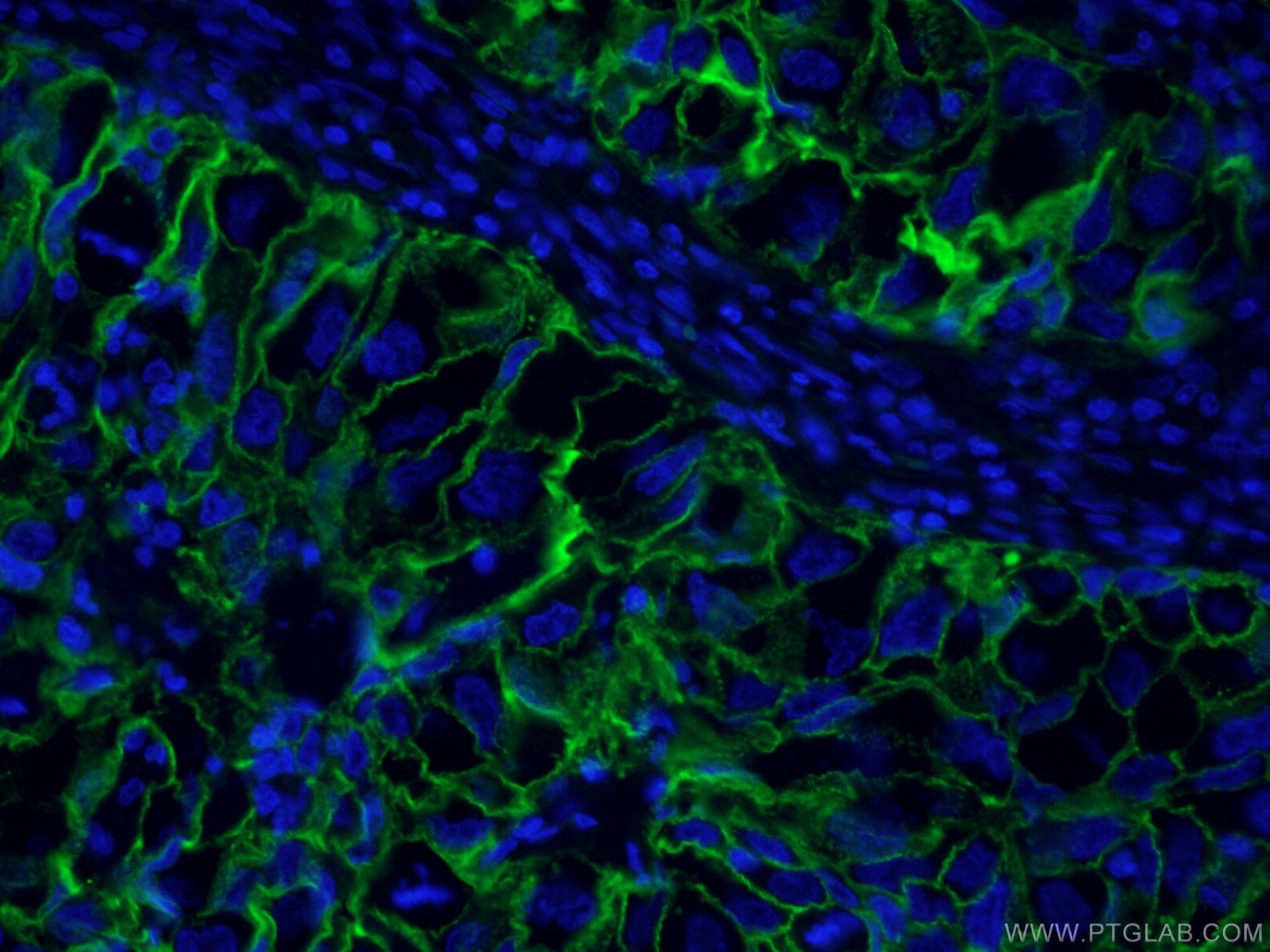
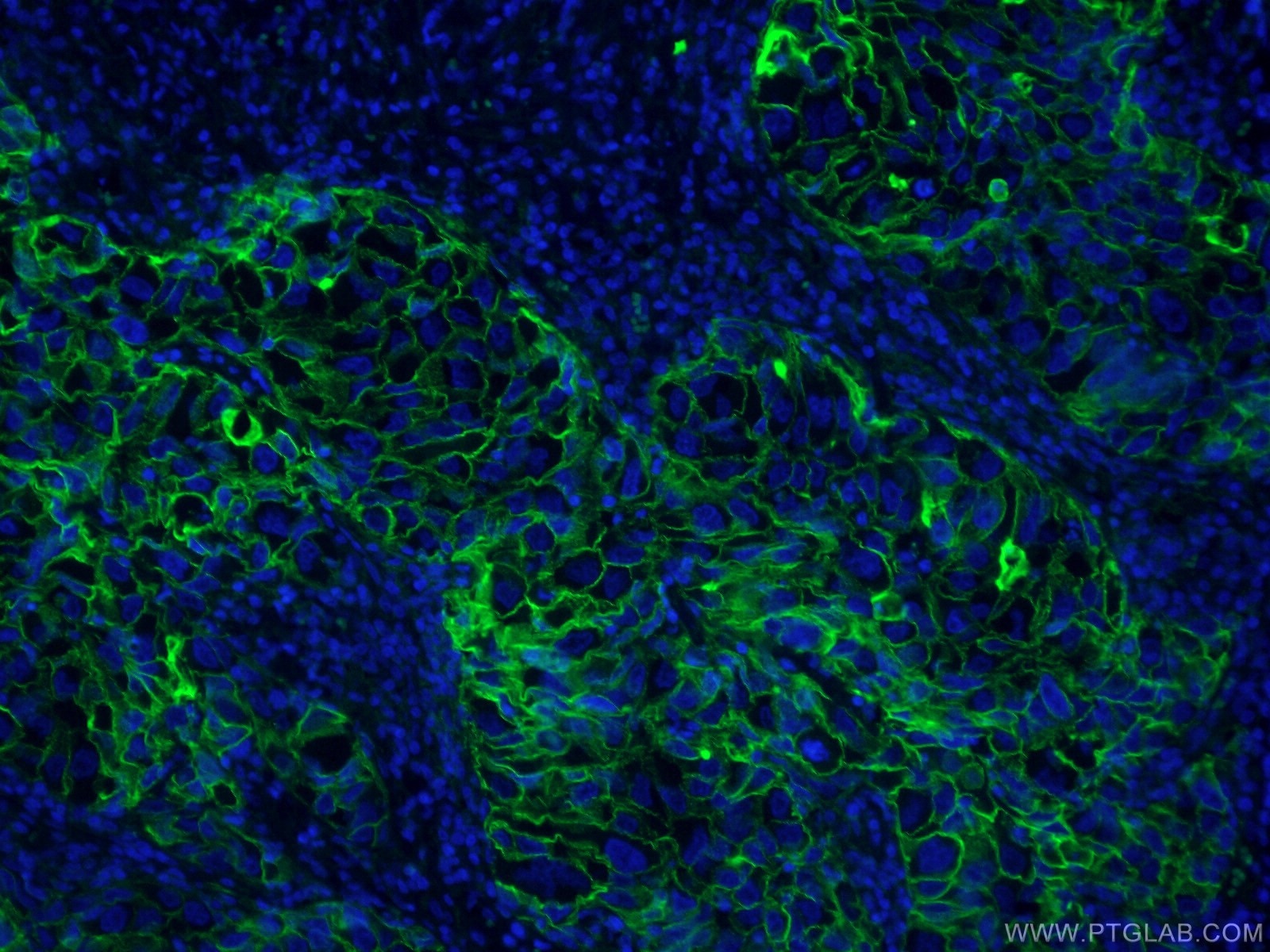
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | humanes Lungenkarzinomgewebe |
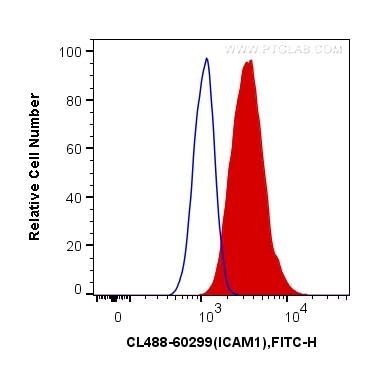
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC | Raji-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:50-1:500 |
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) | FC : 0.80 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Produktinformation
CL488-60299 bindet in IF, FC ICAM-1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2b |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | ICAM-1 fusion protein Ag8309 |
| Vollständiger Name | intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 90 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 85-95 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC015969 |
| Gene symbol | ICAM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3383 |
| Konjugation | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | BS mit 50% Glyzerin, 0,05% Proclin300, 0,5% BSA, pH 7,3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Vor Licht schützen. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr stabil. Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Where is ICAM-1 expressed?
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM-1), also known as Cluster of Differentiation 54 (CD54) is a transmembrane glycoprotein constitutively expressed at low levels in endothelial cells, pericytes and on some lymphocytes and monocytes1. It is located at the cytoplasmic membrane, with a large extracellular region of mainly hydrophobic amino acids joined to a small transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail. It has a molecular weight of 75 to 115 kDa depending on the level of glycosylation.
What is the function of ICAM-1?
ICAM-1 is important in both innate and adaptive immune responses as an adhesion molecule. Although it is constitutively expressed, in the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFα the endothelial cells are activated and upregulate expression of ICAM-12. In blood vessels lined with endothelial cells, leukocytes that are rolling over the surface are able to bind to ICAM-1 and transmigrate through the endothelial barrier and into the tissue. The initial binding of the leukocytes to ICAM-1 causes a Ca2+ release that initiates endothelial cell contraction and weakening of the intercellular tight junctions3, 4. This protein can be used as an indicator of endothelial activation and of vascular inflammation.
What is the role of ICAM-1 in disease?
Beyond the role in the immune response, ICAM-1 has also been identified as the target of attachment for the human rhinovirus, the cause of the common cold. Binding of the virus to ICAM-1 causes the viral capsid to uncoat and leads to release of the genetic material5.
Hubbard, A. K. & Rothlein, R. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression and cell signaling cascades. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 28, 1379-86 (2000).
Long, E. O. ICAM-1: getting a grip on leukocyte adhesion. J. Immunol. 186, 5021-3 (2011).
Lawson, C. & Wolf, S. ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells. (2009).
Lyck, R. & Enzmann, G. The physiological roles of ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 in neutrophil migration into tissues. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 22, 53-59 (2015).
Xing, L., Casasnovas, J. M. & Cheng, R. H. Structural analysis of human rhinovirus complexed with ICAM-1 reveals the dynamics of receptor-mediated virus uncoating. J. Virol. 77, 6101-7 (2003).
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 ICAM-1 antibody CL488-60299 | Protokoll herunterladen |
| FC protocol for CL Plus 488 ICAM-1 antibody CL488-60299 | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |