- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
DCLK1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
DCLK1 Polyklonal Antikörper für IP, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 21699-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Rattenhirngewebe, humanes Hirngewebe, Maushirngewebe |
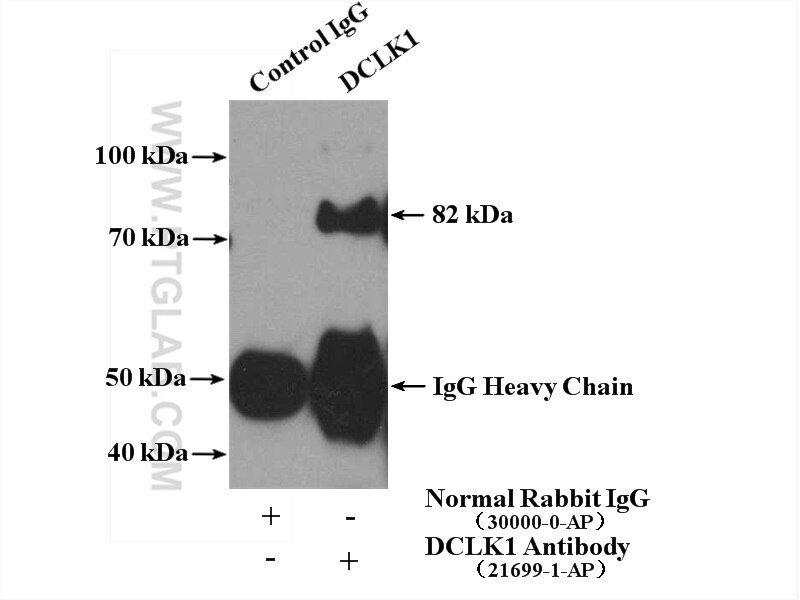
| Erfolgreiche IP | Rattenhirngewebe |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:3000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| FC | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
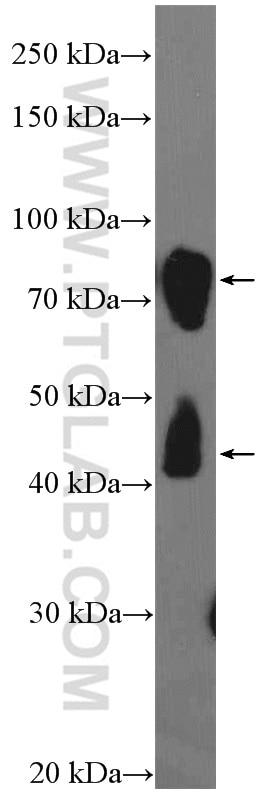
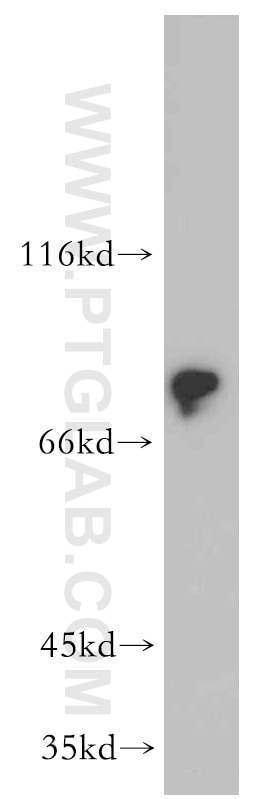
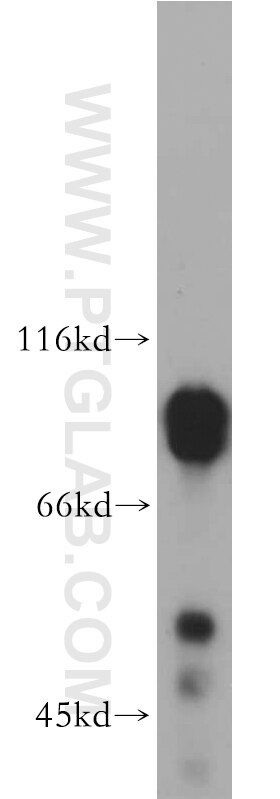
21699-1-AP bindet in WB, IP, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA DCLK1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | DCLK1 fusion protein Ag16292 |
| Vollständiger Name | doublecortin-like kinase 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 729 aa, 81 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 48 kDa, 82 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC152456 |
| Gene symbol | DCLK1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9201 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
DCLK1 (Serine/threonine-protein kinase DCLK1) is also named as DCAMKL1, DCDC3A, KIAA0369 and belongs to the CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. It is a microtubule-associated kinase that can undergo autophosphorylation and it also has microtubule-polymerizing activity that is independent of its protein kinase activity (PMID: 11124993). It plays a unique role in mitotic spindle integrity during early neurogenesis in radial glial cell proliferation and their radial process stability. DCLK1 is a unique marker for distinguishing tumor stem cells from intestinal normal stem cells (PMID: 23202126). This protein has 4 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 82 kDa, 81 kDa, 47 kDa and 48 kDa.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DCLK1 antibody 21699-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for DCLK1 antibody 21699-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Immunity Intestinal Tuft-2 cells exert antimicrobial immunity via sensing bacterial metabolite N-undecanoylglycine. | ||
Redox Biol FUT2-dependent fucosylation of HYOU1 protects intestinal stem cells against inflammatory injury by regulating unfolded protein response | ||
Clin Transl Med Targeting DCLK1 overcomes 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer through inhibiting CCAR1/β-catenin pathway-mediated cancer stemness.
| ||
J Gastroenterol High-throughput screening identified miR-7-2-3p and miR-29c-3p as metastasis suppressors in gallbladder carcinoma.
| ||
Front Pharmacol XMD-17-51 Inhibits DCLK1 Kinase and Prevents Lung Cancer Progression.
| ||
Cell Physiol Biochem MicroRNA-195 Suppresses the Progression of Pancreatic Cancer by Targeting DCLK1. |