GINS3 Polyklonaler Antikörper
GINS3 Polyklonal Antikörper für IP, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus
Anwendung
WB, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 15651-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
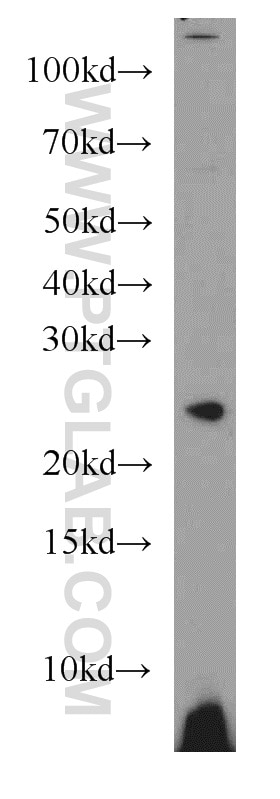
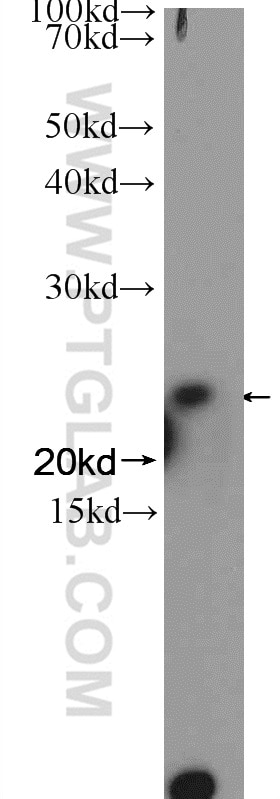
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Jurkat-Zellen, NIH/3T3-Zellen |
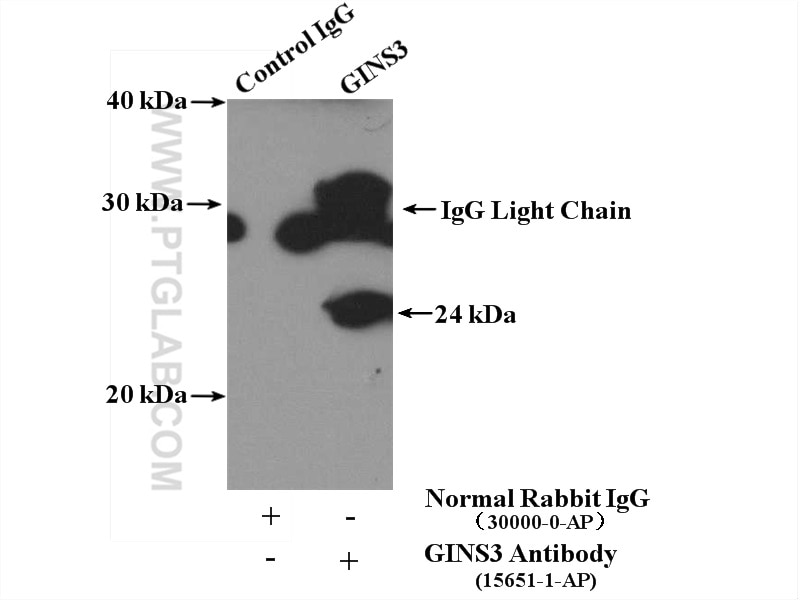
| Erfolgreiche IP | Jurkat-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 3 publications below |
Produktinformation
15651-1-AP bindet in WB, IP, ELISA GINS3 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | GINS3 fusion protein Ag8247 |
| Vollständiger Name | GINS complex subunit 3 (Psf3 homolog) |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 25 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 24 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC005879 |
| Gene symbol | GINS3 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 64785 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for GINS3 antibody 15651-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for GINS3 antibody 15651-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Cell Polε Instability Drives Replication Stress, Abnormal Development, and Tumorigenesis. | ||
J Clin Invest Inherited GINS1 deficiency underlies growth retardation along with neutropenia and NK cell deficiency. | ||
JCI Insight Partial loss-of-function mutations in GINS4 lead to NK cell deficiency with neutropenia |