androgen receptor Monoklonaler Antikörper
androgen receptor Monoklonal Antikörper für IF, IHC, WB, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2a
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
CloneNo.
1F7C12
Kat-Nr. : 66747-1-Ig
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
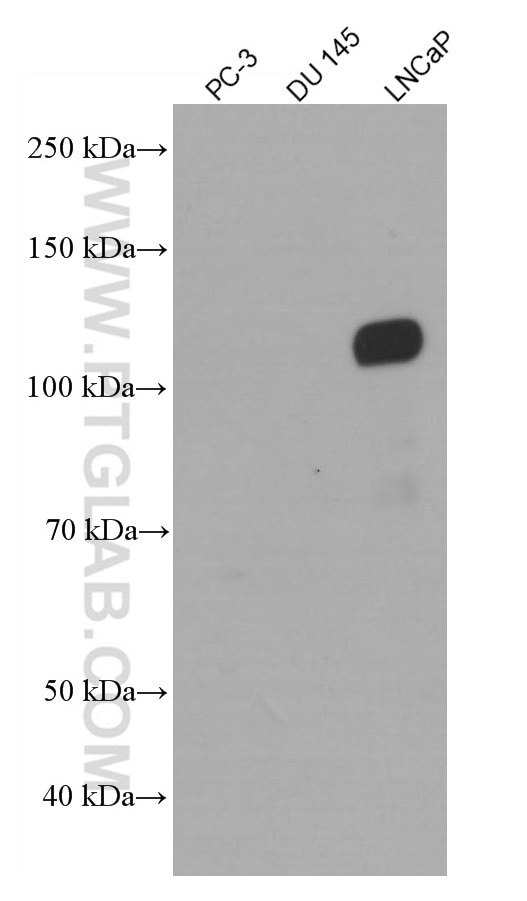
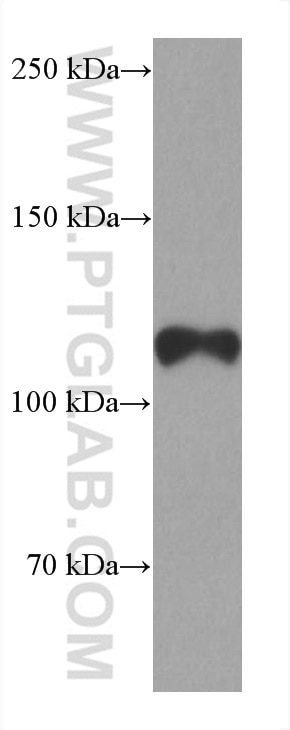
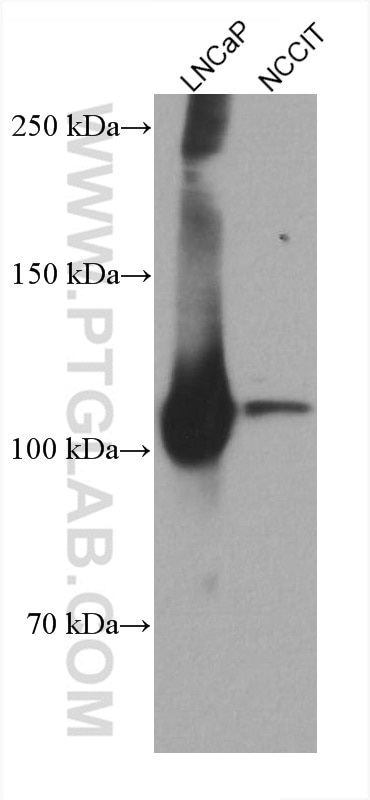
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | LNCaP-Zellen, humanes Hodengewebe, NCCIT-Zellen |
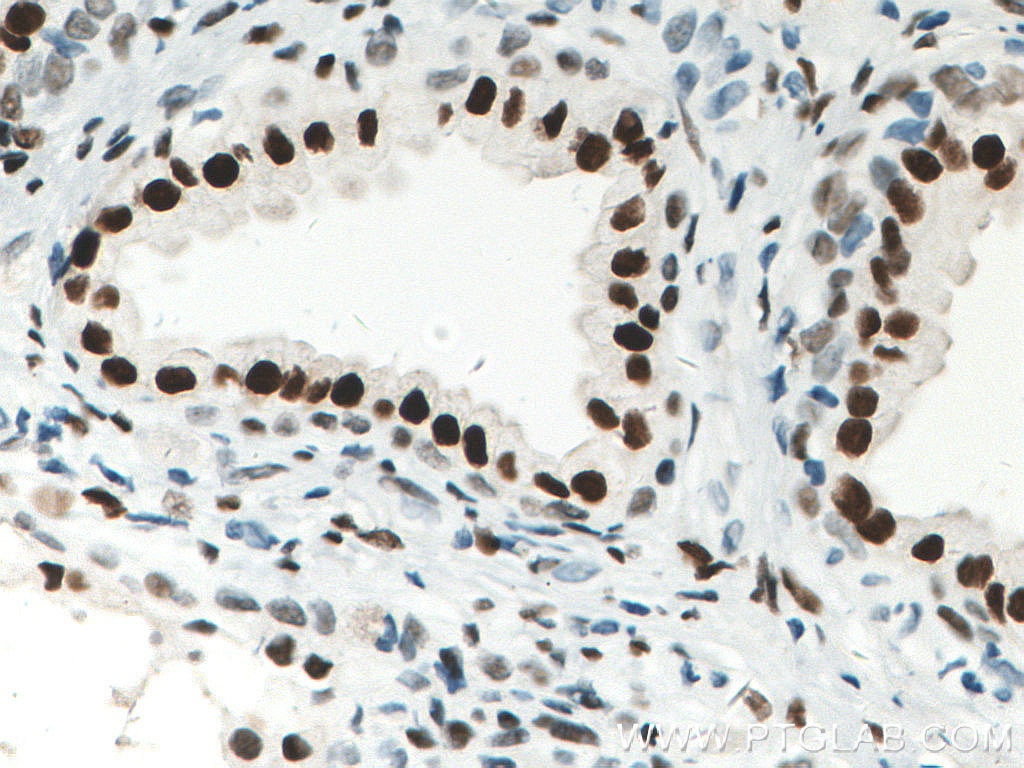
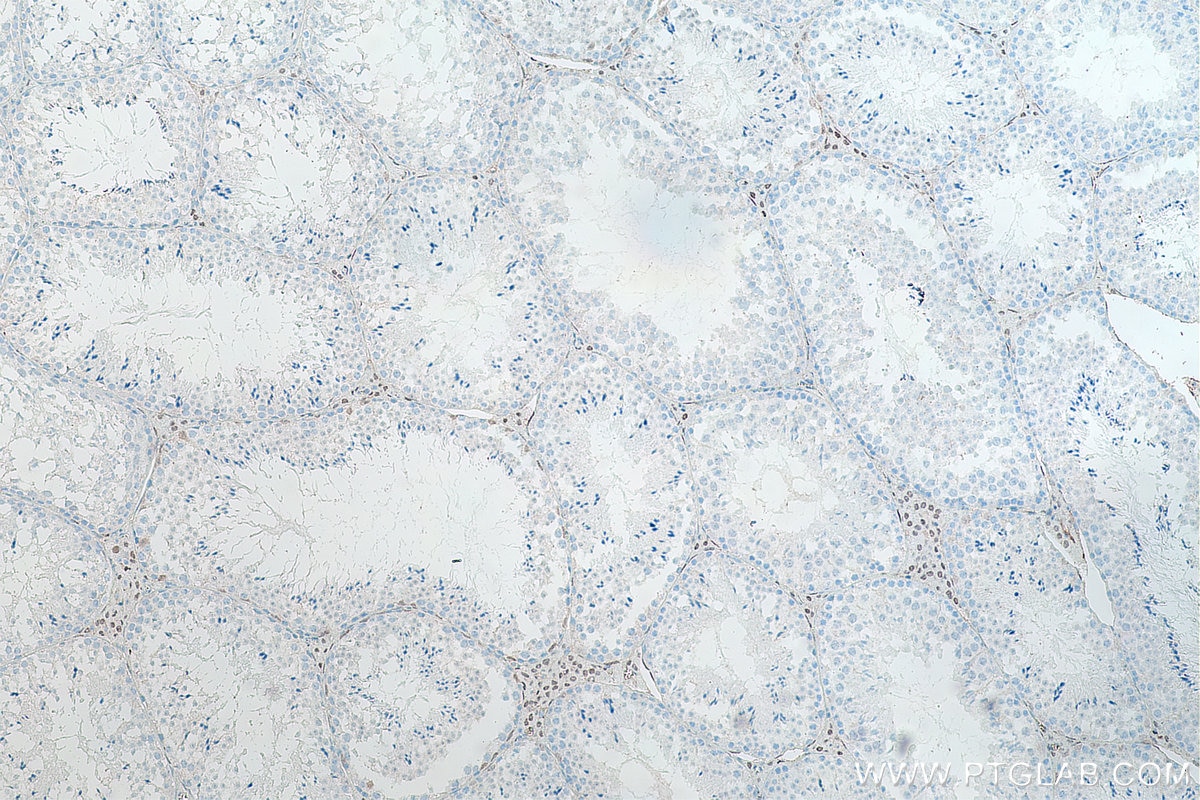
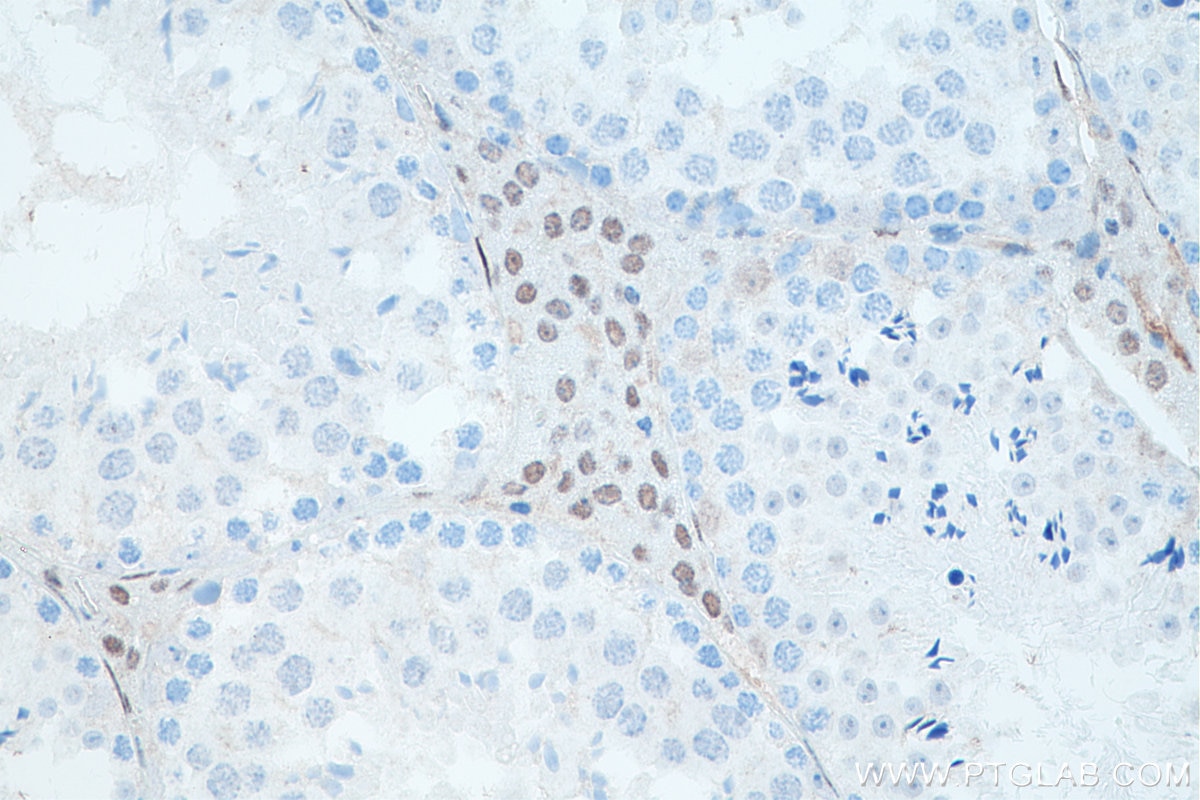
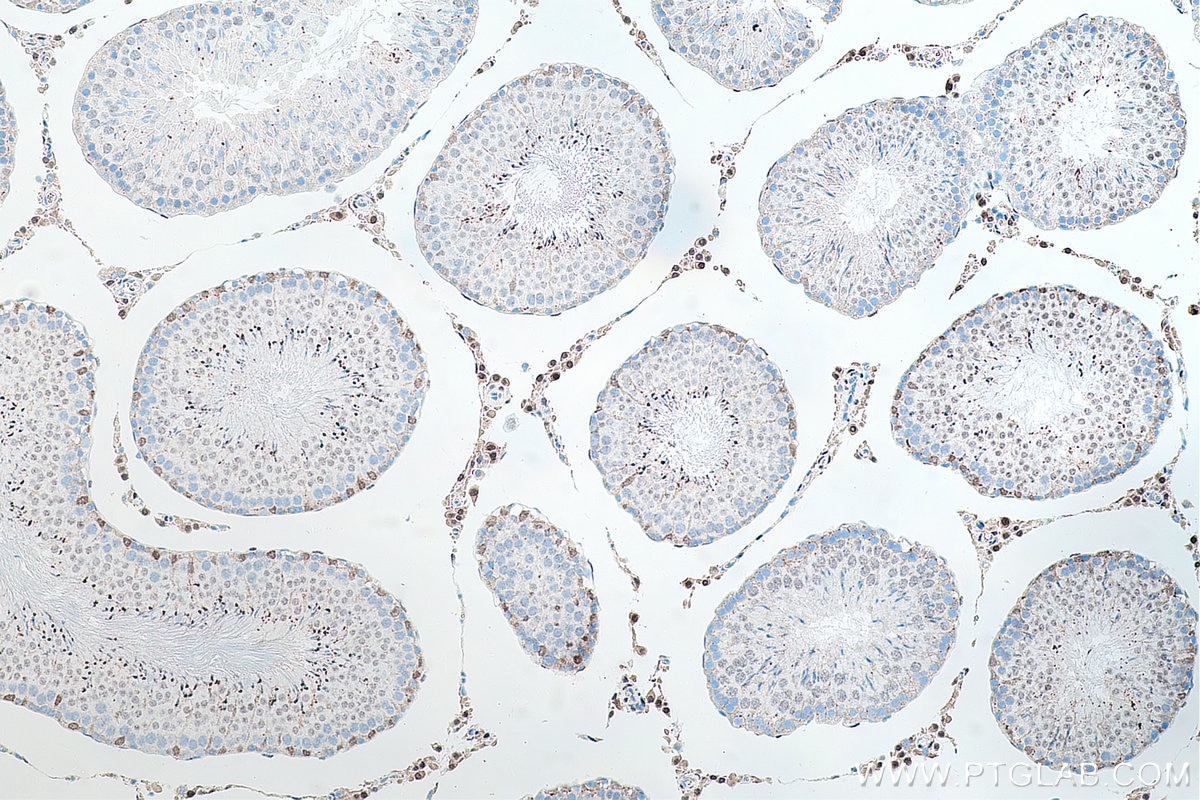
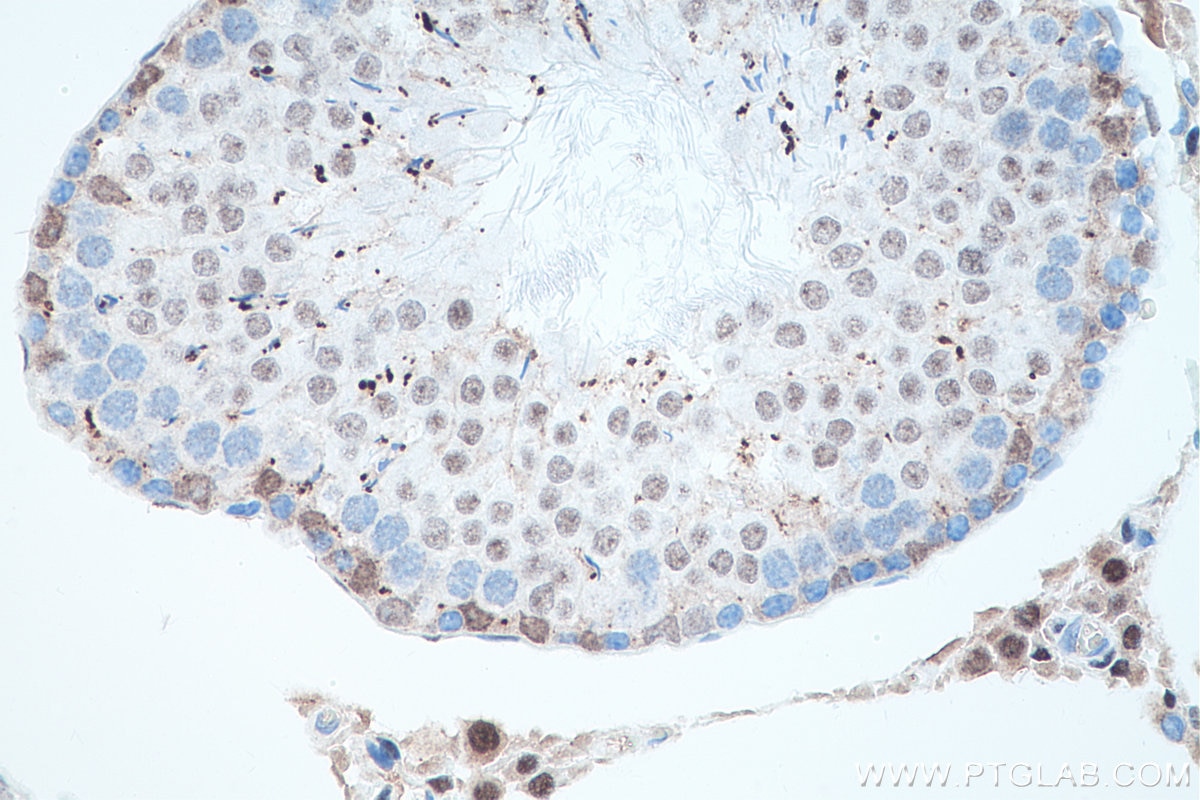
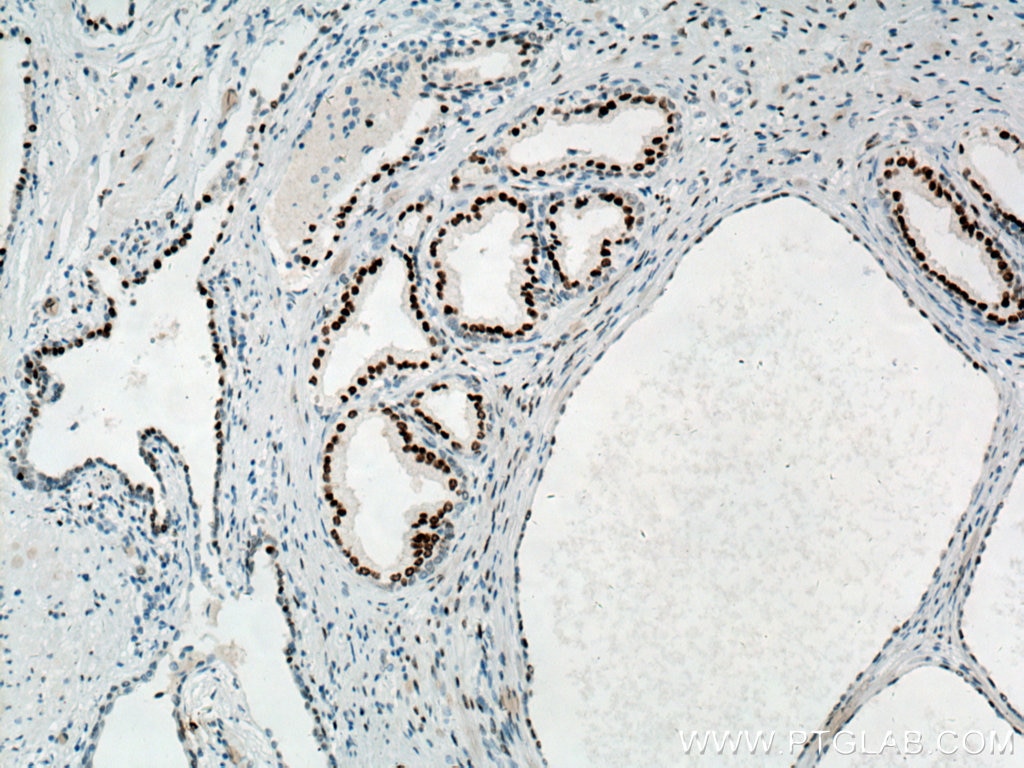
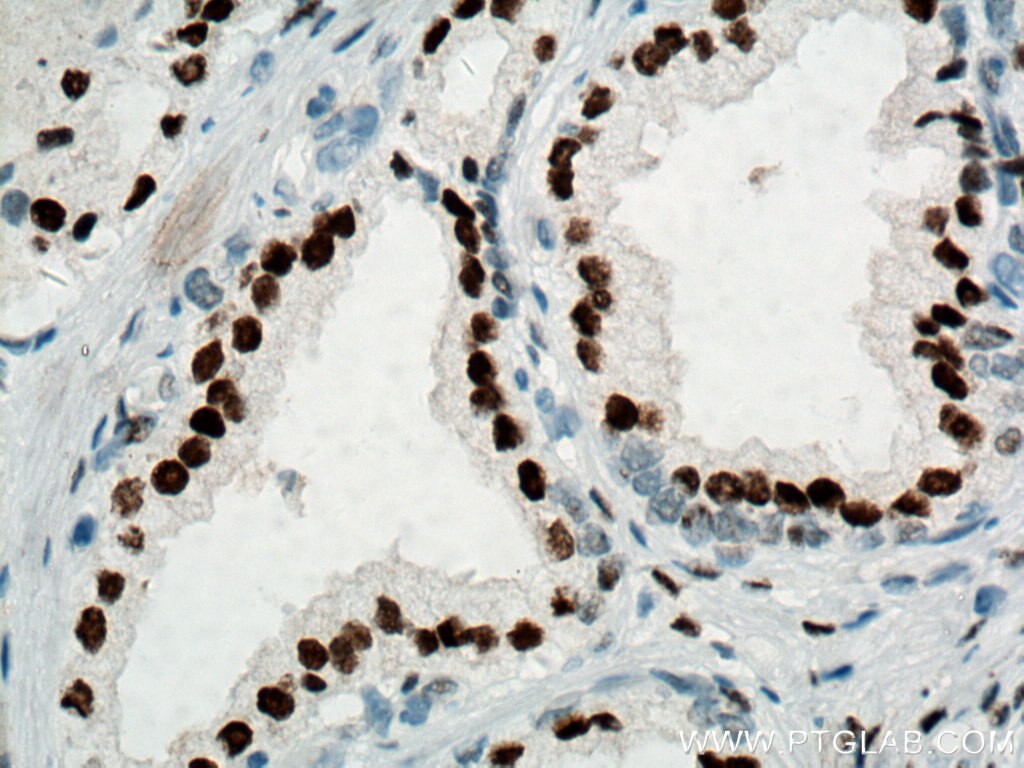
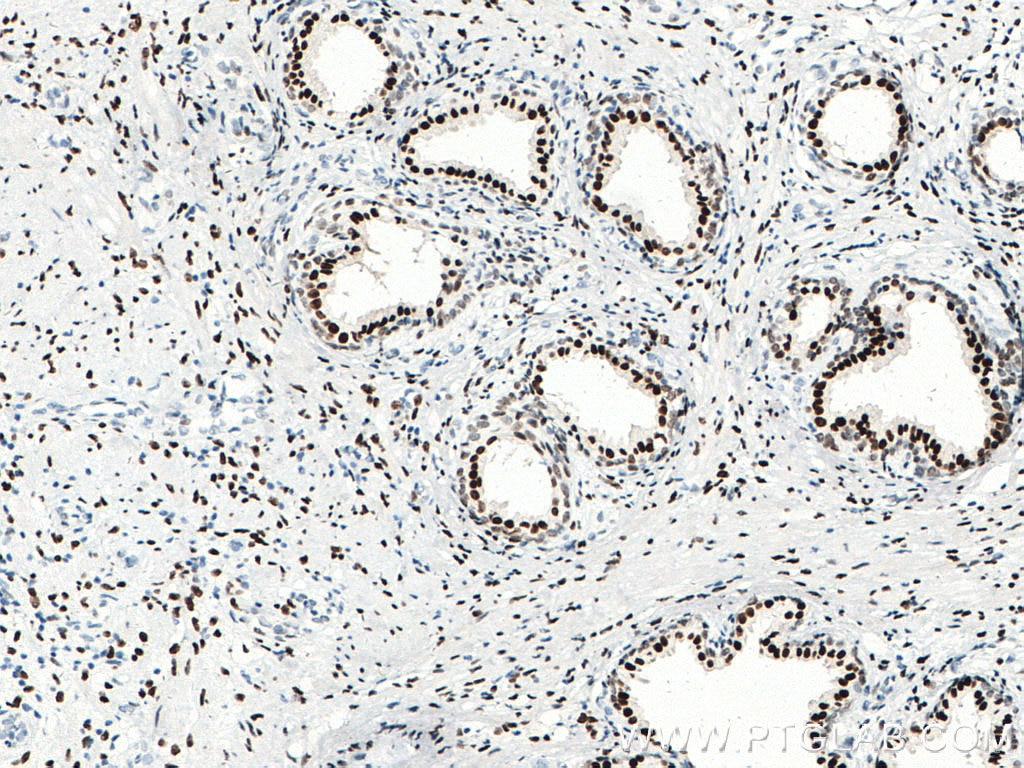
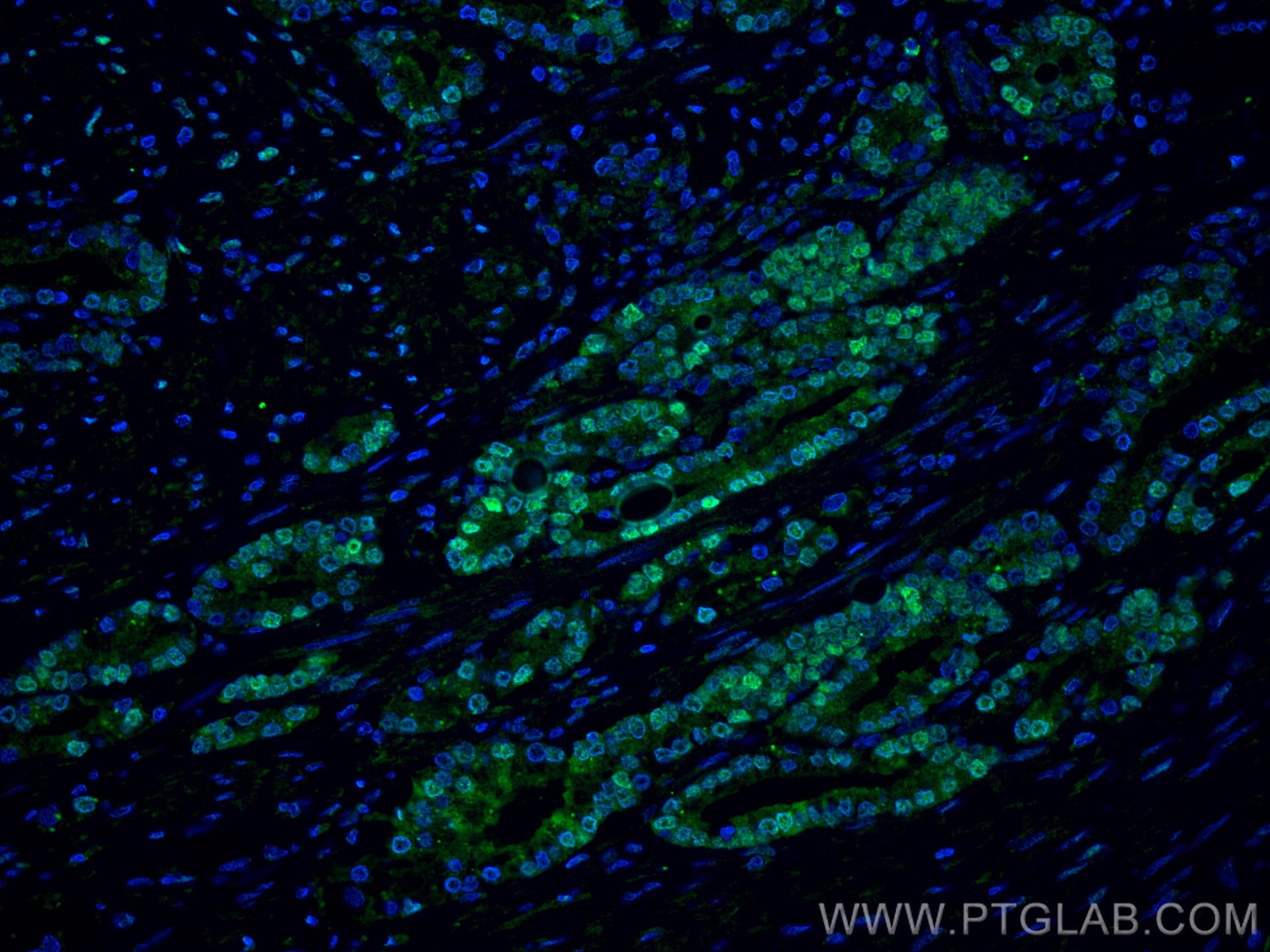
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Prostatakarzinomgewebe, Maushodengewebe, Rattenhodengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
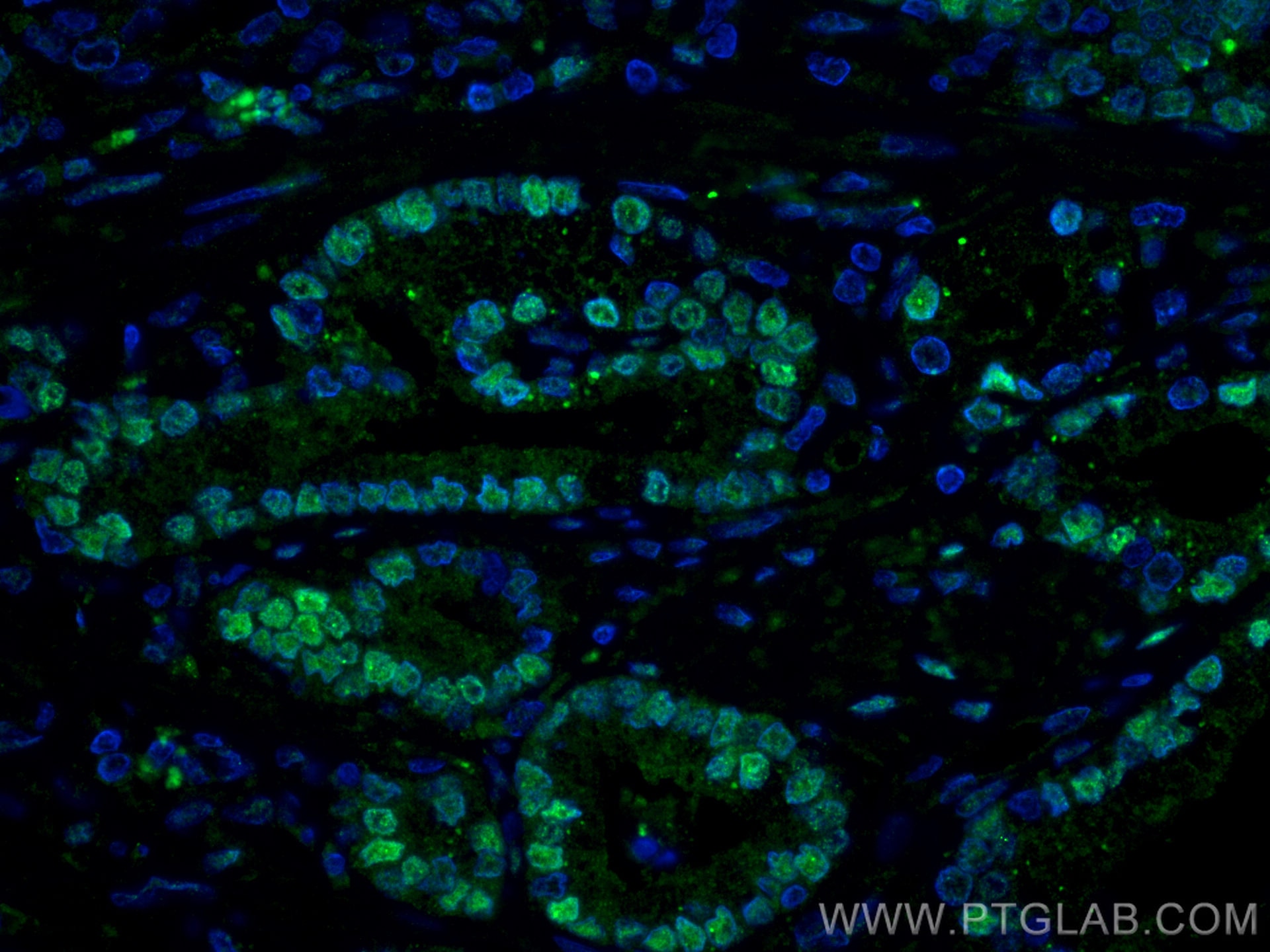
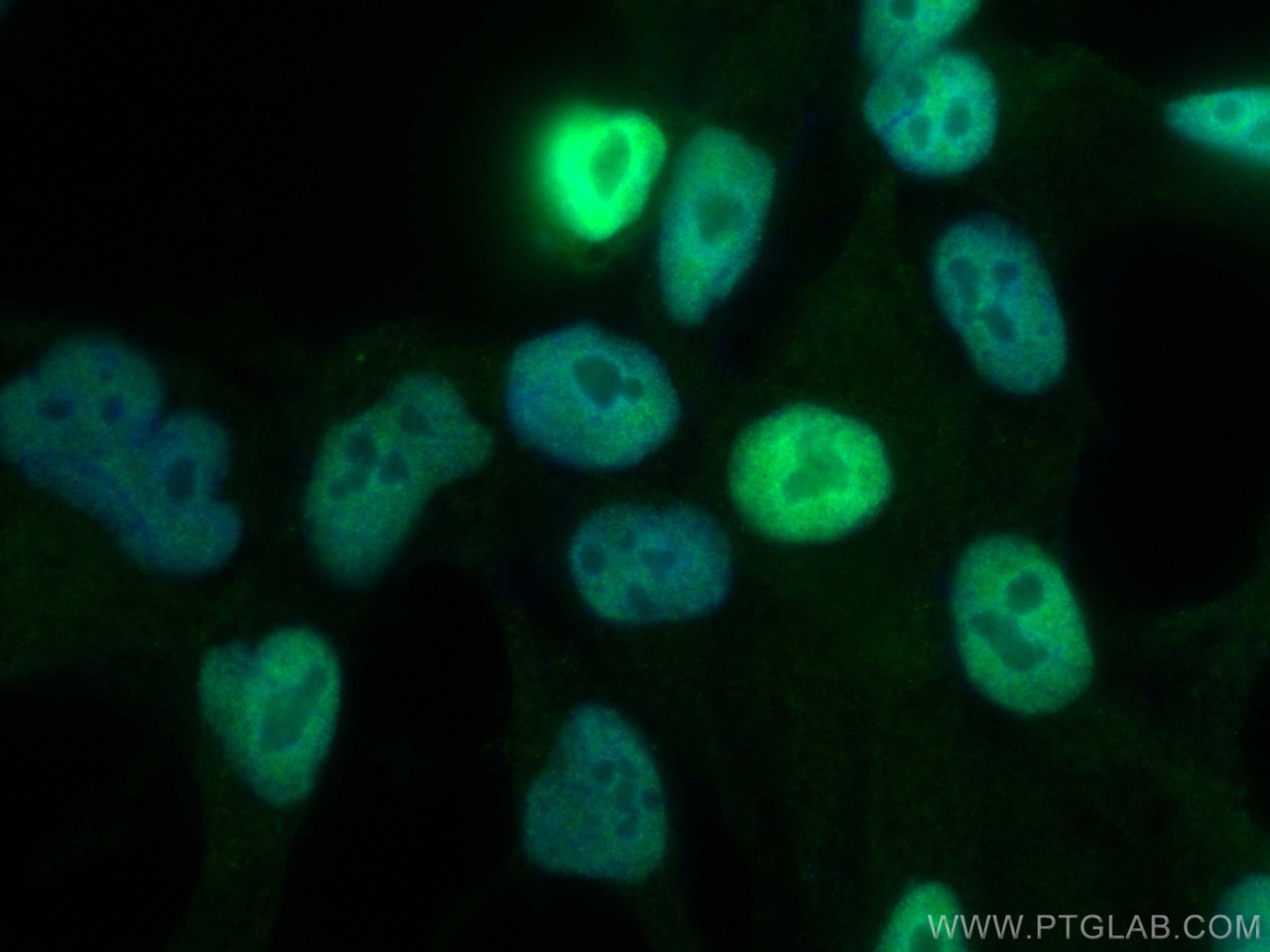
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF | humanes Prostatakarzinomgewebe, LNCaP-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:600-1:3000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:5000-1:20000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF) | IF : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 3 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
66747-1-Ig bindet in WB, IP, IHC, IF, ELISA androgen receptor und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2a |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | androgen receptor fusion protein Ag17291 |
| Vollständiger Name | androgen receptor |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 914 aa, 99 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 110-120 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC132975 |
| Gene symbol | AR |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 367 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Protein-A-Reinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
AR, also named as DHTR and NR3C4, belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family and NR3 subfamily. AR is a ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins. AR is activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3. Defects in AR are the cause of androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS), previously known as testicular feminization syndrome (TFM), which is an X-linked recessive form of pseudohermaphroditism due end-organ resistance to androgen. Defects in AR are the cause of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy X-linked type 1 (SMAX1) which also known as Kennedy disease. Defects in AR may play a role in metastatic prostate cancer. Defects in AR are the cause of androgen insensitivity syndrome partial (PAIS) which also known as Reifenstein syndrome. AR exists various isoforms with MW 110-120 kDa and 75-80 kDa. (PMID: 19244107 )
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for androgen receptor antibody 66747-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for androgen receptor antibody 66747-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for androgen receptor antibody 66747-1-Ig | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Development Human prostate organoid generation and the identification of prostate development drivers using inductive rodent tissues | ||
Chin J Nat Med Eucommia lignans alleviate the progression of diabetic nephropathy through mediating the AR/Nrf2/HO-1/AMPK axis in vivo and in vitro | ||
iScience WTAP boosts lipid oxidation and induces diabetic cardiac fibrosis by enhancing AR methylation | ||
Gynecol Endocrinol N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO related to hyperandrogenism in PCOS via AKT pathway |